The sow is paralyzed after delivery, how to do? Prevention and control measures should be kept in mind!
Sows are prone to paralysis under the conditions of extensive feeding and management, poor feed conditions and cold climate, which generally occur within a few days before delivery and about 30 days after delivery. Some sows suddenly appear weakening or loss of motor ability of their limbs within 3-5 days after parturition. Lumbar paralysis, cripple and paralysis is a serious acute neurological disorder. Before paralysis, most sows have loss of appetite or do not eat, slow action, dry and hard feces, like drinking clear water, arch ground, eating bricks, eating feces and other phenomena, but the body temperature is normal. After the occurrence of paralysis, it is difficult for the sow to stand up, stand still and stand for a long time, the hindquarters are swaying and powerless when walking, and the hind legs drag to the ground during driving, and there are screams, and finally lie still.
Causes of paralysis in sows
First, because the proportion of roughage in diet is high or the content of calcium and phosphorus in diet is insufficient, sows misappropriate calcium and phosphorus in bones before and after giving birth, which will lead to lack of calcium and phosphorus in sows over a long period of time. Especially in high-yielding sows, the disease is more likely to occur. 20 days after giving birth, when the milk yield of sows reached the peak, most of the disease tended to be serious.
Second, the proportion of cereals and legumes in concentrate is too large. Most of the phosphorus in these feeds exists in the form of phytic acid phosphorus, which is not easy to be used by pigs, and will hinder the absorption of calcium by pigs. Overfeeding can easily lead to a serious shortage of calcium and phosphorus in pigs, resulting in paralysis. The main manifestations are mental malaise, loss of appetite, dry, hard and less feces, and then stop defecation and urination. It is difficult for the light to stand and the hindquarters sway when walking. Heavy people can not stand, lying on the ground for a long time, showing a lethargic state. Little or no milk.
Postpartum paralysis
The disease is a nutritional and metabolic disease that occurs suddenly in sows from a few hours to 5 days after delivery.
Diseased pigs show difficulty standing, hindquarters swaying, walking cautiously, hindquarters unstable, muscles sensitive to pain, sharp loss of appetite or refusing to eat, dry or stopped defecation, red yellow urine, normal or slightly hypothermic body temperature. Lack of milk or no milk.
Postpartum paralysis of sows is a kind of disease caused by postpartum physical weakness of sows, inability of limbs to stand and loss of consciousness, also known as postpartum wind, which is a common frequently-occurring disease in sows.

Toxic factors
There are many toxic factors causing hindquarters paralysis in pigs, such as poor feed quality, long-term feeding or one-time intake of moldy and deteriorated feed, improper feed processing methods, and some feeds containing toxic and harmful substances, such as cottonseed cake, rapeseed cake, potato, etc., or unreasonable feeding methods can cause poisoning and paralysis of pig hindquarters. This kind of disease can usually make a preliminary diagnosis based on medical history, on-the-spot investigation and clinical manifestations. Such as salt, distiller's grains poisoning.
Symptoms of salt poisoning: the disease begins with extreme thirst, flushing mucosa, swollen lips, followed by agitation, wandering aimlessly, circling, muscle spasm, sitting dog posture, and finally quadriplegia, unable to stand.
Symptoms of lees poisoning: elevated body temperature, shortness of breath, rash on the body surface, diarrhea, feces with mucus, stench. On the other hand, rapeseed cake, cottonseed cake and potato are poisoned, mostly because they contain toxic substances and are overfed without detoxification.
Measures to prevent paralysis of sows
First of all, the feed should be matched reasonably to strive for a balanced diet. According to sow feeding standards, make full use of local natural resources, try to feed more green feed (not too much at a time to prevent diarrhea) or high-quality hay powder, mineral feed and additives. For pregnant and lactation sows, each sow was fed 20 grams of high-quality bone meal and 20 grams of salt every day. If you do not feed bone meal, you can appropriately increase the proportion of feed with more phosphorus such as wheat bran and rice bran, and feed green roughage with more calcium such as sweet potato vines. Provide high-quality and full-price formula feed, pay attention to the warmth and dryness of the sow house, and appropriately increase the exercise of sows.
Preventive measures of postpartum paralysis in sows
1. The pig diet should be supplemented with shell powder, eggshell powder and calcium carbonate. Sows should be supplemented with bone meal, fish meal and miscellaneous bone soup in late pregnancy and lactation, and high quality hay powder, legume forage (alfalfa) and green feed in winter and spring rainy season.
2. Keep the pig house clean and dry: after giving birth to the sow, the pig house should cover more grass to prevent the cold wind from blowing, and keep the pig house warm, spacious and with plenty of sunlight. Sows should bask in the sun during pregnancy, exercise in the sun for 2 to 3 hours a day, feed feed that is easy to digest, rich in protein, minerals and vitamins, and the proportion of calcium and phosphorus should be appropriate.
Symptomatic treatment as soon as possible. Pig bones or other fresh livestock and poultry bones can be dried and crushed and mixed into the feed to feed pigs, each feeding about 30 grams a day. For severely ill pigs, 40-80 ml of 5%-10% calcium chloride injection is given intravenously, but intramuscular injection or leakage of the drug solution outside the blood vessels is strictly prohibited. Smear the skin with high spirits or 10% camphor alcohol and massage artificially to promote blood circulation and restore neurological function in pigs. While paying close attention to the treatment, we should further strengthen the feeding management. Pay attention to keep warm in winter and cool down in summer. Feed digestible feed to keep the pig house clean and hygienic, increase the thickness of bedding grass, often help sows turn over to prevent bedsores, and minimize stress factors to facilitate sow recovery. (source: raising pigs)
- Prev
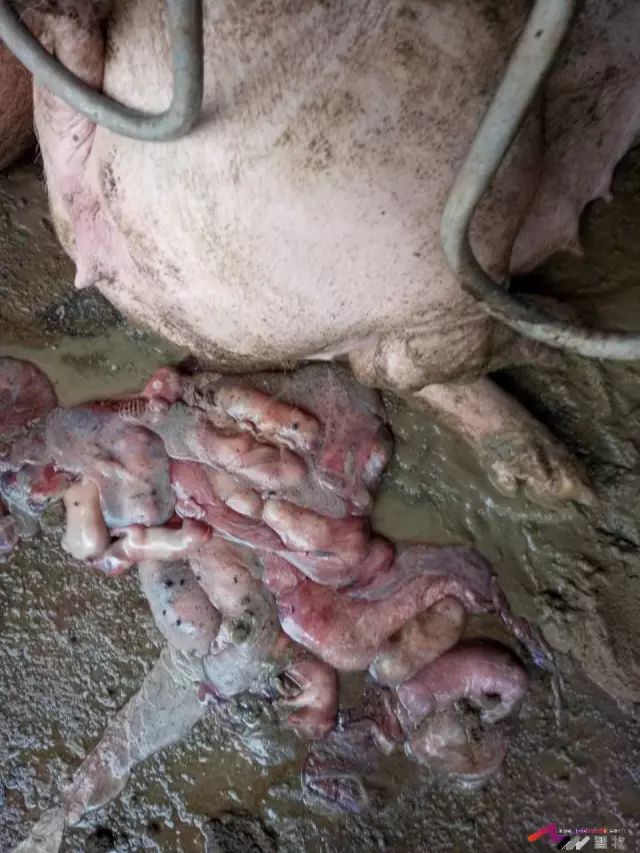
Who is the "culprit" of this sow miscarriage?
Who is the "culprit" of this sow miscarriage?
- Next
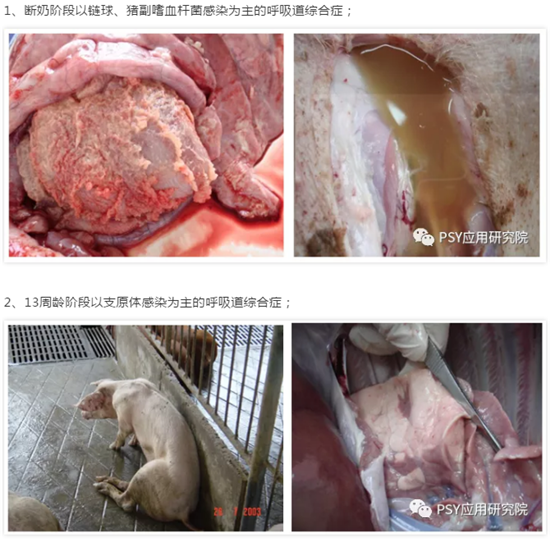
Respiratory disease prevention and control program for growing and fattening pigs, you're welcome to take it away!
Respiratory disease prevention and control program for growing and fattening pigs, you're welcome to take it away!
Related
- On the eggshell is a badge full of pride. British Poultry Egg Market and Consumer observation
- British study: 72% of Britons are willing to buy native eggs raised by insects
- Guidelines for friendly egg production revised the increase of space in chicken sheds can not be forced to change feathers and lay eggs.
- Risk of delay in customs clearance Australia suspends lobster exports to China
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (4)
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (3)
- Five common causes of difficult control of classical swine fever in clinic and their countermeasures
- Foot-and-mouth disease is the most effective way to prevent it!
- PED is the number one killer of piglets and has to be guarded against in autumn and winter.
- What is "yellow fat pig"? Have you ever heard the pig collector talk about "yellow fat pig"?

