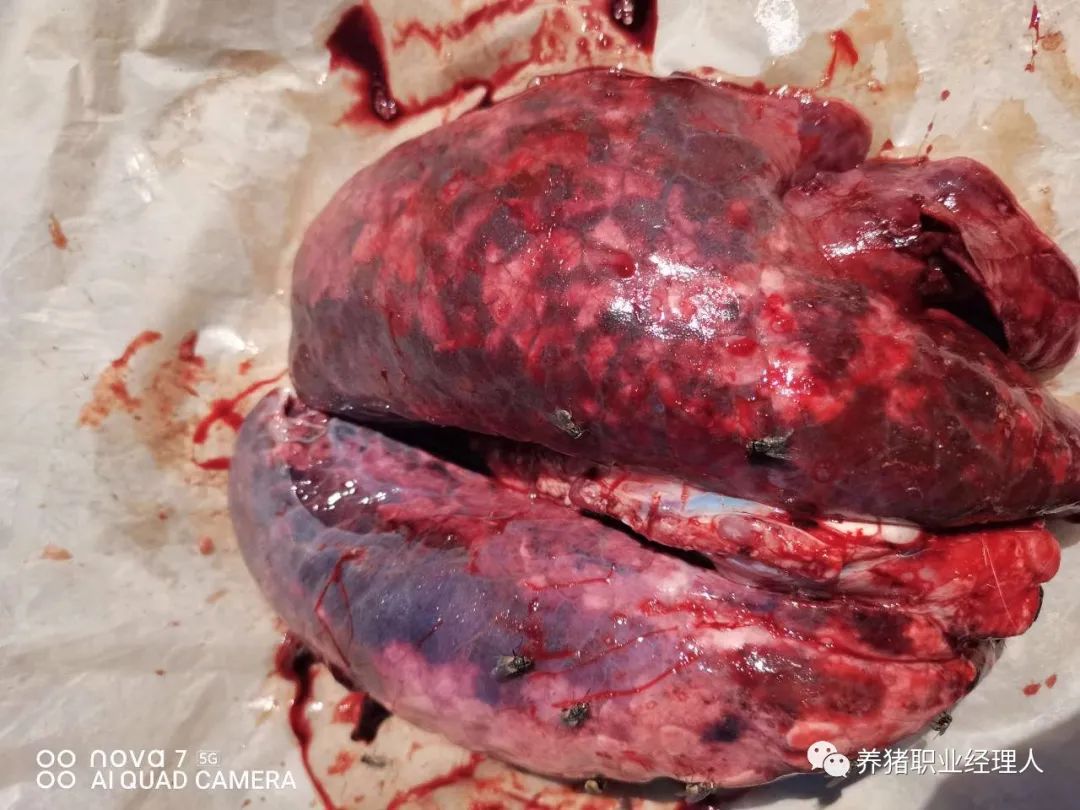
Haemophilus parasuis several issues worthy of attention!
1. Immunosuppression of Haemophilus parasuis
Although Haemophilus parasuis is not an immune disease, many studies have shown that during the epidemic of Haemophilus parasuis, the immune effect of the vaccine is very poor. After Haemophilus parasuis has been effectively controlled and recovered, the immune effect of various vaccines has been effectively improved. It is reported that piglets were immunized twice with classical swine fever cell vaccine (5 at 21 days old and 5 at 63 days old), and blood samples were drawn for testing at the age of 84 days. There were 16 pigs in each batch in a row, and the qualified rate of antibody titer was more than 90%. In the epidemic period of Haemophilus parasuis, the qualified rate of antibody was only about 40%. Although Haemophilus parasuis is not an immune disease, when the epidemic of Haemophilus parasuis in pig farms is serious, the immune effect is very poor, which can be significantly improved by controlling Haemophilus parasuis. The possible reason is that after pigs are infected with Haemophilus parasuis, the virus is inactivated in the body due to a long-term high fever, and some attenuated vaccines, such as classical swine fever and pseudorabies vaccine, cannot be colonized in the body, resulting in immune failure. In addition, Haemophilus parasuis can cause circulatory disturbance, which is also an important reason for the significant decrease of immune response.
2. Inflammatory exudation in the pathology of Haemophilus parasuis
The effusion and cellulosic exudates in pleural cavity, abdominal cavity and articular cavity in pigs with Haemophilus parasuis are the result of inflammatory exudation and cardiac edema in the pathology of Haemophilus parasuis, which is also an important problem that must be solved in the process of treatment.

3. Endotoxin problem of Haemophilus parasuis
Why is it that when some pigs with Haemophilus parasuis are treated with drugs, the symptoms are not alleviated, but aggravate, or even die? This is because Haemophilus parasuis can produce endotoxin like other gram-negative bacilli. Endotoxin is a component in the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria called lipopolysaccharide, which is toxic to the host. Endotoxin is released only when the bacteria die and dissolve or artificially destroy the bacterial cell wall, so it is called endotoxin. At present, the more effective way of anti-endotoxin therapy is to limit the production of endotoxin, and the other is to use endotoxin antagonists. Astragalus polysaccharides, Herba Epimedii and other traditional Chinese medicine preparations can promote the inactivation of endotoxin, reduce its activity and achieve the purpose of adjuvant therapy.
4. Why are some drugs not effective in curing Haemophilus parasuis
In the drug sensitivity test, some drugs are sensitive to Haemophilus parasuis, but the therapeutic effect is not ideal. This is mainly due to the large number of Haemophilus parasuis in serosa, joints, meninges and lungs, while the distribution of capillaries in serosa, joints and meninges is less, and there is a blood-lung barrier between lungs and blood. it is difficult for general drugs to reach these parts of Haemophilus parasuis distribution. Therefore, in the selection of drugs, only drug sensitivity test to select drugs is not enough, we must use drugs with strong penetration and high tissue distribution concentration, only in this way can we go deep into the attachment site of Haemophilus parasuis.
5. Immunity of Haemophilus parasuis
It is recommended to use multivalent oil emulsion inactivated vaccine of Haemophilus parasuis.
Sows: basic immunization, twice every 3 weeks, and then once every 6 months or 40 days before birth.
Piglets: in severely infected pig farms, inactivated vaccines can be used to immunize piglets at 7 days and 21 days of age.
6. Treatment of Haemophilus parasuis
Once Haemophilus parasuis occurs in pigs, ceftiofur and cefquime are the first drugs, followed by ampicillin. In order for antibiotics to reach the brain and joint cavity, injection is usually needed to be effective.
Prophylactic injection can be done by intramuscular injection of amoxicillin or ceftiofur twice or 3 times before weaning, or long-acting oxytetracycline intramuscular injection 3-4 days before the onset of the disease. For breeder pigs, ceftiofur can be injected intramuscularly the day before delivery to reduce the stress of Haemophilus parasuis infection in breeder pigs.
Related
- On the eggshell is a badge full of pride. British Poultry Egg Market and Consumer observation
- British study: 72% of Britons are willing to buy native eggs raised by insects
- Guidelines for friendly egg production revised the increase of space in chicken sheds can not be forced to change feathers and lay eggs.
- Risk of delay in customs clearance Australia suspends lobster exports to China
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (4)
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (3)
- Five common causes of difficult control of classical swine fever in clinic and their countermeasures
- Foot-and-mouth disease is the most effective way to prevent it!
- PED is the number one killer of piglets and has to be guarded against in autumn and winter.
- What is "yellow fat pig"? Have you ever heard the pig collector talk about "yellow fat pig"?