Causes and prevention methods of hoof deformation in dairy cattle
Hoof disease is a common disease in the process of cow production, which causes lameness and paralysis if it is light and paralyzed. If it is not paid attention to, it will affect the production cost and reduce the economic benefit. So how to prevent and cure cow hoof disease? Let's get to know it with the editor.
1. Etiology
The main cause of hoof disease in dairy cows is the imbalance with diet, the insufficient or improper supply of calcium and phosphorus in feed, which leads to the disorder of calcium and phosphorus metabolism and the serious imbalance of calcium and phosphorus ratio, which leads to the decrease of hoof. There is a certain relationship between hoof deformation disease and milk yield of dairy cows. in general, the incidence of cattle with high yield is relatively high, mainly because farmers pursue yield too much, increase the amount of fine feeding too much in feed, too little coarse feeding and poor quality. this will cause the cow body to be in a state of acidosis for a long time, because the hoof leaf is inflamed, resulting in hoof deformation. In addition, if the barn is dark and damp, and the feces are not cleaned in time, it will also cause the horniness of the hoof to become soft and deformed.
2. Symptoms
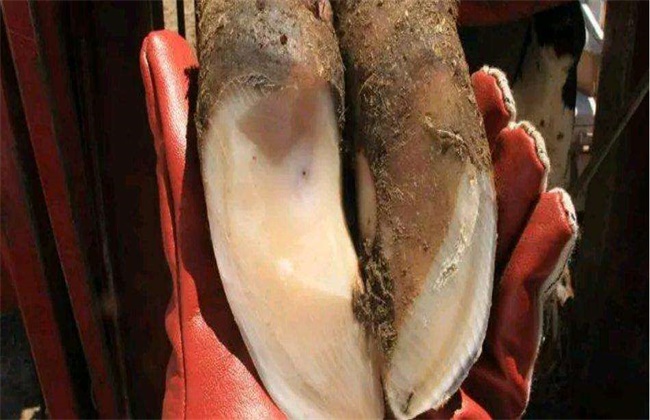
In general, there are three main cases of hoof deformation, one is the long hoof, when the two sides of the hoof exceed the length of the normal hoof branch, the horny of the hoof is excessively extended forward, and the appearance is long. Second, the wide body, the length and width of both sides of the hoof should exceed the normal level, the appearance is large and wide, so it is called large limb plate. The last kind of rolling hoof refers to the low curling of the inside and outside of the hoof. From the bottom of the hoof, the outer edge of the hoof is excessively worn, and the back of the hoof has been turned into the sole of the hoof. Sick cattle often bow their back, it is difficult to walk, and they are dragged.
3. Prevention and cure
Drug treatment can not make the deformed hoof return to normal, so hoof repair therapy is often used in clinic, and corresponding methods are used to give period repair according to the degree of hoof change. Therefore, the key to the prevention and treatment of the disease is to take preventive measures. In production, attention should be paid to strengthening the feeding and management of dairy cows and paying full attention to the supply of protein and minerals. According to the lactation situation of dairy cows, the diet should be reasonably matched, especially according to the milk production of dairy cows, which should be adjusted and supplemented with water. Once the hooves begin to deform, vitamin D3 can be injected to supplement calcium powder in the diet to continue to worsen the stout hooves. In order to prevent the hooves from being soaked in feces and urine, the hooves should always be kept clean and hygienic. The playground should be cleaned and kept dry in time.
The above is the introduction of the causes and prevention methods of dairy cow hoof deformation. I hope it can help you. If you want to know more about it, please follow us.
Related
- On the eggshell is a badge full of pride. British Poultry Egg Market and Consumer observation
- British study: 72% of Britons are willing to buy native eggs raised by insects
- Guidelines for friendly egg production revised the increase of space in chicken sheds can not be forced to change feathers and lay eggs.
- Risk of delay in customs clearance Australia suspends lobster exports to China
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (4)
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (3)
- Five common causes of difficult control of classical swine fever in clinic and their countermeasures
- Foot-and-mouth disease is the most effective way to prevent it!
- PED is the number one killer of piglets and has to be guarded against in autumn and winter.
- What is "yellow fat pig"? Have you ever heard the pig collector talk about "yellow fat pig"?



