Grafting methods of Pear trees
Pear grafting mainly refers to bud grafting from July to August. One is the grafting of pear nursery seedlings and rootstocks after the establishment of the garden. The second is the grafting when updating the variety. In other words, when the inferior varieties with good branching ability are renewed in the annual pear orchard, the high bud grafting method is used to change the head. Grafted pear rootstocks are grafted with "D" shaped buds, and for thicker tiller seedlings, ventral grafting or cutting grafting can be used.

Because of the high density in the sowing nursery, the growth of the grafted pear seedlings is often inconsistent, so it is best to separate the grafted semi-mature seedlings before the next spring in order to expand the nutritional area of the seedlings, and at the same time, cutting off the root system also solves the problem that the main root of the rootstock is too long. after planting, the planed seedlings are planted and managed respectively according to the grafted and ungrafted, sturdy and delicate ones.
1. Grafting methods of pear seedlings
As shown in the figure:
Second, the grafting method and application of replacing new varieties
1. Grafting of branches
(1) split grafting: split pressing is an ancient grafting method, which is often used for branch grafting when the sap has not yet flowed and the bark and wood have not yet left. After sawing the high-grafted tree according to the principle of leaving or leaving the skeleton, flatten the rough saw with a knife, split it longitudinally in the center of the saw, gently pry open the split, gently insert the scion into the rootstock, make the scion thick and thin inside, pay attention to align the rootstock with the forming layer of the scion, do not insert all the cutting surface when inserting the scion, but expose 0.5 cm. One joint is connected to two scions. After being connected, wrap it tightly with a plastic strip, so that a small wound can not be exposed.
(2) subcutaneous grafting: subcutaneous grafting can be carried out when the sap is active and begins to leave the skin. The advantage of this method is that the technique is simple, the knife is operated, the muscle f is the same, and the same dislike net is asked. The method of cutting the scion is: hold the scion in the left hand, hold the scion with the index finger, hold the cutting knife in the right hand to cut the scion, the cutting surface is required to be long, flat and thin, and the length of the cutting surface is determined according to the thickness of the scion, generally 3cm to 6cm. The apex of the back of the large bevel is cut into two small slopes of 0.5 centimeters in the shape of an arrow. After the scion is cut, the saw is flattened with a cutting knife, the bark is cut vertically, and the cut is 1x2 of the length of the large bevel of the scion. Gently pull out with the tip of the knife to separate the skin slightly. When it is not good to leave the skin, insert it with a skid and pry it open. The scion is aimed at the incision, the large slope is attached to the xylem, the small arrow is pressed against the skin, and slowly inserted, and the left hand is pressed and pressed on the vertical incision. Prevent misalignment or insert the scion outside until the large slope is slightly exposed on the cut of the rootstock. Generally 1 branch insert 2 scions, left and right row, thinner branches insert 1 scion. If the wound is too large, the branch can insert 3-4 scions, which is beneficial to the wound healing. Finally, wrap it tightly with plastic strips.
2. Grafting with bald shoots.
(1) subcutaneous ventral grafting: it is used to fill the gap in the bald part of the high grafting tree. Because pear trees can be grafted without bark, first scrape off the old skin on the upper part of the trunk to be grafted, and cut a T-shaped incision. The direction of the vertical mouth is at an angle of 45 degrees with the branch, the horizontal mouth reaches the xylem, the vertical mouth is not cut through, and half of the circular slope is dug on the horizontal mouth, and the cutting method is the same as that under the skin. Pay attention to the use. The curvature of the scion is cut into a large slope, pry up the interface with a pry during grafting, insert the cut scion into the incision, and then tie it up with plastic strip.
(2) with wood bud grafting: with wood bud
Grafting is actually a kind of subcutaneous ventral grafting with shortened scion, which is used for growing branches in bald parts of large branches. A big tree can be grafted without its bark. When grafting, first scrape off the old skin of the part to be grafted, expose the white skin, first cut a T-shaped incision, cut a slope of about 4 cm long on the back of the buds on the scion, and cut 2 small arrowheads on the other side. The hand-held cut scion is inserted into the "T" shaped incision. when the bud is about 1 cm away from the "T" shaped transverse incision, the scion is cut off with a cutting knife, and the buds with wood enter the "T" shaped skin. Then tie it tightly with plastic strips.
3. Grafting on twigs
The main results are as follows: (1) abdominal grafting: it is mainly used for the grafting of fruiting branches with a diameter of less than 2 cm in the inner chamber of the high grafted tree before the tree is peeled. The branch is grafted on the side of the twig of the high grafting tree. Stabilize the base and cut the slope about 3 cm long, and cut the short slope 1 cm long on the opposite side. The grafting part of the rootstock is smoothly cut at an angle of 20 ~ 30 degrees, with a depth of more than 3 cm. Insert the cut scion inward into the rootstock, align the cambium and show slightly white. Tie it tight and wrap it tight.
(2) High bud grafting: it is used to repair the sprouting branches and new shoots on the backbone branches after high grafting. In the part of survival or lack of branches at the end of the bore of the high grafted tree, the sprouting branches were retained, and the buds were grafted on the base of sprouting shoots by T-shaped bud grafting method from July to August.
Time: 2019-06-09 Click:
- Prev
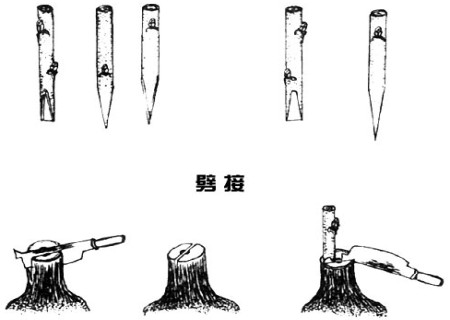
Split grafting technique of Pear Tree
Pear trees are easy to be grafted in fruit trees, and most grafting methods are easy to survive. It is best to use three bud grafting methods: sticking bud grafting, embedded bud grafting and T-shaped bud grafting in summer, and single bud abdominal grafting and split grafting in spring.
- Next

Prevention and Control of Diseases and insect pests of Edible Fungi, simple Family fresh Storage method of Edible Fungi
A simple method of Family fresh Storage of Edible Fungi
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

