Ventral grafting technique of Pear
Grafted pear rootstock grafting I use "Ding" shape bud grafting, thicker to tiller seedlings, can use abdominal grafting or cutting grafting. The growth of the grafted pear seedlings is often inconsistent because of the high density in the sowing nursery, so it is best to separate the grafted semi-mature seedlings before the next spring.
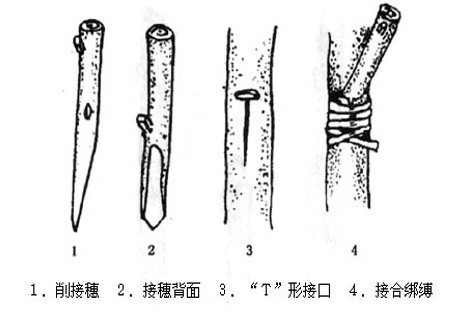
Pear ventral grafting technique:
Mostly used to fill the space of the plant, generally grafted in the bare part of the branch, in order to increase the amount of inner chamber branch and supplement the space, when grafting, first cut a T-shaped incision on the bark of the rootstock, reaching to the xylem, the bark above the transverse incision cut a triangular or semicircular slope to facilitate the insertion and strictness of the scion, the incision site is generally in a slightly convex place or the outside of the curved place, and the T-shaped incision is better when the rootstock is upright or thicker. The ventral scion should be slightly longer, thicker and slightly curved.
Select 1-year-old strong growing branches as scions, leaving 2-3 full buds in each scion. Use a knife to cut a long 3~5cm face in the lower part of the scion, cut it straight, then cut a long 1~1.5cm face on the opposite side of the cutting surface to make the lower end slightly sharp, leave 2-3 buds in the upper part of the scion, the top buds should be left on the back of the large cutting surface, and the cutting surface must be smooth, leaving 0.5cm above the buds to cut. Cut downwards with a knife obliquely at the grafting site of the rootstock, up to the xylem of 1xymoxyla, then quickly insert the scion cutting surface into the rootstock cutting surface to align the cambium and wrap it tightly with plastic sheeting. In addition, there are subcutaneous abdominal grafting and abdominal grafting with basal branches, which are mainly used for the grafting of Chinese chestnut.
Time: 2019-06-09 Click:
- Prev
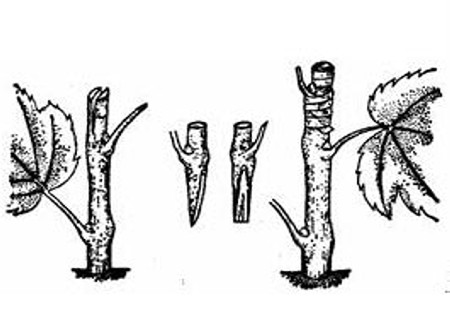
Grafting technique of Twig of Pear Tree
Grafting is the propagation of branches or buds from one plant to the branches, stems or roots of another plant to form a new plant. The seedlings cultivated by grafting are called grafted seedlings. The branch or bud used for grafting is called scion, and the plant that bears scion is called rootstock.
- Next
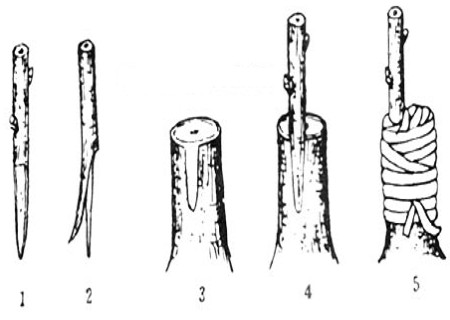
Tongue grafting technique of pear tree bark insertion
Grafting is to artificially connect the branches or buds and other tissues of one plant to the appropriate parts of the branch, stem or root of another plant, so that it can heal and grow together to form a new plant. This branch or bud is called a scion, and the plant that bears it is called a rootstock. When grafted
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

