Grafting technique of Twig of Pear Tree
Grafting is the propagation of branches or buds from one plant to the branches, stems or roots of another plant to form a new plant. The seedlings cultivated by grafting are called grafted seedlings. The branch or bud used for grafting is called scion, and the plant that bears scion is called rootstock.
Grafted seedlings can maintain the characters of excellent varieties (scions), and grow fast, have strong tree potential and bear fruit early, so it is beneficial to accelerate the popularization and application of new varieties, and make use of some characters of rootstocks, such as drought resistance, cold resistance, waterlogging resistance, salt-alkali resistance, disease and insect resistance, etc. enhance the adaptability and stress resistance of cultivated varieties in order to expand the scope of cultivation or reduce production costs. In the production of fruit trees and flowers and trees, rootstocks can be used to adjust the tree potential to dwarf or Arbor trees to meet the different needs of cultivation or consumption; most rootstocks can be propagated with seeds, so the propagation coefficient is large, so it is convenient to popularize and plant in large areas in production.
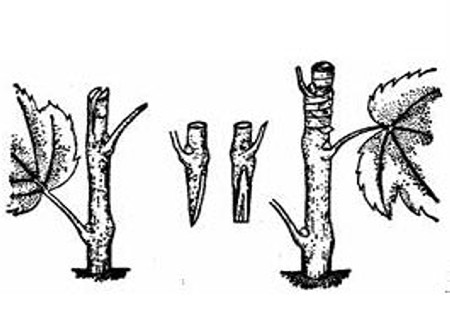
Grafting technique of pear twigs:
The technique of shoot grafting is a kind of branch grafting method which uses the sprouting semi-lignified twigs as scions in the same year. Rootstocks often use twigs and are often used in grapes. They can be carried out in the growing season from the beginning of May to the first and middle of August, but it is better to do them early.
Cut the scion into single bud segments with a quick blade and place it in a bucket filled with cold water to moisturize. The grafting was cut flat at 2 cm above the bud, and at 0.5 cm below the bud, two oblique cutting surfaces were cut downward from both sides of the bud. The shoot of the rootstock was cut from the internodes at 20 ~ 30 cm, and the scion was cut vertically and downward in the center. The scion was inserted into the incision of the rootstock, so that the cambium was aligned, and the grafting interface was wrapped with thin film strips, leaving only the bud outside.
Time: 2019-06-09 Click:
- Prev

A diagram of cutting method of aromatherapy
Duck foot wood is China's fortune tree, many public places, even the courtyard hall are placed a pot of duck foot wood, very elegant. Duck foot wood not only plays a very good role in beautifying and greening the home environment, but also has the role of feng shui. Duck foot wood has a certain role in avoiding evil. There is a saying that leaves are wider
- Next
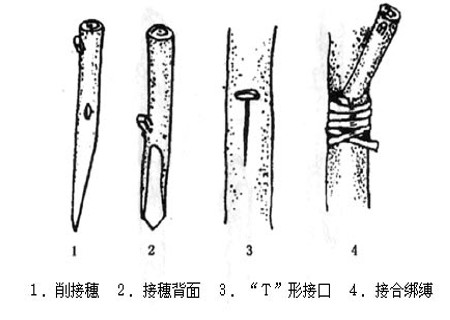
Ventral grafting technique of Pear
Grafted pear rootstocks I use T-shaped bud grafting, thicker to tiller seedlings, can use abdominal grafting or cutting grafting. The growth of grafted pear seedlings is often inconsistent because of the high density in the sowing nursery. It is best to separate the grafted semi-mature seedlings before they are released in the spring of the following year.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

