Causes and prevention measures of postpartum placenta in ewes
Retention of placenta is a common disease of female livestock after giving birth, which is that the mother can not discharge the fetal membrane in time after delivery, resulting in fetal membrane retention in the body, so it is called placental retention. Generally, ewes can be excreted within 4 hours after delivery, if they cannot be excreted for a long time, it can be judged that the placenta does not fall, so what is the reason for the retention of placenta? How to prevent and cure it? Let's take a look.
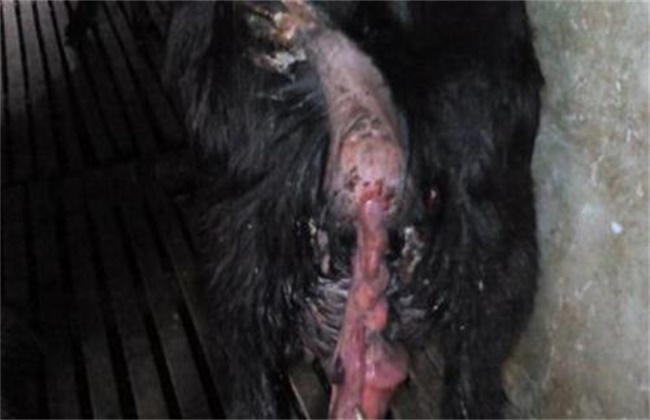
1. Clinical symptoms
According to the size of placenta retention, it can be divided into partial placenta retention and all placenta retention. The retention of placenta in ewes within 24 hours after delivery will have a smaller impact on it, resulting in mental, appetite and body temperature, and very few of them will expand. If the retention time is more than 24 hours, the placenta will decay, lochia and inflammatory substances will occur in the placenta. When these materials are absorbed by the sheep, the ewes will arch the waist or lie down for a long time. And the vulva will also miscarry red and brown lochia, accompanied by fishy smell, ewes will appear lethargic, loss of appetite, body temperature significantly elevated phenomenon.
2. The cause
There are several reasons for the retention of placenta in ewes, one is the physical reasons of ewes, such as too old, weak physique, too thin or too fat, too large fetus and other factors may cause the retention of placenta. Ewes in multiple births and abortion, dystocia and other conditions, the uterine contractility is low, will also lead to placenta retention, lack of exercise during pregnancy, will also cause placenta retention. The second is nutrition, the reproductive performance of ewes is closely related to nutrition to a large extent, if lack of nutrition will first affect the reproductive function of the body, during pregnancy, if ewes are fed with feed lacking minerals, especially when the intake of calcium and phosphorus is insufficient, the uterine contraction is weak during delivery, resulting in the retention of placenta, and the lack of vitamins will also lead to placenta retention. Third, the cause of the disease, pregnant ewes infected with some bacterial diseases, will lead to endometrium and fetal membrane inflammation, in serious cases will cause abortion, in endometrial inflammation will lead to its placenta can not be detached normally.
3. prevention and control measures
500 mL 10% refined salt solution, 0.5 ml 1 g chlorhexidine and 1 g 1.5 g trypsin can be mixed evenly and injected through a rubber tube along the placenta and uterine wall mucous membrane. 1-2 hours later, 1 ml 2 ml% neostigmine is injected subcutaneously behind the ear of the diseased sheep, which can be excreted in 1 hour. If it has not been discharged, surgical treatment can be taken, and disinfection measures should be taken in and around the diseased vagina, and the operator should also do a good job of disinfection, inject 100ml 10% normal saline into the uterus, penetrate into the uterus with hands, peel the placenta, and then slowly pull outward while twisting and turning, so as to raise the position of the uterine horn, and finally pull out the whole placenta, and strengthen nursing after operation to avoid secondary infection.
The above are the reasons for the retention of ewe placenta and the introduction of prevention and control measures, hope to help you, want to know more related knowledge, please follow us.
Related
- On the eggshell is a badge full of pride. British Poultry Egg Market and Consumer observation
- British study: 72% of Britons are willing to buy native eggs raised by insects
- Guidelines for friendly egg production revised the increase of space in chicken sheds can not be forced to change feathers and lay eggs.
- Risk of delay in customs clearance Australia suspends lobster exports to China
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (4)
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (3)
- Five common causes of difficult control of classical swine fever in clinic and their countermeasures
- Foot-and-mouth disease is the most effective way to prevent it!
- PED is the number one killer of piglets and has to be guarded against in autumn and winter.
- What is "yellow fat pig"? Have you ever heard the pig collector talk about "yellow fat pig"?



