What are the common plant diseases in the integrated control of plant diseases and insect pests? Prevention and control of anthracnose of hyacinth
[symptoms] cause the leaf tip to die or produce large brown spots on the leaf surface and petals. Mainly damage leaves and pedicels. Leaf infection, the disease spot mostly occurs in the back of the leaf, the primary brown edge is not obvious round disease spot, showing a rib outward expansion, the edge purplish brown, the central light brown, in the later stage of the disease there are small black spots, that is, the pathogen conidium disk. When the humidity is high, there is gray slime in the disease department. Pedicel infection produces similar symptoms. The leaves often die when the disease is serious.
[occurrence regularity] the pathogen overwintered on the diseased plant or in the soil left with the disease residue by mycelium and conidia disk. Conidia were produced in the second year and spread by Rain Water sputtering to the disease. After that, the disease department continued to produce conidia for re-infection, and the disease spread and reached the peak from July to August. The ascomycetes are produced in late autumn and early winter.
[prevention and treatment methods] the diseased leaves were found by ① and cut off in time. ② careful maintenance, using formula fertilization technology, nitrogen fertilizer should not be too much, pay attention to ventilation and light transmission. ③ sprays 50% Shi Bao Gong wettable powder 1500 times or 25% carbon tetralin wettable powder 500x, 30% basic copper sulfate suspension 400x, 77% Kill wettable particulate powder 600x, 25% make Baike EC 1000 times. Once every 10 days or so, prevention and treatment for 2 or 3 times. When ④ enters the dormant period, watering should be controlled. The humidity of the basin soil is too high and the perishable roots die.
Control methods of physical diseases and insect pests of foliage plants
Some common diseases and insect pests of foliage plants, and put forward suggestions on indoor physical control methods:
Aphids: aphids are small and soft insects that often damage the top tips and tender leaves of begonia, ivy, blood amaranth, Araliaceae and other plants. During prevention and treatment, the leaves can be washed with water or soapy water, or the damaged parts can be removed.
(2) mites: mainly damage the leaves of tortoise back bamboo, variable leaf wood, vine green velvet, rubber tree, hanging bamboo plum and other plants, spread from the lower leaves to the upper, absorb the nutrients of new buds and leaves, and change the color of the leaves. When preventing and controlling, you can sprinkle water from the leaves and rinse mites. Those who do serious harm should be removed immediately.
(3) scale insects: often cause damage to the branches and leaves of leafy wood, bamboo taro, dragon blood tree and pineapple, which often gather on branches and leaves to absorb nutrients. The environment of high temperature, high humidity, poor ventilation and light transmission is the suitable condition for the occurrence of scale insects. Therefore, attention should be paid to strengthening ventilation and light transmission and improving indoor strips. The spread of scale insects is very small, so to do a good job of quarantine, without insect materials, is the most effective control measures. If scale insect damage has occurred. Scale insects can be scraped off with bamboo sticks, or the damaged parts can be cut off.
(4) thrips: damage to the leaves of begonia, hyacinth, poinsettia, etc., often near petioles and veins, crawling on the leaf surface to absorb nutrients. Resulting in loss of green leaves and loss of vitality. If a small number of plants are killed, they can be wiped off with alcohol cotton or washed with soapy water.
(5) anthrax: harmful to wind pears, dragon blood trees, variable-leaf trees, pepper grass, rubber trees, orchids and so on. Invade the leaves, causing black spots on the leaves. The prevention and treatment of this disease should mainly strengthen management, maintain good light transmission and ventilation, avoid watering when watering, should be watered from the edge of the basin, if there are damaged leaves, the diseased leaves should be cut off in time.
(6) Rust: it is harmful to the leaves of Rosaceae and orchid. Orange spots appeared on the leaf surface in the early stage, and brown spores appeared on the back of the leaf in the later stage. Prevention and control methods: disinfect the cultivation medium in advance, strengthen environmental management, maintain ventilation and light transmission, and remove diseased leaves if necessary.
(7) Brown spot: damage to the leaves of dragon blood tree, tortoise back bamboo and palm. Small regular brown spots appeared on the leaves at the initial stage of the damage, and turned gray and white in the later stage. Slowly dry and scorch and die. Prevention and control methods: artificial pruning of diseased leaves and withered branches, and concentrated burning.
(8) soft rot: it is harmful to the leaves of orchid and reticulate grass. At the initial stage, water-immersed spots appeared on the leaf surface and petiole, and then wilted and drooped, losing ornamental value. Attention should be paid to careful management in prevention and control, to avoid watering the leaves and to cut off the damaged branches and leaves.
(9) powdery mildew: damage to Compositae and Rosaceae plants, causing damage to leaves. During the prevention and treatment, we should strengthen the management, keep the room with good ventilation and light transmission, and cut off the diseased leaves.
Control methods of diseases and insect pests of foliage plants
Foliage plants may be damaged by diseases and insect pests in the process of growth. The damaged plants not only affect their growth, but also reduce or even lose their ornamental value. therefore, the prevention and control of indoor foliage plant diseases and insect pests is very necessary, which is a basic skill that flower lovers need to master. Otherwise, it will lose the true meaning of foliage plants to beautify and purify the environment.
There are many kinds of indoor foliage plants, but for each unit or family, the number of applications is small, and the management is more meticulous. If there are diseases and insect pests, although it is not easy to spread to other plants, but the damaged plants tend to develop rapidly. Therefore, the prevention and control methods of diseases and insect pests of this kind of plants are mainly prevention, comprehensive control, strengthening tending management at the same time, creating a good plant ecological environment, promoting plant growth and health, improving its own resistance and other effective cultivation measures.
Before entering the indoor layout, all indoor foliage plants should be strictly inspected, disease-resistant varieties or healthy plants with strong adaptability should be selected and arranged rationally. if slight diseased leaves or a small amount of aphids, mites and scale insects are found, physical methods should be used in time, such as manual pruning, removal of diseased leaves, or washing with soapy water, and then rinse with clean water or wipe with a soft wet cloth. Scale insects can also be gently scraped off with bamboo sticks; if the damage is serious, remove them from the room for treatment.
Indoor foliage plants should not be treated indoors with pesticides, because pesticides are generally toxic substances, which will lead to many adverse consequences if such toxic substances are retained or brought into the indoor air ventilation system. As a kind of decoration, indoor foliage plants often attract people to appreciate their various characteristics, such as some people will smell them, others will touch their branches and leaves. In order to maintain a good relationship of public interest, it should be stipulated that indoor decorative plants do not use pesticides to control diseases and insect pests. If some plants are harmed by diseases and insect pests and cannot be effectively controlled by physical methods, they must be moved outdoors and isolated from indoor healthy plants. Then make other treatments, such as chemical control, or destruction. The plants in the human room must be checked regularly, treated and prevented in time, so as to reduce the degree of plant damage, prevent trouble, keep the room clean, ventilated and transparent, and keep the foliage plants green and fresh, with high ornamental value.
1. Physical control methods
The following lists some common diseases and insect pests of foliage plants, and puts forward suggestions on indoor physical control methods:
Aphids: aphids are small and soft insects that often damage the top tips and tender leaves of begonia, ivy, blood amaranth, Araliaceae and other plants. During prevention and treatment, the leaves can be washed with water or soapy water, or the damaged parts can be removed.
(2) mites: mainly damage the leaves of tortoise back bamboo, variable leaf wood, vine green velvet, rubber tree, hanging bamboo plum and other plants, spread from the lower leaves to the upper, absorb the nutrients of new buds and leaves, and change the color of the leaves. When preventing and controlling, you can sprinkle water from the leaves and rinse mites. Those who do serious harm should be removed immediately.
(3) scale insects: often cause damage to the branches and leaves of leafy wood, bamboo taro, dragon blood tree and pineapple, which often gather on branches and leaves to absorb nutrients. The environment of high temperature, high humidity, poor ventilation and light transmission is the suitable condition for the occurrence of scale insects. Therefore, attention should be paid to strengthening ventilation and light transmission and improving indoor strips. The spread of scale insects is very small, so to do a good job of quarantine, without insect materials, is the most effective control measures. If scale insect damage has occurred. Scale insects can be scraped off with bamboo sticks, or the damaged parts can be cut off.
(4) thrips: damage to the leaves of begonia, hyacinth, poinsettia, etc., often near petioles and veins, crawling on the leaf surface to absorb nutrients. Resulting in loss of green leaves and loss of vitality. If a small number of plants are killed, they can be wiped off with alcohol cotton or washed with soapy water.
(5) anthrax: harmful to wind pears, dragon blood trees, variable-leaf trees, pepper grass, rubber trees, orchids and so on. Invade the leaves, causing black spots on the leaves. The prevention and treatment of this disease should mainly strengthen management, maintain good light transmission and ventilation, avoid watering when watering, should be watered from the edge of the basin, if there are damaged leaves, the diseased leaves should be cut off in time.
(6) Rust: it is harmful to the leaves of Rosaceae and orchid. Orange spots appeared on the leaf surface in the early stage, and brown spores appeared on the back of the leaf in the later stage. Prevention and control methods: disinfect the cultivation medium in advance, strengthen environmental management, maintain ventilation and light transmission, and remove diseased leaves if necessary.
(7) Brown spot: damage to the leaves of dragon blood tree, tortoise back bamboo and palm. Small regular brown spots appeared on the leaves at the initial stage of the damage, and turned gray and white in the later stage. Slowly dry and scorch and die. Prevention and control methods: artificial pruning of diseased leaves and withered branches, and concentrated burning.
(8) soft rot: it is harmful to the leaves of orchid and reticulate grass. At the initial stage, water-immersed spots appeared on the leaf surface and petiole, and then wilted and drooped, losing ornamental value. Attention should be paid to careful management in prevention and control, to avoid watering the leaves and to cut off the damaged branches and leaves.
(9) powdery mildew: damage to Compositae and Rosaceae plants, causing damage to leaves. During the prevention and treatment, we should strengthen the management, keep the room with good ventilation and light transmission, and cut off the diseased leaves.
2. Chemical control methods
If the above physical control methods do not work, the plants should be moved outdoors and chemical control should be carried out. The commonly used methods are:
The main results are as follows: (1) foliar spraying pesticides: according to their different insecticidal mechanisms, pesticides can be divided into three types: internal suction type, contact type and protective treatment type. In the internal inhalation type, insecticides include omethoate, which mainly control scale insects, mites and aphids, and fungicides such as carbendazim, methyl topiramate, etc. It is effective for leaf spot, anthracnose, brown spot, rust and so on. Contact insecticides include dichlorvos and pyrethroids, which can kill larvae, aphids and newly hatched scale insects of chewable mouthparts. Protective and therapeutic pesticides mainly form a film on the surface of plants, which can protect, treat or kill diseases and insects, such as stone sulfur mixture, sulfur gel suspension, polymer membrane and so on.
(2) soil application of pesticides: the effective components of these pesticides can be absorbed by the roots of plants and spread to all parts of the plant to kill leaf painting diseases and insects, or directly kill diseases and insects in the soil, such as formaldehyde and other drugs.
- Prev
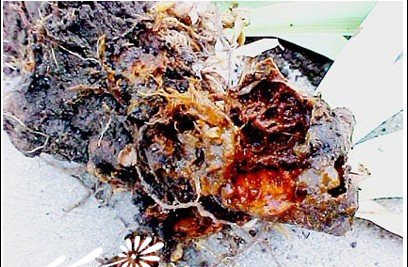
Control methods of hyacinth root rot
Hyacinth cultivation areas occur from time to time, endangering hyacinth and other flowers, resulting in root rot. After the symptom plant is damaged, the growth is weak, dwarf, can not blossom normally, dig up the soil, it can be seen that most or all of the roots on the corm rot. The pathogen of the disease is Fusarium, which belongs to fungi. The pathogen overwintered in the remnant of the diseased plant.
- Next

How to breed daffodils?
Daffodils mainly have lateral buds, lateral bulbs, double-scale propagation and tissue culture. The main results are as follows: (1) when castration bulbs are used for lateral bud propagation, the lateral buds wrapped inside are dug out and used as propagation materials. In autumn, the lateral buds are scattered evenly on the finished surface and covered with a thin layer of soil. The front of the front of Danzah should be watered thoroughly
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

