Control methods of hyacinth root rot
Hyacinth cultivation areas occur from time to time, endangering hyacinth and other flowers, resulting in root rot.
Symptom
After the plant is damaged, the growth is weak, dwarf, can not blossom normally, dig up the soil, it can be seen that most or all of the roots on the corm rot. The pathogen of the disease is Fusarium, which belongs to fungi. The pathogen overwintered in the remnants of diseased plants and spread through Rain Water, irrigation water, field horticulture and so on.
Prevention and cure method
(1) strengthen cultivation management. Hyacinth likes to be cool and cold-resistant, and should be moist and sunny. Like fertilizer, requires rich in humus, well-drained sandy loam. The roots sprouted in autumn, the leaves bloomed in early spring, the stems and leaves were withered and yellow in midsummer, and the bulbs dormant and differentiated flower buds. Separate bulbs breed in autumn. North China chooses to plant in a sunny and sheltered environment, which can survive the winter with a little cover in winter. Apply sufficient base fertilizer before planting, topdressing before flowering, control fertilizer and water in the later stage, and store the ball in a dry, cool and ventilated place after summer dormancy.
(2) instead of planting diseased bulbs, the pot soil of diseased plants should be replaced and planted with disease-free soil, or dimethazone can be used to disinfect the soil.
(3) soak the seeds with 800 times solution of 50% benzoate wettable powder for disinfection.
How to control the soft rot of hyacinth
In the greenhouse, the seriously infected bulb no longer germinates, the bulb becomes soft, and the tissue of the bulb is transparent with white or yellow spots. These infected bulbs also give off an unpleasant smell. The symptom of mild infection is the formation of wet, dark green strips from the base of the leaves, first hindering growth, then wilting until the plant dies.
1. Etiology
The disease is caused by Erwinia. Most of these bacteria are parasitic and mainly infect tissues that are frozen or overhydrated. Another form of infection is infection from wounds where precocious roots or bulbs peel off when the temperature is too high or the soil is too wet. This problem is mainly caused by too high or too wet soil temperature during natural cold treatment in autumn.
The manifestation of soft rot: the top of the bulb showed waterlogged slippery soft rot, the base of the pedicel rotted, the flower did not bloom, the flower bud fell off first, or the abnormal flower was formed in the later stage. After being infected, the buds first turn white, and then they become sticky, soft and smelly. The leaves also produce watery rot, but the disease is not contagious in the greenhouse, and although the infected tissue is usually buttered, the infection does not occur in other parts.
2. Prevention and control methods
(1) bulbs are usually planted under the recommended conditions, that is, natural treatment or low temperature (9 ℃) in the rooting chamber, while not too wet.
(2) the infected bulbs and plants should be removed during planting and throughout the greenhouse period, which can prevent Erwinia from spreading to neighboring bulbs through irrigation water.
Prevention and control of bacterial soft rot of Iris bacterial soft rot is one of the most common diseases of Iris, whether it is bulbous Iris or rhizomatous Iris. The following combined with years of breeding experience, to talk about the prevention and control of Iris soft rot.
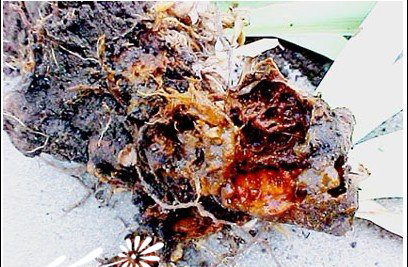
The pathogen of Iris soft rot is bacteria. At present, there are two known species, namely, carrot soft rot Erwinia carrot pathogenic variety of carrot and Amorphophallus Owens, both of which belong to Bacteriacea and Owens. In addition to irises, it also harms many kinds of flowers and plants, such as cyclamen, hyacinth, lilies and tulips. The law of the disease is that germs generally survive the winter in the soil and stubble. They can survive in the soil for several months, and if they are in the remains of diseased plants, they can survive for a long time. It is easier to survive when the temperature and humidity are high. Therefore, in general, the disease occurs more when the soil is moist, where the planting is too dense and the shade coverage is large. If the disease has already occurred, the method that should be taken immediately is to choose the mixture of streptomycin or streptomycin plus oxytetracycline (10:1) to spray the plant and the ground for 2-3 times with good results. After the disease, agricultural streptomycin can also be sprayed once a month, so that the spread of the disease can be controlled in parallel.
- Prev

Control methods of hyacinth mosaic disease
[symptoms] the leaves were damaged, showing yellow and green mosaic shape, gradually developed into stripes and patches, and in severe cases, the leaves were yellowed and twisted; the bulbs grew poorly and became smaller; the flowers were broken, shrunk and not bright; and the plants showed dwarfing. [pathogen and pathogenesis] is a viral disease, the pathogen is hyacinth mosaic virus HMV
- Next

What are the common plant diseases in the integrated control of plant diseases and insect pests? Prevention and control of anthracnose of hyacinth
[symptoms] cause the leaf tip to die or produce large brown spots on the leaf surface and petals. Mainly damage leaves and pedicels. Leaf infection, the disease spot mostly occurs on the back of the leaf, the primary brown edge is not obvious round disease spot, showing a wheel-like expansion, the edge is purple-brown, the center is light brown, and there are small black spots in the later stage of the disease.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

