Agricultural Common sense Science Popularization: the effect of accumulated temperature on crop planting
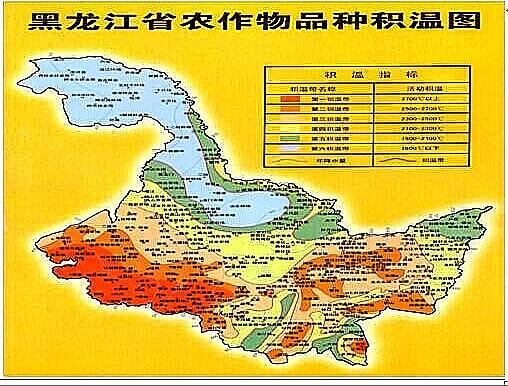
We often talk about the concept of accumulated temperature in agriculture, so what is accumulated temperature? To put it simply, the sum of the daily average temperature of a certain index temperature duration during the crop growth period is called accumulated temperature. Among all kinds of accumulated temperature (0 ℃, 3 ℃, 5 ℃, 10 ℃, 15 ℃), the accumulated temperature and active accumulated temperature in the stable period of daily mean temperature ≥ 10 ℃ are the most widely used. According to the natural landscape and crop distribution, China is divided into 6 temperature zones and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau by using accumulated temperature and lasting days.

1. The equatorial belt is located in the South China Sea island area south of latitude 10 °N, south of the southern limit of the mean polar front in winter. The accumulated temperature is more than 10000 ℃, the days of ≥ 10 ℃ is 365 days, the average temperature in January is more than 26 ℃, and the annual precipitation is more than 1000 mm, which is more than the heat and moisture in the tropics, but the annual variation rate of air temperature is very small, the rainfall in the four seasons is more uniform, and all kinds of tropical plants can grow on the island. In many cases, we do not divide this accumulated temperate zone into five accumulated temperate zones separately, because there are few real agricultural activities in this area.
2. In the tropics, including Leizhou Peninsula, Hainan Island, Taiwan Island and a few places in southern Yunnan, the duration of accumulated temperature ≥ 8000 ℃ and ≥ 10 ℃ is 350-365 days. The average temperature in January is above 15 ℃, and there is no frost in the whole year. The lowland vegetation is mainly tropical monsoon forest, tropical cash crops such as rubber, coconut, betel nut and coffee can grow, rice can be cropped three times a year, sweet potato can be sown in winter, and winter wheat is not suitable for growth.
3. Subtropics, including the Qinling Mountains, south of the Huaihe River and most areas east of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The accumulated temperature is 4500-8000 ℃, the duration of ≥ 10 ℃ is 218-365 days, the average temperature in January is 0: 15 ℃, and the frost-free period is 8-12 months. The natural vegetation includes subtropical monsoon rain forest, monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest and mixed evergreen broad-leaved forest, which is the main producing area of citrus, tea, palm, paulownia and bamboo in China, as well as banana, pineapple, litchi, longan, olive and other economic crops in the south. Rice can be cropped twice a year, while wheat is cultivated everywhere.
Advertisements (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle | | []) .push ({})
4. The warm temperate zone roughly includes the vast areas south of the Great Wall, the Qinling Mountains and the north of the Huaihe River and the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang. The accumulated temperature is 3400 to 4500 ℃, the duration of ≥ 10 ℃ is 171 to 218 days, the average temperature in January is from 6 ℃ to 0 ℃, and the growth period is 5.5 to 7.5 months. The natural vegetation is deciduous broad-leaved forest in the east and arid desert in the west. Crops are cropped twice a year or three crops a year, and one crop a year in some places. Wheat is mainly sown in winter, and apples, pears, persimmons, grapes and other fruits are of good quality.
5. The middle temperate zone, including the south of the cold temperate zone, the north of the Great Wall and the Junggar Basin in Xinjiang. The accumulated temperature is 1600 ~ 3400 ℃, the duration of ≥ 10 ℃ is 100,171 days, the average temperature in January is-30 ℃ ~-12 ℃ to-6 ℃, and the growth period is 3.5 ~ 5.5 months. The natural vegetation is a mixture of coniferous forest and deciduous broad-leaved forest in the east and arid desert in the west. The average temperature in July is less than 20 ℃, rice and castor can grow in most places, wheat and soybean become the main crops in different areas of the belt, but the cold winter season is long, so it is not suitable for winter farming.
6. The cold temperate zone is in the northernmost part of Heilongjiang and the northeast corner of Inner Mongolia Autonomous region. The accumulated temperature is less than 1600 ℃, the duration of ≥ 10 ℃ is less than 100 days, the average temperature in January is below-30 ℃, the summer temperature is not high, the average temperature in July is 16-18 ℃, and the frost-free period is about 3 months. Natural vegetation is coniferous forest, rice, sorghum and so on can not grow, temperate fruit is also completely extinct, can only barely cultivate wheat, potato, wheat and millet.
In the climatic region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, due to the high altitude, the zonal law has been destroyed, so the temperature zone can not be divided according to the above criteria. Although winter is not as easy to be attacked by northern cold air as in the eastern plain of latitude, the temperature in summer is low, and the accumulated temperature in most areas is less than 2000 ℃. In some places, there is a frost-free period all year round, while in some places, the frost-free period is as long as 7 months. Therefore, the situation of the whole Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is very complicated, so another area is listed.
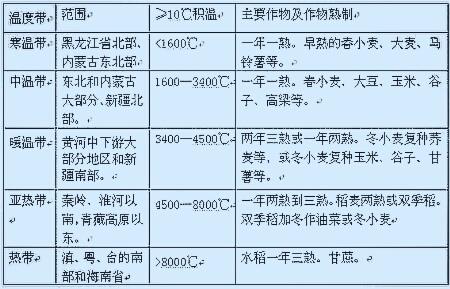
as the main soybean producing area, Heilongjiang Province divides the province into six accumulated temperate zones: the first accumulated temperate zone is more than 2700 ℃; the second accumulated temperate zone is 2500-2700 ℃; the third accumulated temperate zone is 2300-2500 ℃; the fourth accumulated temperate zone is 2100-2300 ℃; the fifth accumulated temperate zone is 1900-2100 ℃; the sixth accumulated temperate zone is less than 1900 ℃, and so on, the northernmost sixth accumulated temperate zone is below 1900 ℃, as shown in the figure:
The division of accumulated temperature and temperature zone is only a guiding division in a large area. In the process of agricultural production, it is necessary to take more appropriate and effective measures according to the specific local conditions in order to better improve the efficiency.
- Prev
Planting also needs a sense of design in landscape design.
In the landscape design, the planting needs to be "sparse can walk the horse, no needle" the landscape gives people a sense of comfort and leisure, the appearance gives people a sense of beauty and tranquillity. Whether it's an isolated plant.
- Next

What are the purple vegetables suitable for families to grow?
Focus on the production and sales of potted vegetables, please add Wechat 178068133 for consultation and cooperation.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

