Key points of Prevention and Control methods of "Invisible Killer" in Pepper planting
What is the "invisible killer" of chili?
Root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.), commonly known as "root-growing potatoes", is a kind of soil-borne parasitic pathogens that do great harm to crops, generally reducing crop yields by 10% to 20%, and more than 75% in heavy cases. Root-knot nematode disease is one of the main diseases and insect pests in pepper planting and production. it mainly affects the root of pepper plant, and the main symptom is the formation of nodular root knot and rotten root in the root, resulting in the weakening of pepper plant growth and gradual death. it seriously affected the production of pepper. From the aspects of agricultural planting management, drug control, physical control and biological control, the author introduces several measures for the control of root-knot nematode diseases in pepper, which can be used as a reference for the majority of growers. The harm knowledge of root-knot nematode can be referred to: the morphology and life history of root-knot nematode, and the disease map of "invisible killer" of several crops.
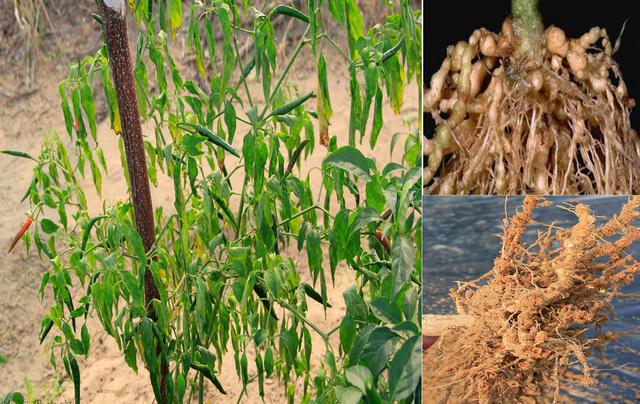

Damage degree of root-knot nematode in pepper
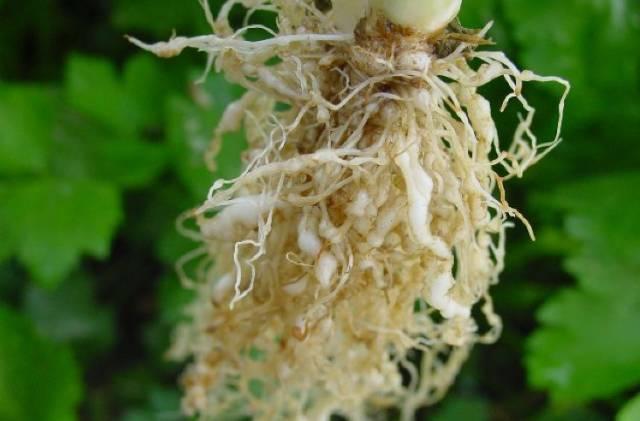

The root-knot nematode of pepper harms the root of pepper, mainly on the fibrous root and lateral root, and the ends of the injured fibrous root and lateral root will form bead-shaped nodules of different sizes.
Pepper root-knot nematode pierced the root with oral needle to form a dense wound, which will cause other diseases to infect pepper root, such as pepper root rot and Fusarium wilt, especially pepper root rot, which is more likely to cause pepper root rot and root rot.
Because the root-knot nematode will cause wounds near the root tip of pepper, it will induce the infection of some bacteria in the soil and accelerate the rot of pepper root system, so that the plant will gradually appear yellow leaves, small growth, wilting and so on.
At present, it is the planting period of hot pepper, if the planted pepper is damaged by pepper root-knot nematode, it is easy to appear the phenomenon of uneven and dead seedlings.
The main points of the methods of preventing and controlling the "invisible killer" of pepper planting
Agricultural planting management and prevention
Implementation of crop rotation: for seriously diseased fields, highly susceptible fast-growing leafy vegetables such as spinach can be used in the later stage of production, and antagonistic crops such as onions and garlic can be arranged in the next crop rotation; for lightly diseased fields, they can be attracted in the fallow period. A small number of areas can consider appropriate idle fields in winter, combined with low temperature freezing to alleviate the disease.
To select nematode resistant varieties, there are few nematode resistant varieties in pepper.
Cultivate healthy seedlings: choose healthy and full seeds, soak the seeds in warm soup for 15 minutes and 30 minutes under the condition of 50-55 ℃, and then sow the seeds. Fumigant film fumigation can be used for seedling bed and substrate disinfection. 10 kg of 0.5% formaldehyde solution or 15 g of 98% methanolone granule per square meter of seedling bed can be used for disinfection. The seedlings can be raised after the film is fully released. Non-fumigating agents can also be used for soil contact killing, using 2.5% avermectin EC 5g per square meter or 0.5% avermectin granules 18g 20g, 10% thiazophos granules 2.0g / m 2.

Biological control
The soil was sterilized by high temperature baking or water flooding in the greenhouse, and attention should be paid to the application of phosphorus, potassium fertilizer and biological bacterial fertilizer before cultivation. In the summer after pulling hot pepper seedlings, the soil was ploughed 40-50 cm deep, 200 kg of quicklime was mixed per mu, and 500 kg of straw was added immediately. After 15 days, the greenhouse was covered with high temperature and covered with plastic film after flooding. 15 days later, the damage of nematode disease can be effectively reduced.

Physical control of field soil
Calcium cyanide treatment: the previous vegetables were watered 5-7 days before pulling seedlings. After pulling seedlings, the incomplete rotten farm manure or broken crop straw was scattered evenly on the soil surface. Immediately, 60-80 kg ∕ mu of calcium cyanide was evenly sprinkled on the soil surface, rotary tillage soil 10 cm to make it mix evenly, irrigated again, covered with plastic film, high temperature greenhouse for 7 days and 15 days, then removed the plastic film, and ridge planting could be done after 7 days of air release. Before cultivation, attention should be paid to the application of phosphorus, potassium fertilizer and biological bacterial fertilizer in the treated soil.
Chemical fumigation and disinfection: first, choose isothiocyanates, using 98% Mirabilon granule 10g / mu, or 20% horseradish suspension 25g / mu, or 35% Weibaimu water agent 100ml / mu. The second is to use 40 liters of chloropicrin per square meter, or 10 grams of 3-dichloropropene, 20 grams of thioyl fluoride, 20 grams of methyl iodide, etc., or 40 kilograms of dimethyl disulfide per mu. Third, mixed fumigation, mixed with chloropicrin and other fumigants, has a good comprehensive control effect on many kinds of soil-borne diseases and pests represented by root-knot nematode, such as chloropicrin + 1-dichloropropene (1-dichloropropene), chloropicrin + dimethyl disulfide (1:1) and chloropicrin + methyl iodide (2-pur1-1-dichloropropene).
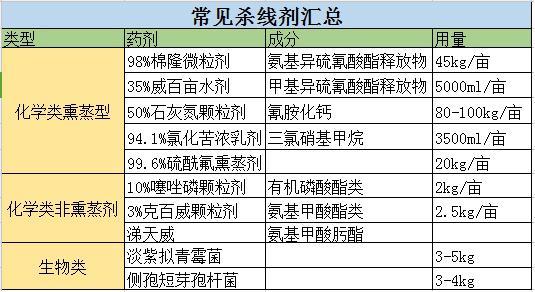
Control of Pepper Seedling stage
In terms of chemical use, 2.5 kg of 10% thiazophos granules can be applied per mu of ditch, covered with soil and closed with water, and planted loosely after a week. 10% parathion granules 3kg or 3% chlorazophos granules 3kg / mu can also be applied per mu, or 40% phoxim EC 2kg + 1.8% avermectin EC 200g mixed hole irrigation treatment. In the aspect of biological medicine, we can choose 200 million live spores / g Paecilomyces lilacinus 2-3kg soil dressing evenly, or 2.5kg soil-mixing ditch application or hole application, 200m live spores / gram thick spore Verticillium 2kg-3kg soil dressing evenly, or 2.5kg soil mixing ditch application or hole application.
Control of capsicum in growing period
10% thiazophos granules can be used per mu 1.5 kg. Or 0.5% avermectin granules 15.0-17.5 g, 5% thiophanate 0.3-0.4 kg, 3.2% phoxim 0.3-0.4 kg, 200 million live spores / g Paecilomyces lilacinus 2.5 kg, 200 million live spores / g thick spore Verticillium 2.0-2.5 kg soil dressing side ditch is concentrated on the root of the plant. Each plant was irrigated with 2000 times of 2.5% avermectin EC 300ml 500ml.
Under-film pipeline drip irrigation: use 35% sodium methyl dithiocarbamate aqueous agent with a concentration of less than 1000 mg ∕ liter and 30 liters per square meter; fumigant agents such as mirabilone, horseradish, dimethyl disulfide and other fumigants can be used for under-film drip irrigation.
Intercropping trapping: fast-growing leafy vegetable crops with high sensitivity, such as pakchoi or spinach, can be sown within one week after crop colonization, nematodes in the soil can be trapped, and crops can be pulled out and trapped repeatedly in 20-25 days for seriously diseased fields. Please follow the author: agriculture in typhoon days
- Prev

Planting green manure crop in orchard-- rat thatch and sowing points
The cultivation or wild green plants planted in peach trees are collectively referred to as green manure when they are applied directly or after composting to the soil as fertilizer. Specializing in growing crops for green manure.
- Next

Huaimihui Agriculture: planting techniques of Sophora pseudoacacia
Generally speaking, Robinia pseudoacacia can be planted by sowing, cutting and grafting. Robinia pseudoacacia likes sunshine, can withstand cold, slightly endure shade, and is not tolerant to drought and shade.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

