Key points of variety selection and planting techniques of lentil
In the countryside, Xiao Fan's family found that rural people actually prefer to eat lentils, but lentils are generally grown in the south, in fact, there are also plants in the north, but because of winter, the north is not particularly many.
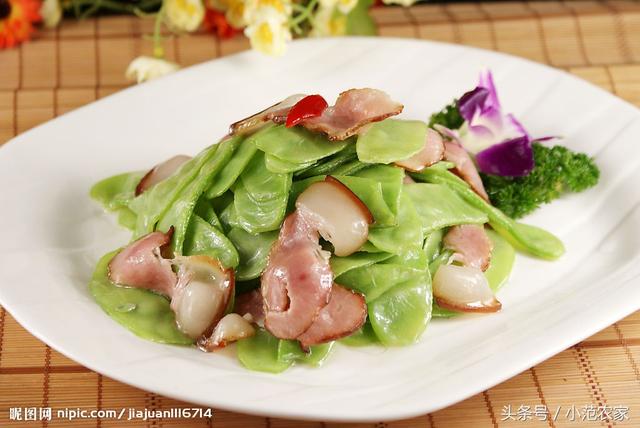

Lentils, also known as eyebrow beans, moth eyebrow beans, lotus root beans, magpie beans, along the ledge beans, is a cultivated species of the genus Leguminosae, annual or perennial herbaceous vines, which can be perennial in the frost-free areas of the south. Eat young pods or ripe beans.
Like warm and afraid of cold, death in case of frost. The suitable temperature for growth is 20-30 degrees Celsius, the optimum temperature for flowering and fruiting is 25-28 degrees Celsius, and the temperature can withstand 35 degrees Celsius.

1. Select the improved varieties according to the cultivation conditions. The existing lentils are divided into white lentils, green lentils and purple lentils according to their pod color. The main varieties cultivated in China are:
① purple-edged lentils. That is, pig ear lentils, trailing. The leaves are dark green, the veins and petioles are purple, the pods are wide and flat, the color is green and fat, the stitches on one side are dark purple, and the pods are crisp and tender.
Each pod contains 5-6 seeds, mature seeds are black, cooked with good quality, high yield, middle and late maturity, strong heat resistance, weak cold resistance, like water and fertilizer, and luxuriant growth.
② white lentils. Trailing, much branched, strong growth. The whole plant is green. The flowers are white, the pods are narrow, long and thin, light green, the pods are thin and tender, the seeds are white, and the flavor is good.
. The whole growth period of spring sowing is 160-170 days. Extremely resistant to drought.
③ black seed white lentil. Trailing, strong growth potential, purple on stem light green nodes, dark green leaves, purplish red flowers, high pod setting rate, light green narrow pods, seeds per pod
5-6 seeds, black seeds. Drought resistance, barren resistance, heat resistance, cold resistance, long harvest time.

④ purple lentils. Trailing, strongly branched, dark purple stem, green leaves, dark purplish red veins and petioles, long inflorescences, many pods, narrow, long, thick pods, purplish red
Contains 3-5 seeds, cooked soft cotton. Late ripening, heat-resistant, cold-resistant, drought-resistant, long harvest time and high yield. Cultivation techniques of lentil
2. Planting mode. There are many lines of direct broadcast in late spring, and tender pods are harvested one after another from summer and autumn to early frost. Monoculture or intercropping with corn, using corn straw as support, or intercropping with garlic
It can also be planted on the edge of the field.

① sowing density: the plant spacing of short vine precocious cultivation is 30cm 45cm, the row spacing is 65cm 70cm, and the plant spacing of long vine hedgerow pruning cultivation is 45cm, the row spacing is 100,130cm.
Rice; herringbone pruning cultivation for 133 cm border, species 2 rows, plant spacing 35 cm, leaving work road 66 cm between borders.
② sowing method: ditch or hole sowing, sowing depth of 5 cm to 7 cm, should be covered with plant ash after sowing.
Sowing rate of ③: 57kg / ha for monoculture and 6kg / ha for mixed cropping.
3. Field management
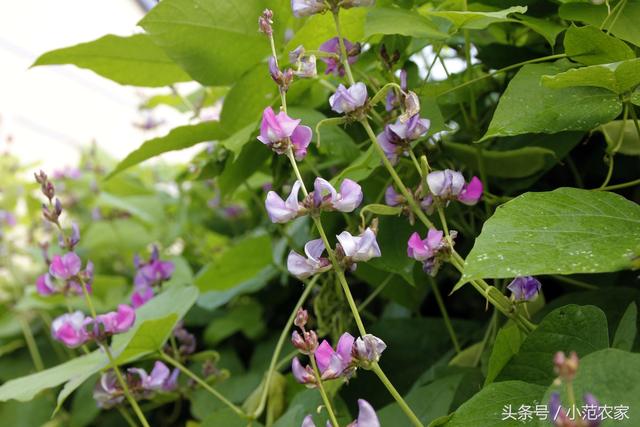

① water and fertilizer management: less water was needed at seedling stage, and more water was needed after vine elongation and podding stage. Generally, 1 / 2 water is watered during the growing period, and the flowering and pod period is about 10 days without rain.
Water it. After watering, ploughing and weeding, combined with topdressing, to prevent flowers and pods from falling and overgrowing. Ploughing should be shallow to prevent root damage. Organic matter fertilizers such as rotten chicken manure can be applied before podding. After setting pods, apply a small amount of chemical fertilizer.
② frame to draw the vine, pruning: set up the frame before drawing the vine, or use the rope to lead the tree and go to the house in time after drawing the vine. When the main vine has 5 or 6 compound leaves, the heart is removed to promote multiple lateral vines, waiting for the side.
When the vine has 4 leaves, it can blossom and bear pods earlier, but the yield is lower. Generally, if you use a hedge or herringbone frame to cultivate, pick the heart when the stem vine grows to the top of the frame, which can promote the early maturity of the pod.
③ control of diseases and insect pests: lentil diseases are less, insect pests are mainly aphids and red spiders, can be sprayed with low toxic agents to control as soon as possible.
4. Harvest
Lentils have a long growth period (160-300 days), blossom and bear pods 60-65 days after emergence, and young pods can be harvested one after another. It can be harvested for 90,120 days. Generally produce tender per hectare
15000-18750 kg pod. The shelf life of fresh pods and tender beans is short. If stored at a relative humidity of 85%-90% and 0-2 degrees Celsius, fresh pods can be preserved for 21 days and tender beans with pods for about 7 days. The mature seeds were harvested for 150-210 days for long vines and 60-75 days for precocious short vines. Mature pods are harvested and dried when they are dried and stored after threshing and cleaning.
Lentils are easy to get rust, brown spot, but also to prevent lentil moth, small gray butterfly and tobacco pests.
- Prev

Dental implants are so expensive, how long can they last?
The use time of dental implants is determined by both dentists and patients. Dental implants are not only related to the doctor's implant technology, implant brand, but also to the patient's body shape.
- Next
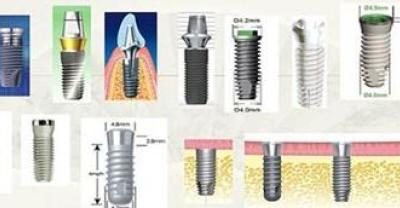
A picture to let you know "implant teeth"!
Does dental implant put a "seed" in the mouth to make the tooth sprout? If you believe so much, you are still Too young Too simple Too naive~ today, hippo.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

