PGS may save repeated embryo implantation failure
Repeated implantation failure (RIF) refers to a patient who is treated with IVF and is still unable to conceive after multiple consecutive embryo transfers. At present, the accepted standard is that women under the age of 40 have been transferred more than 3 times, or more than 4 highly rated embryos are still unable to get pregnant. The success rate of repeated implantation failure can be improved by blastocyst culture and preimplantation genetic screening (PGS).
PGS may save repeated embryo implantation failure
The cause of repeated planting failure is complex. Embryo and endometrium are the two main factors that affect the success of embryo planting. The relationship between them is like seeds and soil. Good seeds can not germinate smoothly without fertile soil, and bad seeds can not germinate even in good soil. What we are going to discuss today is how to "discern the eye" to identify a real "potential stock" and select a powerful seed with high appearance and high potential.
High "appearance" does not mean high "potential"
There are different methods to select high potential embryos: morphological score, blastocyst culture, preimplantation genetic screening, metabonomics and so on. At present, the widely used embryo morphology scoring method is simple and convenient to operate, and there is a certain correlation between the score and the embryo implantation rate, but it can not fully represent the quality of the embryo and the potential of implantation development. The dynamic real-time imaging technology based on morphology (time-lapse) can also play a certain role in selection, but the instrument is expensive, and it is still controversial whether real-time imaging technology is really helpful to screen good embryos.
Embryonic metabonomics is to analyze the vitality of embryos by detecting the metabolic components of embryo culture medium. due to the need for special detection techniques, the data is difficult to accurately correspond to clinical outcomes, and the feedback of test results is not timely, so its application is limited. How can we find the power school with high appearance and high potential in a batch of embryo seeds? Let's take a look at the "secret weapon" in our hands.
1. Blastocyst culture
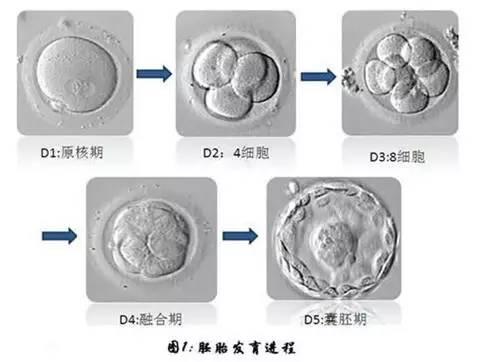
Blastocyst culture is a kind of sequential culture. on the basis of the third day, the embryo continues to be cultured in vitro to day 5 ~ 6, which is a process of embryo optimization and screening. That is to say, only the embryos with good potential can persist until the final formation of high-score blastocysts. Patients with repeated implantation failure can consider blastocyst culture to further screen embryos and test the potential of embryos. There is sufficient evidence to show that the clinical pregnancy rate after transfer is higher than that of cleavage embryo transfer when developing to blastocyst. Assisted hatching technology (AH) can help embryos hatch and promote embryo implantation.
two。 Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS)
Embryonic chromosome aneuploidy is one of the reasons for the failure of embryo implantation. For repeated implantation failure, PGS can be considered to further select embryos and select the real improved embryos with normal chromosomes for transfer, which can improve the implantation rate.
What is PGS?
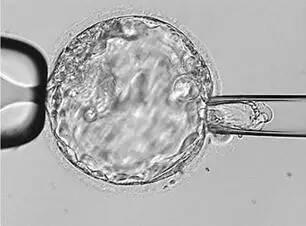
Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) refers to the screening of embryo genome and the selection of normal embryo implantation in the procedure of in vitro fertilization (IVF), in order to improve the outcome of IVF. In short, it is through the gene detection technology to select the right potential embryo seed implantation.
Which patients are suitable for choosing PGS?
At present, there is an international consensus that the people who adapt to PGS include these categories:
1) the woman is older than 35 years old (AMA)
2) recurrent spontaneous abortion in 2 or more times (RM)
3) repeated implantation failure (RIF), high score embryo transfer for 3 or more times without pregnancy
4) severe male infertility (SMF), severe oligoasthenospermia and teratospermia
5) others: selective single embryo transfer (eSET), etc.
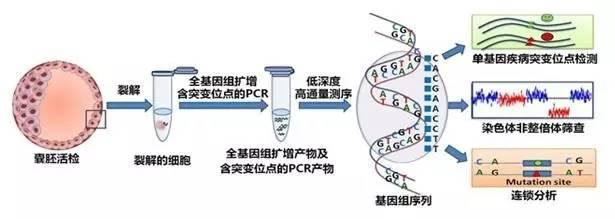
With the development of biopsy technology and genomic molecular diagnosis technology, embryo screening using blastocyst biopsy combined with new whole genome chip or sequencing technology has become the standard matching of PGS. It is no longer a myth to select powerful embryo seeds with high appearance and high potential.
In our center, more than 80 patients with unexplained repeated implantation failure and recurrent abortion were screened for embryos by PGS, and a continuous pregnancy rate of ~ 70% was obtained. Through the strict selection of excellent seeds to improve the embryo implantation rate and reduce the abortion rate is leveraged, which is an effective measure to improve the outcome of repeated implantation failure.
The author of this article:
Wu Wei, deputy chief physician
Jiangsu Provincial people's Hospital Reproductive Center
The most authoritative reproductive and genetic diagnosis and treatment service platform, "Puhe gestation" is by your side. (WeChat account: puheyunyu)
- Prev
Planting traditional Chinese Medicine is another good way for Farmers to get Rich
Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz is a traditional large variety of traditional Chinese medicine, which has strong cold tolerance, wide suitability, simple management and large market demand. In terms of planting, only.
- Next

Periodontal implants give you a third set of teeth
Human life only deciduous teeth, permanent teeth two pairs of natural teeth. Permanent teeth will grow out of deciduous teeth, permanent teeth lost one less, can not be regenerated. But since...
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

