Planting management of Rosa roxburghii Tratt and control of common diseases and insect pests
Planting management of Rosa roxburghii Tratt and control of common diseases and insect pests
1 planting and management
1.1 Scientific planning and selection
Rosa roxburghii Tratt is suitable for growing in warm, humid, sunny and fertile soil. Therefore, it is necessary to reasonably plan the areas suitable for pear planting according to local conditions. And Rosa roxburghii is rich in resources and variety, so it is necessary to select varieties scientifically according to local characteristics and market demand.
1.2 cultivation of strong seedlings
The branches that have been lignified in the current year are used for propagation. To select strong branches and autumn green branches for cutting, the rooting rate of cuttings is about 45%, which can be treated with indolebutyric acid and naphthylacetic acid, and the rooting rate can be increased to more than 70% after treatment. Or it can be propagated by cutting with mature branches growing for 1 to 3 years, and can be cut in spring, summer and autumn. The rooting rate is very high, preferably in summer and autumn, and the highest rooting rate can be up to 100%. The length of branches propagated by cuttings should be controlled at 13-16 cm, not too short or too long. The soil used in the seedbed must be fertile, fine, loose and have good water retention. Watering should be carried out immediately after cutting to ensure that the soil is moist and covered to enhance heat preservation and moisture retention to facilitate rooting.
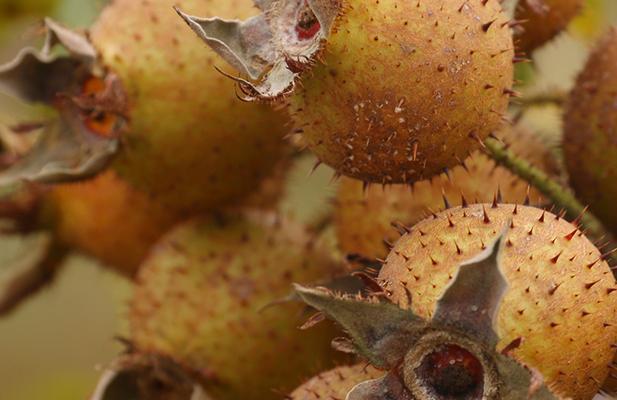

1.3 Scientific planting
Whether the planting technology of Rosa roxburghii seedlings is scientific and whether the management after planting is good or not has a great impact on the survival rate, shortening the slow seedling period and ensuring the normal growth of plants. It must be planted in the planting hole at the top of the Zhengding hole or at the top of the groove. The suitable depth and width of the planting hole is 33 cm, and the root should be extended in all directions. Be sure to irrigate the root water on the day of planting, and if the slim used is taller, you should also use a tie pole to prevent survival from being affected by wind shaking. After planting, according to the weather conditions, water once every 5-7 days to ensure that the soil is moist. If the tree plate is covered, the watering interval can be longer, and the watering management after planting can not stop until the rainy season.
1.4 attach importance to orchard management
The focus of orchard management is to remove weeds in the orchard and improve the deep soil permeability, to enhance the soil water conservation, fertilizer conservation and heat preservation capacity to provide security, but also tree disk mulching in the dry season. In spring, summer and autumn, quick-acting fertilizer was applied 7 to 10 days before shoot emergence, usually mainly nitrogen fertilizer, in order to promote branch and leaf growth, and the amount of fertilizer should be increased gradually in the second and third years. Before sprouting in summer and autumn, each plant was topdressing with 0.05-0.10 kg urea or 5 kg clear dung water. When the shoot leaves are shaped in each season, potassium dihydrogen phosphate or other efficient compound fertilizer is sprayed on the leaves to promote the maturity of the shoot leaves.

2 prevention and control of common diseases and insect pests
2.1 powdery mildew
Powdery mildew mainly harms young shoots and leaves, as well as buds, flowers and young fruits. It is mainly transmitted by conidia by wind, which is the most in the daytime, accounting for more than 90% of the whole day, and the most is after 10:00, and less at night. The onset period of the disease is from late April to November, and the symptoms are not prominent from July to August due to the inhibitory effect of high temperature. The longer the seedling age, the more serious the disease, the disease of young leaves is generally serious, and the disease of old leaves is relatively mild [1]. The plants with better fertilizer and water management have relatively light disease because of their strong growth potential and strong resistance. Rosa roxburghii planted on hillsides and fields generally has mild disease because of its short plant, few branches and strong permeability, while the plant planted in Bazi land has more serious disease because of its dense growth, tender branches and leaves.
Comprehensive control should be carried out in view of the disease. First of all, select sunny hillside land as the main planting area; strengthen water and fertilizer management to enhance plant disease resistance; scientific pruning modeling to increase plant permeability, pay attention to the cultivation of vegetative branches and fruit branches, enhance disease resistance; at the same time, cut off susceptible branches to prevent the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms to reduce the incidence of disease. Secondly, drug prevention and treatment. Biological agents such as 25% Fenning 2000 times solution, antimycin 120 or antibiotic BO-10 can be used for prevention and treatment.
2.2 Brown spot
The main damage site of the disease is the leaves, among which the old leaves suffer the most. The onset period is from May to October, and the most serious is from July to August. Comprehensive control of powdery mildew, 70% mancozeb or 50% carbendazim can be sprayed every 15 days, a total of 4 times, the control effect is better.
2.3 Bituminous coal disease
The disease mainly occurs in leaves and branches, the initial symptoms of the disease is black-brown mildew spots, gradually spread and finally gathered into a piece of black bituminous coal. The disease is easy to occur in dense shady and wet areas, and the occurrence of the disease is closely related to aphids and whitefly. The disease can be controlled with 40% omethoate and has a good effect on aphids and whitefly.
2.4 Pear heart borer
The small heart borer of Rosa roxburghii is the main borer of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, which will cause flower and fruit drop in the early stage and black dung in the fruit in the middle stage, which has a serious effect on the yield and quality of Rosa roxburghii. During prevention and control, the harvested pear orchards were pruned in November to strengthen field management, or 50% phoxim EC was mixed with fine soil to spread poisonous soil.
2.5 pests of the yellow diamondback moth
Huang Xi'e is the most serious pest among the pests of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. The period of more serious damage is from mid-June to early July, because of the large number of larvae in the forest. The control method is to clean up the garbage in the forest garden in time, and spray it with 70% phoxim 1000 times liquid during the early hatching period of the larvae, and the control effect is better.
2.6 APHIS gossypii
The main harmful parts of APHIS gossypii are tender shoots and flower buds, and the onset time is mainly from mid-April to November. The control method is to cut off insect branches after autumn and remove weeds and fallen leaves in the garden at the first time; fully protect and make good use of parasitic bees and predatory ladybug beneficial organisms; when insect pests occur in a large area, it can be sprayed with 1 000 times of 25% aldicarb (ethyl thiophanate).

- Prev

How to fertilize when growing tomatoes? Topdressing technique of Tomato
Tomatoes are very popular fruits, which can be eaten raw, cooked or processed into tomato juice. They all have unique flavor and are very popular in the market. And in tomatoes.
- Next
Don't fall into the misunderstanding of immediate dental implants.
After missing teeth, most middle-aged and elderly people choose to install removable dentures because of their convenience and cheapness, but as they grow older, the situation in the mouth will not.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

