The high-yield cultivation of Pueraria lobata is so simple. The old farmer who planted Pueraria lobata for 8 years shares the secret of Pueraria lobata planting.
Click to follow us and update the agricultural planting technology every day to help you get rich with high yield and high income.

First, seed selection and seedling cultivation
There are many kinds of Pueraria lobata, including Pueraria lobata, etc., among which Pueraria lobata (Pueraria lobata, Pueraria lobata) has good root shape, spindle shape, smooth epidermis, less wrinkles, less fiber, sweet taste, high flour yield, drought tolerance, early maturity and high yield. From December to February of the following year, among the harvested kudzu vines, choose the disease-free, stout, full-eyed middle vine for planting, bury it in a 20-centimeter shallow hole in the original harvest, cover the weeds, or take it back indoors and cover it with slightly moist river sand. About 20-30 days before planting, the vine stem was raised and cut into 2-3 nodes with a sharp knife. According to the specification of 20 × 10 cm, it was obliquely inserted into a loose and fertile seedling border with a width of 1 meter, and watered every other day. The new buds growing out of the stem can be planted with soil and transplanting when the length is 5-10 cm, and the seedling action should be light so as not to damage the seedlings.

II. Land selection and preparation
Choose sunny, good drainage and irrigation, low groundwater level, no waterlogging, deep soil layer, loose and fertile red-yellow loam or sandy loam planting, it is best to choose rotation. Deep ploughing and soil preparation is carried out in the winter leisure season, and the flat ground is ridged by 1-1.2 meters with a ridge height of 30m and a ditch width of 30cm. In the center of the ridge, the planting holes are planted with a depth of 1.0m and a width of 40cm. The hillside is 1.2 meters wide according to the contour line, and then it is divided into 50 × 50 cm planting holes with a distance of 1 meter and a row spacing of 1.0 meters 2.5 meters (depending on the slope). The planting hole is thick and fine about 30 days before planting, and the weeds and fertile topsoil are layered backfilled to 15-20 cm higher than the hole surface, generally requiring 2.5-5 kg of rotten barnyard manure or 10-15 kg of soil fertilizer per planting hole. 0.5 kg of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer or ternary compound fertilizer, fertilizer should be evenly mixed with organic fertilizer and soil when the planting hole is backfilled.
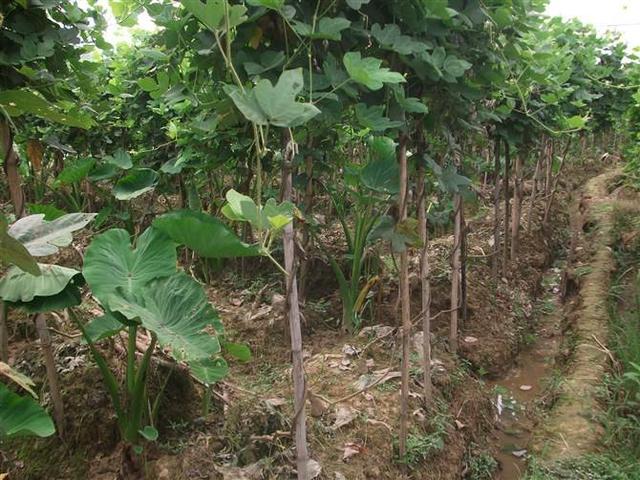

Third, planting time
Plant from mid-February to late April every year. Planting specifications: row 1.0-1.2 meters (Baogou), plant spacing 1.0 meters, single row and single plant planting, 500-600 plants per mu (according to the topography and slope of the slope). Before planting seedlings, dig a small hole about 15 centimeters deep, plant the seedlings at an angle of 30 degrees with the ground into the hole, compact the soil with both hands, and sprinkle the root water.
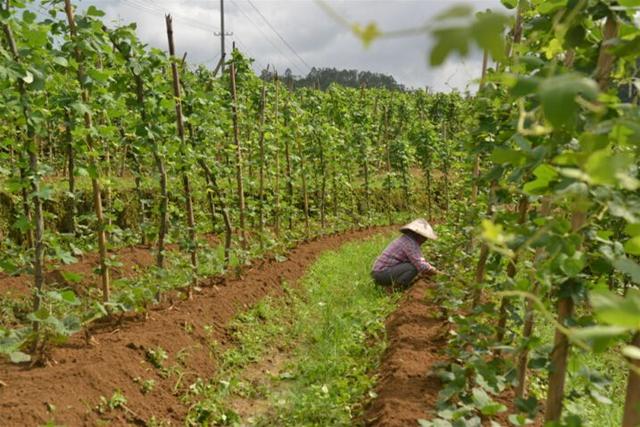

IV. Strengthen management
1. Replenish seedlings and hedges
After transplanting for 5 days, the seedlings can be properly diluted with human and animal dung water to fix roots, and pay attention to inspection, and replant dead seedlings in time. A month or so after planting, when the height of the seedling reaches 50 cm, insert a multi-bifurcated hedge or bamboo hedge 1.5-2.0 meters high between two rows (the slope can lay twigs between two or two rows), choose one strong seedling to stay, and remove the other weak seedlings. Put the two adjacent vines on the hedge, so as to ensure ventilation and light and improve the photosynthetic efficiency of kudzu seedlings.
2. Topping, pruning and sprouting
This is an important measure to control the growth of the aboveground part of Pueraria lobata, promote the underground growth and make the root tuber form rapidly. When the main vine of kudzu seedlings grows to about 1 meter long, the top will be removed, leaving 3-4 lateral vines, and the rest will be cut off. The left lateral vines should be evenly distributed, top when the length is 1-1.5 meters, and remove the lateral buds. After that, the lateral buds were picked every 15 days or so.
3. Fertilizer and water management
Fertilizer and water management is the key to ensure high yield and high quality of Pueraria lobata. The first topdressing was carried out 20 days after planting and applied with 0.3-0.5% urea water. After that, 25 50g of ternary compound fertilizer was applied every 1-2 months, and the amount of fertilizer application was gradually increased. It should be flushed in sunny days and applied in holes in rainy days. Water management should keep the soil moist all the time. Pueraria lobata is resistant to drought and waterlogging, so it should be watered less at the initial stage of planting, rather than dry rather than too wet, and waterlogging should be eliminated in time after rain.
4. Pest control
There are few diseases and insect pests in the whole life of Pueraria lobata, and the occasional ones are leaf spot, downy mildew, leaf blight, rust, leaf miner, shell worm, beetle, red spider and so on. Mancozeb, carbendazim, thiophanate, methyl thiophanate and trimethoprim were used to control diseases, while trichlorfon, dichlorvos, cypermethrin, trichlorofol and other pesticides were used to control pests.

5. Timely harvest
High-yield Pueraria lobata can be planted and harvested in the same year, or it can be planted for 2 years before harvest. After late November, Pueraria lobata began to enter the mature stage. When most of the leaves of Pueraria lobata turn to green and yellow, and the leaves are brittle and hard, and there is no stamina to grow, you can choose a sunny day to harvest. When harvesting, you can dig up the soil from the root of the plant directly from the ground, expose the head of the root tuber, cut the large root from the base of the stem with a sharp knife, and avoid injuring other remaining tuber roots and fibrous roots. At the same time, some overwintering base fertilizer can be applied to lay the foundation for next year's kudzu harvest, and then cover the soil. If the harvest is not finished in that year, it can be planted in the next year. In February of the following year, the old vines of more than 0.5 meters are cut off and 3 lateral vines are re-cultivated, so that the yield is higher and the quality is better. Pueraria lobata can be harvested continuously for 3-5 years at one time.
Welcome to subscribe to follow this headline, we share the latest agricultural planting technology and agriculture-related information every day, welcome to share and forward likes, if you have any good suggestions or want to know about planting technology, welcome to leave a message, we will extract some of the issues that you are most concerned about and invite agricultural technical experts to share professional guidance.
- Prev

High-end balcony planting-design a garden in a broken flowerpot
The father of a small farmer found that now every family will more or less plant flowers, trees, fruits, vegetables, and even succulent plants on the balcony of the family. But everyone obeys.
- Next

Fruit planting scams are everywhere, and it is not profitable to grow Garbo fruit in the rural areas of the north.
The cultivation of Jiabao fruit in northern rural areas is precious, rare and high in nutrients, and a lot of its advantages can be listed if necessary. Although northerners rarely see it, but.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

