Aerosol cultivation, romantic planting
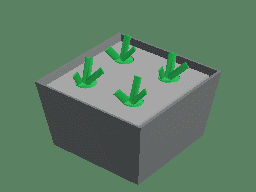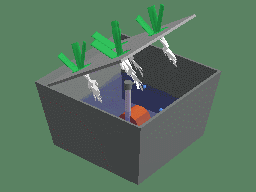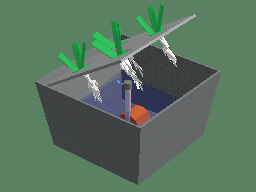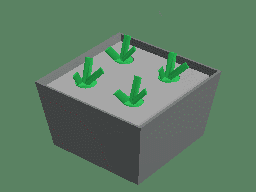
Animation demonstration of spray cultivation
Spray cultivation, also known as aerosol culture or spray culture, is a soilless cultivation technique that uses a spray device to atomize the nutrient solution into a small droplet and spray it directly to the plant root system to provide water and nutrients for plant growth. The crop is suspended in a closed cultivation device (trough, box, or bed), while the root system is exposed inside the cultivation device, and the nutrient solution is atomized through the spray device and sprayed to the root surface.
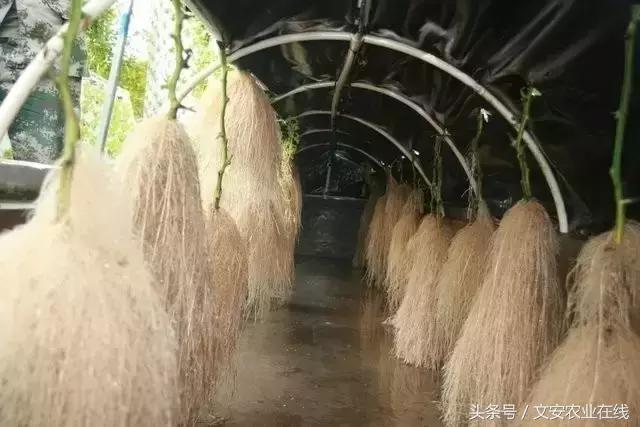


It is the best way to solve the contradiction of root water vapor in all soilless cultivation techniques. at the same time, it is also easy to automatically control and carry out three-dimensional cultivation to improve the utilization rate of greenhouse space. It can double the crop yield. However, due to the continuous circulation of liquid supply, it is easy to cause problems if there is a power outage for a long time (more than 30 minutes) or pump failure, and can not circulate in time.

Aerosol Culture of Potato
All kinds of aerosol cultivation introduced in the past are used for the cultivation of leaf vegetables and melons and fruits. A common feature of them is that the products that can be harvested for human use are the branches and fruits of the original aboveground parts. In fact, aerosol culture is the best cultivation method for harvesting root system or all kinds of tuber rhizomata. it is not only beneficial to the development of root system and tuber, but also very convenient to harvest in batches at any time. or selectively harvested according to standard specifications, some plants with harvested roots as medicinal plants are more conducive to the formation of developed roots and greatly increase the economic yield.

So what are the advantages and convenience of aerosol culture for underground utilization plants such as lily, potato, sweet potato and so on?
First of all, aerosol cultivation of these crops, like other leaf vegetables, melons and fruits, the formation rate of biological yield is greatly accelerated, which is several times higher than that of soil cultivation. Secondly, its underground part can be inspected at any time, which is more convenient to observe and study the development of underground part, and to provide more field data for the formulation of management measures and the study of cultivation techniques. For example, the effect of foliar spraying paclobutrazol on potato tuber development is more convenient and intuitive than that of cultivation in soil. In addition, when the soil-cultivated plants want to harvest the underground part, most of them are excavated at one time, resulting in different products and different quality, while the underground part is harvested by aerosol culture, just like picking melons and fruits, they can be harvested in batches and selectively, and the tuber bulbs harvested can achieve consistency in size and quality. by using this method, the overall economic yield is several times higher than that of one-time harvest. This may be related to the less waste of plant nutrition and the full conversion of biological yield into economic yield.

In addition, from the point of view of the technology itself, aerosol culture is also more convenient in operation and production. It can check the development of the underground part at any time, and can regulate and control the culture liquid at any time according to the development. What is more important is that the underground development is completed in the air. Its morphological development is not affected by soil mechanical resistance, and its ontogeny is extremely uniform, showing relative consistency of morphology. For example, potatoes show a consistent round or oval shape. It's like eggs of the same size. The management labor is also greatly reduced, there is no need to weed and loosen the soil, there is no need to cultivate soil and preserve soil moisture, the root tuber can develop without any barrier in the aerosol, so that its variety potential can be brought into full play, and the yield is several or dozens of times higher than that of ordinary soil cultivation.
- Prev

Pot planting techniques of ornamental lotus
First, pot selection: small lotus varieties are planted in pots (diameter 26 cm, height 20 cm); medium-sized lotus varieties are planted in pots (caliber 30 cm, height 21 cm).
- Next

Campus vegetable Garden: the planting method of lentils
Lentil (scientific name: Lablab purpureus (Linn.) Sweet), general name lentil, alias falx lentil, puffy bean, rattan bean, hedge bean, magpie bean.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

