Planting techniques of pineapple Sakya in North China
Planting techniques of pineapple Sakya in North China
The editor said: pineapple Sakya has a good price and can be used as a family farm in the north. Pineapple Sakya contains the anti-cancer ingredient "Annona lactone", known as "anti-cancer pioneer". Pineapple Sakya is suitable for planting in general mountains and slopes. After planting for 2 years, it can blossom and bear fruit manually. It can produce fruit all the year round. In high yield, the yield per mu is 2000-3000 jin, the output value per mu is more than 50,000 yuan, and the mature picking becomes soft for 2-3 days.

The experiment was carried out in the energy-saving solar greenhouse in the garden farm base of Ningxia Academy of Agriculture and Forestry in Yinchuan, Ningxia.
2 planting technique of pineapple Sakya
Bagged seedlings of more than 2 years old are the best. The basal diameter of the seedlings is more than 0.7-1.5 cm, and the height is 60-100 cm;. The trunk is fully lignified and the root system is well developed.
2.2 soil regulation before planting
Sakya is a shallow root plant, and the most suitable soil is sandy soil or sandy loam soil with fertile soil, good aeration and good drainage, and the most suitable soil pH is 5.5-6.5.
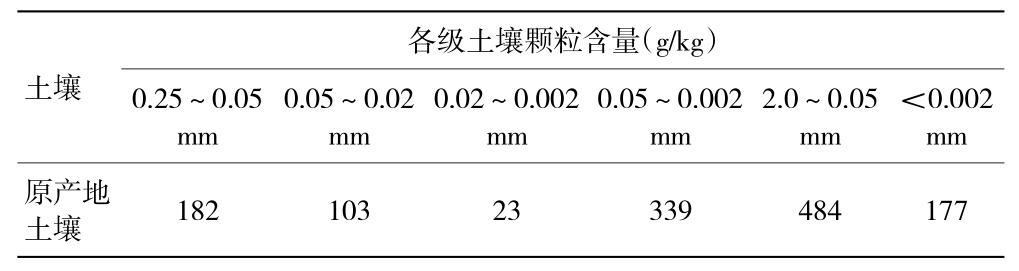
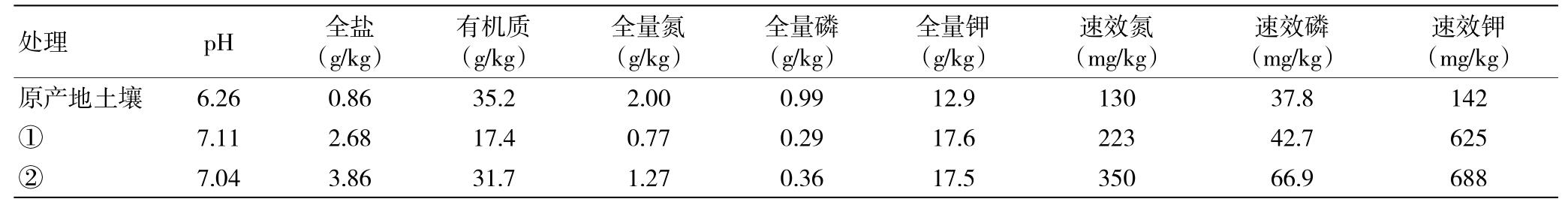
Before planting, the soil particles and physical and chemical properties of the origin of the seedlings were determined (Table 1 and Table 2). It can be seen from the table that the pH and total salt content of the soil of origin is much lower than that of the local soil. Therefore, the root-limiting cultivation mode was selected to adjust the proportion of the nutrient soil of the seedlings. The nutrient soil in the root limiter was divided into two treatments: substrate ∶ garden soil ∶ sand ∶ furfural residue = 1 ∶ 2 ∶ 2 ∶ 1, treatment ② nutrient soil ratio: matrix ∶ garden soil ∶ sand ∶ furfural residue = 1 ∶ 2 ∶ 2 ∶ 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that although the total salt content of the adjusted nutrient soil has been increased, the pH has decreased by 9.7% and 10.5%, respectively. The survival rates of the two treatments were investigated in October 2016, reaching 97.3% and 94.2%, respectively.
Table 1 composition of soil particles in place of origin
2.3 planting time
Pineapple Sakya seedlings were planted on October 5, 2012 and April 20, 2015, respectively, and their survival rates were investigated. The results showed that the survival rate of pineapple Sakya in spring was 94.3%, while that in autumn was only 67.8%, which indicated that planting in spring was more beneficial to the survival of pineapple Sakya than in autumn.
Taiwan pineapple Sakya is a tropical and semi-tropical plant. It likes a warm and humid climate. The climate conditions with an average annual temperature of 21: 23 ℃, annual rainfall of 1 200% and 1 800 mL, and air humidity of 70% and 95% are most suitable for its growth.
Table 2 physical and chemical properties of soil of origin
Young Sakya pineapple trees can withstand 0 ℃ low temperature in a short time. According to the environmental data of the second generation energy-saving solar greenhouse in Ningxia without any heating measures (take 2011 as an example), the lowest temperature in December and January in Ningxia is only 0.7 ℃. Therefore, after planting Sakya in the solar greenhouse in autumn or winter, it is necessary to take some measures to increase the temperature, such as hot blast stove, sodium lamp, stove and so on. At the same time, under the premise of increasing the temperature of solar greenhouse, the soil temperature can be increased appropriately.
2.5 Illumination management after planting
The light is strong in Ningxia, so after the pineapple Sakya is planted, especially in spring and summer, the single-layer shading net can be used to shade the sun, and the shading net can be withdrawn slowly after about a week.

3 cultivation and management techniques of pineapple Sakya
3.1 shaping and pruning
3.1.1 the shaping and pruning seedlings of young trees were trimmed to 60 cm after planting, and 3 pairs of leaves in the middle and upper part of the trunk were cut off to promote the germination and formation of the main branches. When the length of the main branch reached 60 cm, the top was cut again, and when the leaves were mature, the two pairs of leaves in the middle tail were cut off to promote the secondary branches; when the secondary branches were about 40 cm, the top was cut off, and when the leaves were mature, the two pairs of leaves in the middle tail were cut off to promote and cultivate the third and fourth branches. The angle between the main branch and each branch and the ground is kept at 45 °~ 70 °. Only one branch is left in each leaf axil, and the extra one is cut off.
3.1.2 shaping and pruning of fruiting trees and regulation of yield period for fruiting trees, as for fruiting trees, flower bud differentiation can be carried out as long as there is a certain accumulation of nutrients because of the lax environmental requirements for flower bud differentiation of Sakya. The technique of adjusting the birth period of Sakya is mainly combined with plastic pruning. Winter pruning is generally carried out from early February to late March in spring, which can cultivate summer fruits, while summer pruning is usually from June to September every year. Autumn, winter and spring fruits can be cultivated.
In the shaping and pruning of the fruit tree, in addition to the residual branches, thin and weak branches, disease and insect branches after the fruit was cut off, the erect upper dorsal branches were mainly cut off to make the plant as dwarfed as possible. The regulation of flowering and yield period is mainly achieved by artificial forced defoliation, while vigorous trees can achieve high yield through intensity pruning. ① retracts and prunes the crown with high intensity. Cut back the large branches on the periphery of the crown to about 30 cm from the base of the third and fourth branches. At the same time, ② also retracted and pruned the third and fourth branches, retaining only 4-6 nodes, while the stout branches in the canopy above 0.5 cm generally retained 2-4 nodes. ③ back branches, weak branches, disease and insect branches, only long branches, all cut off from the base.
After 5-7 days of retraction and pruning, new shoots can germinate. When the new shoots grow to about 10 cm, they can be thinned and 2-3 shoots per branch can be left. When the new shoot grows to 30 ~ 40 cm, the heart can be picked in time, and the flower bud differentiation can be completed after ripening, among which more than 80% of the shoots can form flowers.
3.2 Fertilizer and water management
3.2.1 Fertilizer management of young trees Sakya has a great demand for fertilizer. (1) the 2-year-old trees were fertilized with 5 kg organic fertilizer, 0.45 kg urea, 0.35 kg superphosphate and 0.1 kg potassium sulfate per year. Organic fertilizer was applied at one time before winter shearing, and chemical fertilizer was applied after the first, second and third times of new shoots were ripe and before the beginning of winter shearing, respectively. the amount of fertilizer applied in winter cutting is the highest, accounting for about 55% of the total amount used in the whole year, and 15% each in the other three times. to promote the growth of tree potential and the formation of tree crown.
3.2.2 Fruit trees aged 3-4 years should be fertilized with 15 kg organic fertilizer, 2 kg superphosphate, 0.5 kg potassium sulfate and 1.2 kg urea every year, and organic fertilizer should be applied once before and after winter pruning. Chemical fertilizer was applied in four times, the first before and after winter shearing in February and March, the second from May to June, the third from September to October, and the fourth before winter fruit harvest from December to January of the following year.
3.2.3 Water management requires timely and appropriate irrigation depending on the specific situation. Sakya is most afraid of stagnant water, which can easily lead to root rot.
3.3 determination of harvest time
When the scale groove between the scales on the surface of the fruit expands and appears milky yellow, it shows that the pineapple Sakya is fully ripe and can be harvested. After harvest, it should be cooked for 3 to 5 days before eating.
(4) pest control techniques
Pineapple Sakya has few diseases and insect pests in Ningxia. at present, red spider damage has been found. in cultivation and management, 2% avermectin EC can be sprayed 2000 times, or 20% acarine wettable powder 1 000 times.

- Prev

Campus vegetable Garden: the planting method of Chinese Cabbage
Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. Ssp. Chinensis Makino (var. Communis Tsen et Lee) the scientific name is common cabbage, commonly known as.
- Next

Planting method of potted glass begonia
Glass crabapple is a kind of herb that can blossom all the year round, the suitable temperature is 18-25 degrees, it is a kind of plant with great decoration color. So, you know, glass.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

