Mysteries of dissolved oxygen in aquaculture
In the process of shrimp culture, the chemical indexes and physical properties of water quality are usually indicated by physical and chemical factors such as dissolved oxygen, pH value, ammonia nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, nitrite, salinity, water color, transparency and so on. the changes of these indexes and characters directly affect the growth, yield, quality and benefit of Penaeus vannamei. The level of dissolved oxygen has an important effect on the growth of shrimp, which directly affects the feeding and growth of shrimp. Dissolved oxygen is an essential substance to ensure the normal and healthy growth of prawns, and plays a leading role in regulating the oxidation and decomposition of many substances in the water environment, and is an essential substance to improve water quality and sediment. In the process of shrimp culture, the dissolved oxygen in the bottom water should not be lower than 4mg/L, and it is better to keep it above 6mg/L. Insufficient dissolved oxygen in water can decrease the exercise ability of shrimp, lose appetite, increase feed coefficient, decrease physique and increase diseases; at the same time, insufficient dissolved oxygen will promote the production of harmful substances such as ammonia nitrogen, nitrite and hydrogen sulfide in pond water, and increase its toxicity, which can cause a large number of shrimp death. Therefore, the monitoring and regulation of dissolved oxygen is the central link of shrimp culture management.
1 relationship between dissolved oxygen and shrimp culture and production.
1.1 the content of dissolved oxygen in water affects the products of organic matter decomposition.
The main results are as follows: (1) when the dissolved oxygen is sufficient in the water, the organic matter decomposes rapidly under the action of aerobic bacteria, and the decomposed products are CO2, N03 -, PO43-, H02 and other substances that are harmless to cultured shrimp and beneficial to the growth of aquatic plants.
(2) when the dissolved oxygen is insufficient, the reproduction of aerophobic bacteria in the water layer or bottom is dominant, the speed of sawing organic matter is slow, and the decomposition products are mostly substances that are toxic to shrimp (such as H2S, NH3, CH4). When the dissolved oxygen is insufficient, the denitrification and the disappearance of NO3- will occur in the water, the concentration of NH3 will increase, and the reduction of SO42- ions will produce H2S. At the same time, the anaerobic condition accelerates the release of phosphorus and ammonia nitrogen from the sediment, slows down the oxidative decomposition, and slows down the degradation of pollutants in seawater. In turn, it causes the death of shrimp and causes the problem of bottom consumption.
1.2 the decrease of dissolved oxygen in water affects the growth and development of cultured shrimp and the environment of shrimp ponds.
The dissolved oxygen is decomposed in the shrimp pond. after the pond water is anoxic, the shrimp responds slowly, grows slowly, reduces feed intake, decreases resistance, and even dies. The increase of organic waste in shrimp ponds leads to the problem of bottom consumption.
2 consumption and variation of dissolved oxygen in shrimp ponds
2.1 the main factors of oxygen consumption in shrimp ponds are:
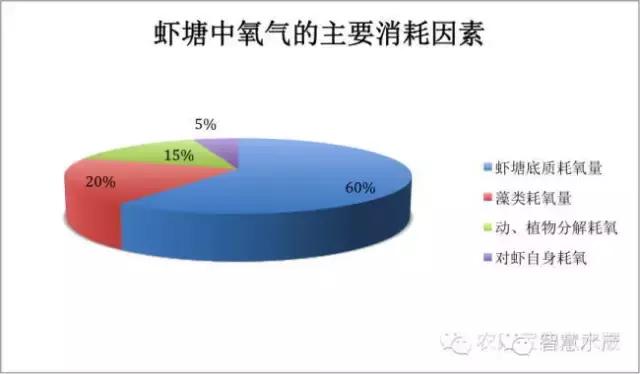
Respiration of prawns, respiration of phytoplankton (algae), oxygen consumption of plankton and death decomposition of plants in ponds, oxidation of organic matter in water and sediment of shrimp ponds, etc. The oxygen consumption of shrimp in shrimp ponds is relatively small, while the oxygen consumption of sediment in shrimp ponds is the main factor affecting the dissolved oxygen in the culture environment, accounting for about 60% of the total oxygen consumption in shrimp ponds, followed by algae accounting for about 20%. The oxygen consumption of animal and plant decomposition accounted for 15%, and the oxygen consumption of shrimp was 5%.
2.2 dissolved oxygen in shrimp ponds has obvious seasonal and diurnal changes.
The diurnal variation of dissolved oxygen content in intensive shrimp ponds showed that the dissolved oxygen content was the lowest before sunrise in the early morning, and reached the highest value at about 1600 in the afternoon, and the monthly change was mainly shown in that the average value of the high peak value in the surface layer in July and August was much higher than that in May and June.
3 countermeasures
In order to ensure that there is enough dissolved oxygen in the growth process of Penaeus vannamei, corresponding measures must be taken to regulate the dissolved oxygen in water.
3.1 reasonable arrangement of seedling density and reasonable feeding
The seedling density should be arranged reasonably according to the depth of the shrimp pond, the bottom quality, the temperature of the whole production cycle and other relevant conditions. Feed reasonably according to the number of seedlings, the size of shrimp and other related factors to prevent excessive residual bait and increase oxygen consumption.
3.2 cultivation of phytoplankton
Although the effect of phytoplankton on dissolved oxygen in water has a dual nature, under normal sunshine conditions, a pond with abundant plankton can produce 10-2Og of oxygen per cubic meter of water per day, and the respiratory oxygen consumption of phytoplankton accounts for about 5% of the oxygen production of photosynthesis. At the same time, these plankton can also absorb a large amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and other components, thus accelerating the self-purification capacity of pond water; therefore, in the middle and later stages of shrimp culture, by appropriately increasing the density of phytoplankton, the dissolved oxygen in the culture environment can be greatly improved. A large number of phytoplankton also consume a lot of oxygen in the case of lack of light. Therefore, to seek the appropriate reproduction of phytoplankton to maintain its stability in the whole culture process is an important technology of water quality management.
3.3 frequent injection of new water or application of microbial preparations
In general, the concentration of dissolved oxygen in seawater is saturated. By adding fresh sea water, the water with high concentration of dissolved oxygen can be brought into the shrimp pond and the dissolved oxygen in the shrimp pond can be increased obviously. For shrimp ponds which are lack of water source or inconvenient to inject water, beneficial microbial preparations such as photosynthetic bacteria and Bacillus can be used to regulate the water quality.
3.4 Chemical oxygenation
Increase the level of dissolved oxygen in the pond by using chemicals that can produce oxygen in the water, such as calcium peroxide and sodium percarbonate.
3.5 correct use of aerator in aquaculture water can effectively increase the content of dissolved oxygen in water.
The role of aerator in shrimp culture can be roughly summarized as follows:
① increases the contact area between air and water
② promotes the mixing of bottom water and surface water, maintains the balance of water temperature, and increases the dissolved oxygen of bottom water. ③ makes shrimp pond water circulate and collect pollution, and improve the sewage discharge effect of shrimp pond.
④ increases the dissolved oxygen, promotes the oxidation and decomposition of organic matter in the pool, and reduces the formation of harmful substances.
⑤ is beneficial to the growth of algae and stable water color.
⑥ can improve dissolved oxygen, help to cultivate aerobic bacteria, inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, prevent and reduce the occurrence of diseases. The time of starting the aerator should be determined according to the content of dissolved oxygen in shrimp ponds and the culture density of culture days, so as to keep the content of dissolved oxygen in pond water above 5mg/L all the time.
In addition, the nanotube pond bottom aeration pump is a new pond aeration technology which came into being in the process of shrimp culture technology becoming more and more mature. These pumps blow fresh air to the bottom of the pond through the blower, increase the content of dissolved oxygen in the bottom of the shrimp pond, make the shrimp full of vitality, not only increase the yield, but also improve the quality. Its working principle is mainly the use of nanotechnology, through the air compressor to compress the air into the nanotubes distributed near the bottom of the pond for aeration, in order to achieve the effect of increasing oxygen from the bottom of the shrimp pond. Compared with the traditional surface mechanical oxygenation, it has the advantages of uniform oxygen area, balanced oxygen level, less mechanical energy consumption, obvious effect of improving bottom environment and so on. it is a new pond culture technical measure which is being popularized year by year.
Use intelligent equipment to monitor dissolved oxygen and ensure dissolved oxygen in Tangkou.
With the development of science and technology, many aquatic products people have begun to use aquatic intelligent measurement and control instruments to effectively realize the real-time monitoring of dissolved oxygen at the mouth of the aquaculture pond, and automatically turn on the aerator when the minimum value of dissolved oxygen is reached. And can remotely control the start and stop of fishing machine equipment such as aerator, so as to make oxygen increase more scientific and intelligent.
Welcome to follow China Aquaculture Wechat official account: zgsc0879 to communicate and interact with 100, 000 aquaculture friends.
- Prev
How to feed water for breeding bees
Bees must collect water to maintain various physiological activities in the body, such as food decomposition, absorption, transportation, excretion of metabolites, and feeding larvae.
- Next

Loach breeding cost analysis accounting: raising loach to make money? Loach farming costs and profits
I. Loach breeding cost: How much does it cost to breed loach on one mu of land? It's hard to say its cost in different locations. You can base it on the cost of an acre of pond.
Related
- On the eggshell is a badge full of pride. British Poultry Egg Market and Consumer observation
- British study: 72% of Britons are willing to buy native eggs raised by insects
- Guidelines for friendly egg production revised the increase of space in chicken sheds can not be forced to change feathers and lay eggs.
- Risk of delay in customs clearance Australia suspends lobster exports to China
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (4)
- Pig semen-the Vector of virus Transmission (3)
- Five common causes of difficult control of classical swine fever in clinic and their countermeasures
- Foot-and-mouth disease is the most effective way to prevent it!
- PED is the number one killer of piglets and has to be guarded against in autumn and winter.
- What is "yellow fat pig"? Have you ever heard the pig collector talk about "yellow fat pig"?

