What are the advantages and disadvantages of immediate planting? What does immediate dental implant mean? is immediate implant bone graft immediate restoration?
Implant restoration is a new trend in repairing dentition defects. With the increase of patients' demand for oral health, immediate repair has been paid more and more attention.

Advantages of immediate planting:
Immediate implantation can shorten the treatment time of patients. Usually, delayed implantation needs to be reimplanted 3 months after tooth extraction, while immediate implantation is performed immediately after tooth extraction, so the treatment time can be shortened by 3 months and the patient's masticatory function can be restored as soon as possible. At the same time, immediate implantation will carry out tooth extraction and implantation at the same time, which reduces the number of operations and reduces the pain of patients compared with delayed implantation. In addition, one of the main advantages of immediate implantation is that it can reduce alveolar bone resorption and maintain alveolar bone height. In the delayed implant, the alveolar fossa left after tooth extraction will cause partial absorption of the surrounding alveoli in the healing process, while in the later implant, the preparation of the implant fossa will grind off a certain amount of bone. Immediate implantation in the alveolar fossa on the basis of the preparation of implant fossa, can save bone grinding and reduce the absorption of alveolar bone around the extraction fossa, therefore, can better maintain the height of the alveolar crest.
However, it should be noted that the operation of immediate planting is more complex than that of delayed planting, and every step of planting operation needs to be done strictly.
Important factors that affect immediate planting success:
(1) strict control of indications:
The indications for immediate implantation are: traumatic lost teeth with a small amount of bone loss; bad teeth that need to be extracted for root fracture; untreatable teeth; severe periodontal bone loss without overdose of periodontal diseased teeth; healthy surrounding soft tissue with enough periosteum to be used; systemic diseases without surgical contraindications. For patients with more serious periodontal disease or periapical inflammation, such as periodontal pocket or adjacent soft tissue overflow, periapical swelling, larger granuloma or cyst, wound overflow or lack of adequate bone support may occur during tooth extraction. It is not suitable for immediate implantation if the wound is located near the mandibular nerve canal, maxillary sinus and nostril, which may cause injury during implantation. Patients with systemic diseases will affect the healing of implant wounds, and immediate implantation is not suitable.
(2) reduce the trauma of tooth extraction during operation.
In the process of tooth extraction, the integrity of the alveolar bone in the alveolar septum and the alveolar bone wall around the extraction fossa should be preserved as far as possible to avoid fracture and advocate minimally invasive tooth extraction. In the process of tooth extraction, once the fracture of the bone wall occurs, it will affect the decrease of the early supporting force of the implant, while the tearing of the tissue will cause the wound healing time to be too long, prone to infection and incomplete wound closure.
(3) prevention of intraoperative and postoperative infection.
Infection is another important factor leading to planting failure. The prevention of infection can be divided into two aspects: the removal of infection from tooth extraction wound during operation and the control of wound infection after operation. For some molars without thorough root canal treatment, there must be different degrees of infection around the apical, and there is residual infection in the alveolar fossa after tooth extraction. Therefore, it is necessary to scratch thoroughly to clean the infected alveolar fossa. After operation, antibiotics should be used locally and systematically according to the condition of the patient and the size of the wound to prevent infection. If infection occurs, it is bound to affect the combination of the implant and alveolar bone, resulting in implant failure.
Immediate implant surgery:
1 preoperative preparation:
Routine dental films were taken to understand the local bone tissue and adjacent tissues, and curved sectional films were taken in the bicuspid or molar area to observe the position of the maxillary sinus and inferior alveolar nerve canal and to measure the bone mass between the roots.
2 extraction of teeth:
The main results are as follows: (1) the principle of non-traumatic root extraction-the bone defect around the implant is the main reason that affects the initial stability of the implant.
(2)。 Therefore, attention should be paid to prevent alveolar bone injury and fracture during tooth extraction, and forceps extraction should be used as far as possible. multiple teeth should be divided into roots and extracted by mesial and distal force. (2) after scraping the residual periodontal ligament, we should carefully check whether there is any soft tissue residue in the wound, and if so, we must scrape carefully with a spoon to remove the residual periodontal ligament.
3 preparation of planting bed:
First, the wound of tooth extraction is deepened with a guide drill, and then the implant bed is expanded step by step from fine to coarse with a series of expanding drills, and the implant bed with suitable size and depth is prepared. generally, the depth of the implant bed should make the root of the implant implant 3-5mm. The key to successful implantation is to effectively prevent and reduce the heat loss of alveolar bone in the implant area during the preparation of the implant bed. Bone tissue is very sensitive to thermal injury. In vivo microscope, it was found that bone tissue was damaged by heating lmin at 50 ℃. The heat tolerance of bone tissue was 47 ℃.
In order to prevent the thermal damage of bone tissue as far as possible, the following measures should be taken: 1) drill bit sharp, drilling from small to large, each increasing 0.2mm.2) drilling pressure should be light, usually using up and down pulling method. 3) low penetration rate < 800rpm. 4) rational use of cooling water, when the planting bed preparation is deep, the surface flushing saline can not cool the deep wound, intermittent shutdown is often used, and the bit is pulled out. Rinse directly with normal saline, which can not only lower the temperature, but also flush out the deep bone detritus. An internal cooling device can also be used. In addition, the bit should be close to the palatal bone wall in the alveolar fossa and parallel to the long axis of the adjacent teeth [7] to prevent the labial bone wall from piercing.
4Implant of implant:
The bone fragments in the implant bed were washed with normal saline and implanted into the implant. the top of the implant was flush with or slightly lower than the alveolar crest 1-2mm. Because of the thin buccal bone wall and too much lateral side of the buccal bone, the implant is generally placed in the alveolar fossa of the palatal root.
- Prev
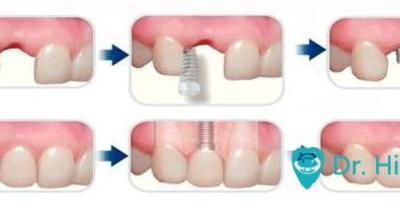
Is dental implant better than dental inlay?
What is the implant tooth (click on the upper right corner to pay attention) the implant tooth is implanted with an artificial root (similar to a screw) on the alveolar bone of the missing tooth.
- Next

What are the advantages and disadvantages of dental implants?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of dental implants? Dental implants have always been an eye-catching way to repair missing teeth in the neighborhood, because of missing teeth, chewing food is very hard, teeth.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

