When is it suitable to grow asparagus?
Ipomoea aquatica, also known as water spinach, Ipomoea aquatica and so on, is an annual herb of the genus Ipomoea. Hollow cabbage is one of everyone's favorite vegetables. It tastes crisp and delicious. At the same time, hollow cabbage can be used not only for vegetables, but also for medicinal purposes, so it has high planting value. So, when is it suitable to grow asparagus? How do you plant it? Now the planting time and method of asparagus are introduced as follows.

Picture: asparagus
1. Planting time of asparagus
Asparagus is usually planted from April to July every year and likes sufficient light, but it also has strong adaptability to close planting and loose requirements on soil conditions, but because it likes fertilizer and water, it is still better for the soil with relatively viscous weight and strong water and fertility conservation. Leaf tips grow a large number and rapidly, requiring large amount of fertilizer, strong fertilizer tolerance and high demand for nitrogen fertilizer.
Second, the planting method of asparagus
1. Soil preparation and fertilization: hollow cabbage has fast growth rate, strong branching ability and needs more fertilizer and water, so it is appropriate to apply sufficient basic fertilizer. Generally, 1500-2000 kg of mature organic fertilizer and 100kg of plant ash are applied per mu, which are fully mixed with the soil to form a border (bag ditch) of 500cm high and 130cm wide.
two。 Soaking seeds to promote germination: the seed coat of hollow cabbage seeds is thick and hard, if sowed directly, it will germinate slowly because of low temperature, and in case of long-term low temperature, overcast and rainy weather, it will cause seed rot, so it is appropriate to accelerate germination. Soak the seeds in 50-60 ℃ warm water for 30 minutes, then soak the seeds in clean water for 20-24 hours, pick up and wash them and put them at a temperature of about 25 ℃ to accelerate germination. Rinse the seeds with clean water once a day and sow after the seeds break the skin and show white spots. The seeds can be sown when 50% of the seeds are 60% white.

Picture: asparagus
3. Sowing and fertilization: turn the soil deeply before sowing, apply 2500-3000 kg per mu of rotten organic fertilizer or 1500-2000 kg of human feces and urine, 50-2000 kg of plant ash, rake flat and fine after mixing with the soil. Hollow cabbage can be sowed or striped, with seed consumption of 1.5-2.0 kg per mu. After sowing, it can be covered with fine soil about 25 cm thick. Strip sowing can draw a shallow trench with a depth of 2-75 cm, with a distance of 375 cm, and then spread the seeds evenly in the ditch and cover it with fine soil. Then cover the border with thin film and cover the thermal insulation material, and the mulch can be opened after emergence.
4. Fertilizer and water management: hollow cabbage is a crop harvested many times, so in addition to applying sufficient base fertilizer, it is necessary to carry out multiple stages of topdressing in order to achieve high yield. at seedling stage, 10-15% rare manure can be applied, the dosage per mu is 1000-1500 kg, when the seedlings have 3-4 true leaves, 15-20 kg of compound fertilizer and 2-4 kg of urea are mixed, and 5-8 kg (per mu) of compound fertilizer is used for each harvest. Asparagus needs a lot of water and should be watered frequently to keep the soil moist. It is necessary to plough and weed in time during the growth period, and there is no need for weeding and ploughing after ridge closure.
5. Pest control: the main diseases and insect pests of asparagus are white rust, wheel spot, aphids, Plutella xylostella and curly worms. Please read the article "pest control techniques of asparagus" for specific control methods.

Picture: asparagus
6. Harvest method: the harvest of hollow cabbage generally adopts the method of pinching, when the first harvest is more than 30 cm in the plant, leave the lower part 9-12 cm, harvest the tender shoots on it, and then start the second harvest when the new shoots growing from the axils of I leaves are 15 cm long, but 2-3 leaves should be left in the lower part to promote more new shoots and ensure high yield. After the third harvest, only 1-2 leaves were left under each new shoot to prevent too many new shoots and premature senescence of the plant. At the same time, too many dense branches at the base of the plant were removed to achieve the purpose of renewing and maintaining a reasonable population.
[editor's conclusion] asparagus likes a warm and humid climate, is resistant to heat and inflammation and is not resistant to frost, so it needs special attention in the process of planting. The above introduces the planting time and method of asparagus. I hope it can be helpful to you!
- Prev

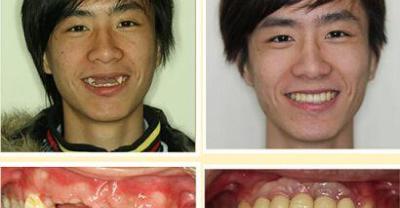
Who is suitable for dental implants? What are the points for attention before and after dental implants? are there any sequelae of dental implants?
The loss of teeth brings a lot of trouble to people's life, and the rapid development of artificial dental implant technology does not need to damage neighboring teeth, and the function and appearance of natural teeth.
- Next
Grow happiness in your own world
The sound of rubbing leaves came from the woods. it was the fingers of autumn. The sun warms the wall and the night cools it. The old leaves have been rubbed off in autumn, you should listen.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

