Methods of cultivating High-yield Edible Fungi
At present, a large number of cultivated edible fungi, such as Pleurotus ostreatus, Lentinus edodes, Flammulina velutipes, hericium Erinaceus, fungus fungus, Tremella fuciformis and Agaricus bisporus can be divided into mycelium stage and fruiting body stage or two growth and development stages. There are similarities and differences in the conditions required by each kind of mushroom in these two stages. At this time, their biological characteristics determine that if they can create the good conditions they need, they can achieve high yield and high quality.
Nutrients, mainly carbon, nitrogen and mineral elements
1. Carbon nutrients are not only the main components of mycelia and fruiting bodies, but also the source of energy for their growth and development. Carbon accounts for about 50% of the mushroom body composition (dry matter) 65%. The culture medium such as cotton hull and sawdust used in cultivation is the main source of carbon.
two。 Nitrogen is the main raw material of protein and nucleic acid. It is also the main component of mycelium and fruiting body, and it is also the material basis of delicious flavor of edible fungi, especially rich in amino acids (as many as 18 kinds), which can not be formed without nitrogen.
Carbon and nitrogen nutrients for the normal development of edible fungi not only need a sufficient quantity, but also require a reasonable proportion, commonly known as the ratio of carbon to nitrogen. The suitable proportion of all kinds of mushrooms is 20:1 in the mycelium growth stage and 30m / 40VR in the fruiting body development stage. In the production, due to the different kinds of culture materials, sometimes wheat bran, corn meal, soybean cake powder, ammonium nitrate, urea and so on are added to adjust the ratio of carbon to ammonia. No matter what mushrooms are stereotyped, or even do not follow the original formula, arbitrary changes, lack of this and that, it is difficult to achieve high yield and high quality.
3. Mineral elements such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, iron, zinc and other mineral elements and trace elements are needed for the normal growth of edible fungi. Although the amount of these substances is small, they are all important, and generally the content in the main materials can meet the needs. Sometimes such as magnesium sulfate, charcoal (potassium) and chicken manure (phosphorus) are added.
2. Moisture and humidity
Water is one of the main components of mycelium and fruiting body, and what is more important is the metabolism of life activities, which cannot be carried out without water. The moisture content of fresh mushroom body is as high as 85% and 90%. The water in the culture medium is the main source of water for the growth and development of edible fungi, but too much water is disadvantageous. The suitable water content is 65%, 75%. Use the material to absorb enough water and sew it out with your fingers without dripping. Taking cottonseed hull as an example, the weight ratio of feed to water is about 1: 1. 2: 1. 5, if added too much, it will hinder the mycelium growth.
Humidity, mainly refers to the relative humidity of the air, which is not only directly related to the growth and development of edible fungi, but also affects the distribution of water in the material, especially during the development of the fruiting body, if the humidity is insufficient, the yield will be reduced, and if it is less than 60%, the fruiting body will not grow. Below 45% primordia stop differentiation, or even dead primordia. The suitable air humidity is 85% Mel 93% (fruiting body growth period). It is a necessary measure to increase the relative humidity of the air by spraying water in the process of cultivation. Especially in the later stage, the yield can be increased by injecting water into the medium or soaking the medium.
Third, humidity
All kinds of mushrooms need to grow and develop normally under certain temperature conditions. The temperature requirements of mycelium and fruiting body are different in the process of growth and development, and some of them "like" the condition of changing temperature. For example, if Pleurotus ostreatus can be stimulated by 10 ℃ temperature difference every day, it is beneficial to the formation and development of fruiting body. For several mushrooms cultivated above, the suitable temperature for mycelium growth is about 25 ℃ (Auricularia auricula 30 ℃), and the optimum temperature for fruiting body development is about 15 ℃. Volvariella volvacea likes temperature, the fungal line is better developed at 35 ℃, and the fruiting body is well bred at 30 ℃ and 32 ℃.
Temperature is an important factor affecting the growth and development of edible fungus. At present, natural season cultivation is mostly used in production, mainly according to natural temperature conditions (artificial air conditioning is also mainly to create temperature conditions). With the progress of science and technology, edible mushroom varieties are being improved, and changing their temperature characteristics is one of the main goals, such as Pleurotus ostreatus and Lentinus edodes, which have been cultivated in low, medium temperature, high temperature, and even wide temperature type. As a result, the corresponding varieties can be selected according to the temperature conditions of the cultivation period and the cultivation period can be extended.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide
If there is not enough oxygen in all kinds of edible fungi, the mycelium will grow badly and the fruiting body will not grow well. Because the edible fungus itself releases carbon dioxide in the process of growth and development, the cultivation site should be ventilated and ventilated.
5. Light
Edible fungi do not have strong requirements for light, and the mycelium can grow in the dark. Some scattered light is needed during the differentiation and growth of fruiting body, and strong light is avoided. Completely dark, fruiting body dysplasia and slow. Light can increase its color, and the color is light without light. The light is also related to the temperature. Planting edible fungi in the greenhouse in the north needs sunlight to heat up, but we should pay attention to prevent the temperature from being too high, the light too strong, and shading with grass curtains and so on.
6. PH
Edible mushrooms prefer slightly acidic environment. Generally, the ph value is not more than 7 (neutral), which is between 5.5 and 6.5, but Pleurotus ostreatus is more alkali-tolerant and can grow at ph 8. Hericium Erinaceus is acid-resistant and can grow under ph5. Sugar and other acidic substances will be added in the cultivation process, and the culture medium will also become sour in the process of high-temperature sterilization. Attention should also be paid to the local water quality, that is, its ph. In batching, attention should be paid to creating a suitable pH environment, and some acid fertilizers such as lime or ammonium nitrate are added.
Adding calcium and nitrogen can adjust the ph value of the culture material.
In order to prevent excessive acid or alkali, add a certain amount of gypsum, can play a buffering effect.

- Prev

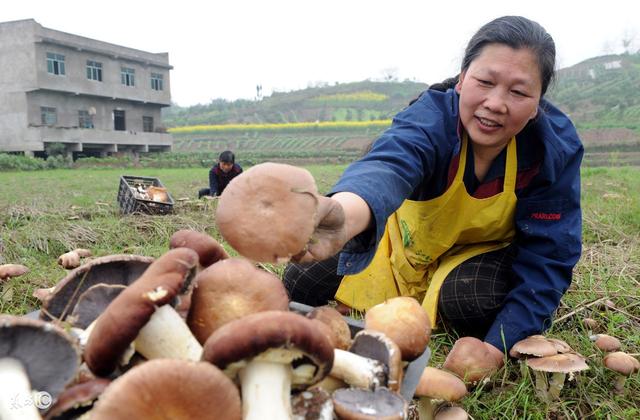
Sugarcane produces edible fungi!
In Chengmai, Hainan, there is an enterprise that has planted edible fungi with sugar cane! "this is a pocket mushroom, taste crisp, known as the best mushroom," the enterprise is responsible for.
- Next
Cultivation formula of common edible fungi
Mushroom name: Pleurotus ostreatus (per square meter) 1. Cottonseed shell 20 kg, calcium superphosphate 0.4 kg, gypsum powder 0.6 kg, urea 0.1 kg.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

