Talking about Edible Fungi (2)
Morphological structure of Edible Fungi
We know that edible fungi are macrofungi, which are composed of two parts: mycelium and fruiting body. Edible fungi rely on hyphae to absorb nutrients from the ingredients. When the mycelium grows to a certain stage and accumulates enough nutrients, it can grow into a large usable fruiting body.
Mycelium: mycelium is the nutrient body of edible fungi, composed of tubular hyphae, which are multicellular. According to different stages of development, it can be divided into primary hyphae and secondary hyphae. Spores germinate to form primary hyphae. Primary hyphae are paired to form secondary hyphae, which contain two nuclei, called binuclear hyphae. Binuclear hyphae have the ability to produce fruiting bodies, general edible fungi with fine hyphae, such as Lentinus edodes and Auricularia auricula, have a lock-like union on the binuclear hyphae, while edible fungi with thicker hyphae, such as straw mushrooms, do not have a lock-like union on their binucleate hyphae.
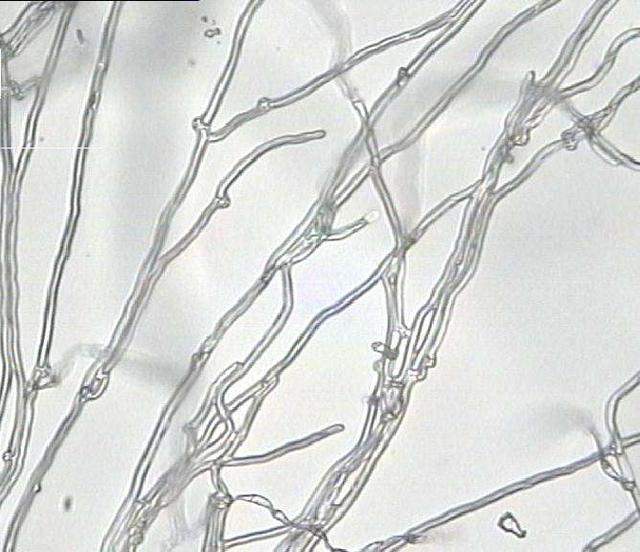
Lock joint
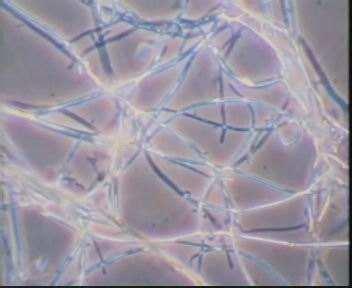
Mycelium
Fruiting body: it is the reproductive organ of edible fungi. It is the edible part of what we usually call "mushroom"ear" and so on. The fruiting bodies are various in shape, some are ear-shaped (fungus), some are head-shaped (hericium Erinaceus), and some are umbrella-shaped (straw mushroom). What we usually eat is an umbrella fruiting body, which is usually composed of stalks, caps, pleats and other appendages.
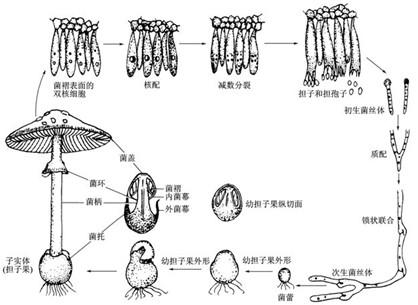
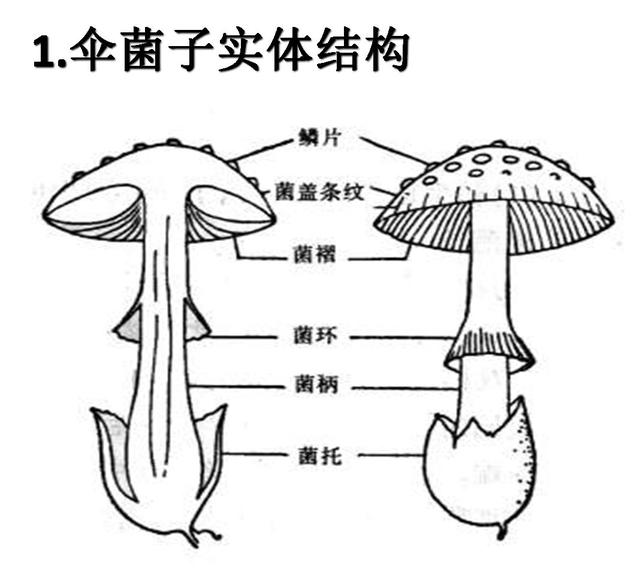
Morphological structure of edible fungi
The development process of edible fungi
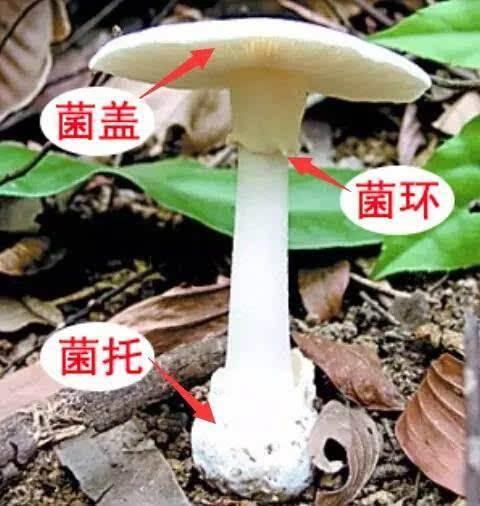
Stalk: also known as mushroom stalk or mushroom foot, plays an organ to support the cap and transport nutrients, some born in the middle of the cap called mesophyte (straw mushroom), some partial (shiitake mushroom), some Pleurotus ostreatus (Pleurotus ostreatus). There are often two appendages on the stalk, the ring and the receptacle, not on every kind of edible fungus. The fungus ring is born on the stipe, the membranous ring structure, and the receptacle is born at the base of the stalk, cup-shaped, bract-shaped and so on.

Stalk and cap
Mushroom cap: mushroom cap, mushroom umbrella. The place where the bacteria fold is born, the protective tissue of the reproductive organs.
Fold and tube: located under the cap, knife-shaped is called fold, tube-shaped is called tube, is the place where basidiospores are produced.
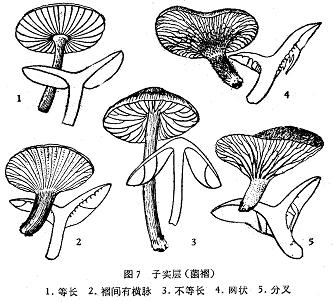
Bacterial fold
Bacterial tube
5. Spores: they are divided into basidiospores and ascospores, which are produced by basidiospores and ascospores respectively, belonging to sexual spores and the basic unit of reproduction of edible fungi.
- Prev
Non-pathogenic diseases of edible fungi
Second, unsuitable living conditions and improper cultivation and management measures or genetic variation of non-pathogenic diseases will cause obstacles to the growth and development and physiological obstacles of edible fungi.
- Next

The cultivation method of edible fungus: how to grow the planting method of edible fungus? High yield cultivation techniques of Edible Fungi
At present, a large number of cultivated edible mushrooms such as Pleurotus ostreatus, Lentinus edodes, Flammulina velutipes, hericium Erinaceus, fungus, Tremella fuciformis and Agaricus bisporus can be divided into mycelium stage and seed stage.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

