At the breeding site, if you do not understand the mold and its toxins, the loss of profits will become normal.
In recent years, the increase in aquaculture capacity inevitably brings new challenges, and the imperceptible and hidden threat caused by mycotoxins is one of the emerging challenges with wider scope and greater impact.
What are molds and mycotoxins?
1. Mold
Mold belongs to fungi and is a kind of multicellular microorganism, which can be divided into infectious and toxic according to its pathogenicity.
There are two main categories. It propagates in the form of seeds or spores and exists widely in nature.
2. Mycotoxin
Any fungus that can produce toxins and cause acute or chronic poisoning in humans and animals is called intoxication.
Pathogenic fungi. Toxic secondary metabolites produced by molds are called mycotoxins.
Common pathogenic mycotoxins
Aflatoxin Aflatoxins
Ochratoxin Ochratoxin
Corn gibberellin ketene (Zearalenone)
Vomiting toxin (Deoxynyvalenol)
Tmur2 toxin (Tmur2 toxin)
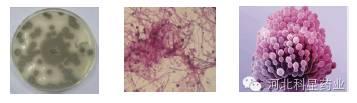
Clinical manifestations caused by several mycotoxins
1. Zearalenone
With the characteristics of estrogen, the ovaries of laying hens and breeder hens shrunk, the laying rate decreased, and the fertilization rate of breeding eggs decreased, which led to obvious precocious characteristics of young hens and overdevelopment of chicken crown at 15 days of age.
2. Vomiting and Tmur2 toxin
The clinical manifestation is enteritis, which is more serious when bacteria are present.
Focus on the destruction of intestinal epithelial cells, resulting in cell necrosis.
Cause mucous secretions or ulcers in the mouth, crop, glandular stomach and muscular stomach, sometimes swelling of the glandular stomach.
3. Aflatoxin
Immunosuppression, immunity decreased, protein synthesis was blocked, blood biochemical disease resistance index value decreased in an all-round way; bursa of Fabricius atrophied in advance in young and young chickens; liver increased fat deposition, liver became yellow and brittle; in chronic poisoning, the liver was pale and fragile, and the gallbladder became smaller. The results of microscopic observation showed that there were vacuoles in hepatocytes and bile duct hyperplasia. Reduce weight gain, feed conversion rate, egg production and egg weight; affect calcium and phosphorus metabolism and utilization-leg disease; affect iron and copper metabolism and utilization; dead pottery rate increased.
4. Ochratoxin
The most obvious effect is severe kidney disease, pale and enlarged. The most important features of ochratoxin poisoning are:
The main results are as follows: (1) the growth of poultry is slow and the feed conversion efficiency decreases.
(2) the amount of drinking water increases and the situation of wet feces is serious.
(3) the pigmentation of broilers fed with aflatoxin diets was not good.
Harm of mold and mycotoxin
1. The universality of the harm
The death of 100000 turkeys in Britain in 1960 caused scientists to be at risk of mycotoxins.
The harm of in-depth study. At present, hundreds of mycotoxins have been found in animals.
There are different toxicities, metabolic pathways and target organs. The harm caused by mycotoxins is global.
The problem exists in almost all feed materials and human food materials.
Mycotoxins are often not easy to detect before they are produced in large quantities. When you find mildew and change color, say
Ming microbial reproduction has been in an exuberant stage, feed quality has been seriously damaged. United Nations Food and Agriculture Group
According to the survey, all kinds of grains, oilseeds and feeds contaminated by fungi account for about the total amount of grains, oilseeds and feeds in the world every year.
10% of.
China is the hardest hit country of mycotoxins, losing billions of yuan due to mycotoxins every year.
It is hard to imagine the degree of harm and loss in broilers and eggs (breeds). Mycotoxin is not present.
There is antigenicity, any low dose of mycotoxin feed can not cause livestock and poultry to produce antibodies, and
It will have a negative impact on the feeding effect. Low-dose mycotoxins accumulate as a result of long-term feeding.
The prolonged period resulted in explosive poisoning, and the limited standard of mycotoxin in feed (safe dose) was not safe.
Mycotoxins in feed do not exist alone, not only the major known mycotoxins, but also mycotoxins.
With unknown mycotoxin components. Any two or more mycotoxins exist at the same time and play a role in each other.
The effect of strengthening toxicity is stronger than that of their respective negative effects.
2. Harm to chickens
The main results are as follows: (1) the chicks grow slowly, eat slowly, the legs and claws are light and white, and the pigmentation is poor. Late feeding
Slow, no increase in material, a sharp increase in the ratio of feed to meat.
(2) diarrhea, feed stool, the use of a large number of enteritis and coccidial drugs are ineffective, seriously affecting the feed reward
(3) recurrent attacks of enteritis and coccidiosis, increased susceptibility to Escherichia coli, fear of drug withdrawal, and increased drug costs.
(4) due to severe immunosuppression, the antibody in the body could not reach the proper titer after the vaccine was immunized.
Easy to be infected with atypical Newcastle disease and other viral diseases
(5) Chicken flocks have liver and kidney problems and serious spotted kidneys, and the appearance of the autopsy is very similar to that of renal branches.
(6) there is a hook phenomenon in the flock of chickens, so they do not dare to eat large feed pellets, but only eat finer pellets and scraps.
(7) the size of the individual is different, and the weight is light.
(8) the egg production of laying hens decreased and the eggshell became white, but salpingitis and virus drugs had no effect.
(9) loose feathers and white chicken feet
(10) Chicken flocks spit water, which looks like Newcastle disease.
(11) the phenomenon of neck stretching and mouth opening was found.
Conditions for the production of mycotoxin
1. Matrix: fungal toxin-producing strains mainly grow and produce toxin in food, grain, forage grass and other plants, and in milk and eggs.
The ability of producing toxin on the matrix of animal origin is low.
2. Temperature: the growth and reproduction of mold is closely related to temperature. Most of the optimum temperature is 25-30 ℃, low.
When the growth is weakened at 10 ℃ or more than 40 ℃, the ability of toxin production will also be affected.
3. Humidity: the moisture of the substrate and the humidity of the air are closely related to the growth, reproduction and toxin production of fungi.
The optimum condition for fungal toxin production is 17%-18% water content of matrix.
Problems existing in actual Livestock and Poultry production
The main results are as follows: 1. Corn mildew is widespread: in recent years, due to climatic factors, maize lodging in the mature period continues to occur, resulting in corn mildew in situ, improper preservation and so on.
2. Some laying hens and breeder farms often have wet material in the trough due to water leakage in the drinking fountain; caused by long-term intake of wet material
- Prev
Tuoniang pomelo? Is there another online celebrity of agricultural products? Help me up and have a look!
Tuoniang pomelo? Is there another online celebrity of agricultural products? Help me up and have a look!
- Next

Did the close relatives of the piranha go to the Yangtze River? And citizens put 40 trucks of fish into the river at one time!
Did the close relatives of the piranha go to the Yangtze River? And citizens put 40 trucks of fish into the river at one time!
Related
- A course of planting techniques and methods on how to grow carrots
- How to plant the latest tulips?
- Is it better to pick tea in the morning or in the afternoon? When is the best time for tea to be picked? what is the third or fifth tea?
- Launch Yuanxiao Happy combination Haocha + Tea Yuan healthy Taste
- Penghu Tourism "Fireworks 20 Parade with You"
- 2022 West Lake Happiness holds "Digital Revitalization Voucher" and draws iphone13 and laptop.
- Banqiao Fuzhou social houses are designed to change start-up combined with police elimination to create a safe and livable environment
- The convenient measure of "mechanical weeding" in Xinbei has been abused and the Agriculture Bureau has imposed heavy penalties on the illegal land consolidation.
- Changgeng University Joins Hands with Four Memory Factories to Rescue Memory Talent Shortage
- The list of Taiwan's top 100 MVP managers is listed by the Director-General of the Farmers' Association of Sanxia District.

