How much is the price of sweet potato per jin?
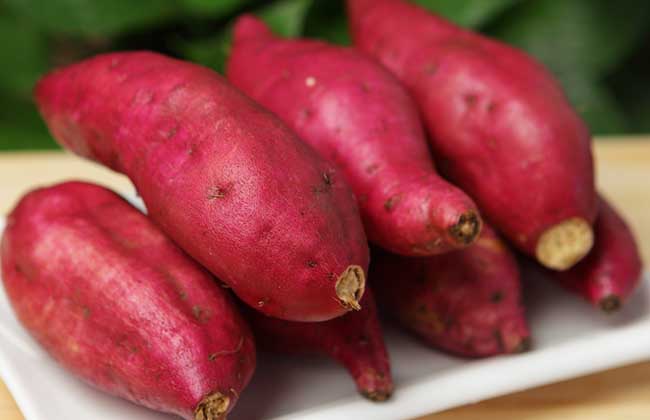
Sweet potato, also known as sweet potato, red potato, sweet potato, etc., is an annual herb of the sweet potato family. It is generally believed that it originated from Mexico and tropical America from Colombia, Ecuador to Peru. At the end of the 16th century, it was introduced from South Asia to Jianjian and Guangdong, and then spread to the Yangtze River, Yellow River basin and Taiwan Province. Nowadays, China's sweet potato planting area and total output are the first in the world. Next, let's take a look at how much sweet potatoes cost per jin.
How much is the price of sweet potato per jin?
.stabs td {text-align:left;text-indent:0.5em} highest price (yuan / kg), lowest price (yuan / kg), average price (yuan / kg) sweet potato Hebei 2.402.202.20 sweet potato Hubei 1.801.401.60 sweet potato Shaanxi 1.601.401.50 sweet potato Henan 1.001.001.00 sweet potato Inner Mongolia 2.402.402.40
Note: the price of sweet potato varies from place to place, and the price varies greatly with the change of season every year. At the same time, due to the relatively high yield per mu of sweet potato, the price is generally cheaper when it is first produced in autumn. and with the sweet potato planting area expanding year after year, the output continues to increase, making the price rise weak.
How many jin does sweet potato yield per mu?
There is no fixed figure on the yield of sweet potato per mu. According to different planting conditions, the yield will be different, with the characteristics of wide adaptability, strong stress resistance, drought and barren tolerance, less diseases and insect pests, and so on. Generally, the yield per mu can reach 4000kg to 6000jin per mu, and the high-yield cultivation can reach more than 10,000 jin. However, due to the differences in natural conditions and cultivation level, the per unit yield level is also extremely uneven.
Where is the origin of sweet potatoes?
Sweet potatoes in China are mainly distributed in Beijing, Shanxi, Shandong, Henan, Tianjin, Hebei and Northeast provinces, Inner Mongolia, Yunnan, Sichuan, Hubei, Gansu, Anhui, Fujian, Shaanxi, Hunan, Guangdong, Jiangsu and Jiangxi. The main producing areas in China are Anhui Si County (the hometown of Chinese potato), Hebei Lulong, Fujian Liancheng, Henan Kaifeng and Dengzhou and Tanghe Tongzhaipu, Shandong Sishui, Sichuan Nanchong and other areas.
What kind of environment does sweet potato need to grow?
1. Temperature: sweet potato likes warm and cold, and the ground temperature is about 10 ℃. It takes 5 days for 15 ℃, normal for 17-18 ℃, 3-day for 20 ℃, and one day for 27-30 ℃. When the temperature is 25-28 ℃, the stem and leaf grow faster, but the potato expands slowly when the temperature is above 30 ℃. The respiratory consumption was more than 38 ℃, and the stem and leaf grew slowly. The stem and leaf grew fast when the temperature was below 20 ℃, and stopped growing at 15 ℃. The duration below 10 ℃ became frost, and the stem and leaf withered.
2. Light: sweet potato likes light. Under the condition of sufficient light, the leaf color is thicker, the leaf age is longer, the stem is sturdy, the stem transport tissue is developed, and the yield is higher. If the light is insufficient, the leaves are yellow, the leaves are more deciduous, the leaf age is short, the stem is slender, the transport tissue is underdeveloped, the organic nutrients formed by assimilation are less transported to the root tuber and the yield is low.
3. Moisture: sweet potato is a drought-tolerant crop, but too much and too little moisture is not conducive to yield increase. Sweet potato is afraid of flooding, especially after fruiting, it has a great impact on the yield. The unbalanced growth rate of tuber inside and outside of the soil caused by the uncertainty of soil dryness and humidity often leads to the phenomenon of bark cracking. In short, sweet potatoes are afraid of both waterlogging and drought. The masses say, "dry long firewood roots, wet long whisker roots, non-dry and wet long roots." In order to obtain high yield of sweet potato, we should timely and properly irrigate according to specific conditions, drain waterlogging in time and thoroughly, and strengthen ploughing and preserving soil moisture in dry land.
4. Nutrients: sweet potato has strong fertilizer absorption ability and resistance to barren, but sufficient fertilizer must be applied for high yield. in addition to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, sulfur, iron, magnesium and calcium also play an important role. among the three elements, sweet potato has the most requirements for potassium, followed by nitrogen and phosphorus. According to the analysis, every 1000 jin of sweet potato contains 3.5jin of nitrogen, 1.75jin of phosphorus and 5.6jin of potassium. Therefore, increasing the application of potassium fertilizer, timely and appropriate amount of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer can significantly increase the yield.
5. Soil: it is better for sandy loam and sandy soil with rich organic matter, loose, aerated and good drainage in deep soil layer. when the soil is sticky and heavy, the skin color of root tuber is not good, rough, irregular potato shape, low yield and not resistant to storage. However, sandy loam and sandy soil generally have low fertility and poor water retention, so fertilization and other measures should be adopted to gradually improve soil fertility in order to obtain high yield. Sweet potato is more resistant to acid and alkali, and the range of pH value is about 4.5 to 8.5, but 5.2 to 6.7 is suitable. When the soil salt content is more than 0.2%, it is not suitable to plant sweet potato.
Related
- A course of planting techniques and methods on how to grow carrots
- How to plant the latest tulips?
- Is it better to pick tea in the morning or in the afternoon? When is the best time for tea to be picked? what is the third or fifth tea?
- Launch Yuanxiao Happy combination Haocha + Tea Yuan healthy Taste
- Penghu Tourism "Fireworks 20 Parade with You"
- 2022 West Lake Happiness holds "Digital Revitalization Voucher" and draws iphone13 and laptop.
- Banqiao Fuzhou social houses are designed to change start-up combined with police elimination to create a safe and livable environment
- The convenient measure of "mechanical weeding" in Xinbei has been abused and the Agriculture Bureau has imposed heavy penalties on the illegal land consolidation.
- Changgeng University Joins Hands with Four Memory Factories to Rescue Memory Talent Shortage
- The list of Taiwan's top 100 MVP managers is listed by the Director-General of the Farmers' Association of Sanxia District.



