Teach you about the seeds of plants.
The mature seed consists of seed coat, embryo and endosperm. Embryo is composed of radicle, embryo, hypocotyl and cotyledon. Some plant seeds have endosperm, such as corn, wheat, rice and so on. Some plant seeds have degenerated endosperm, from which nutrients are transferred to cotyledons, such as beans.
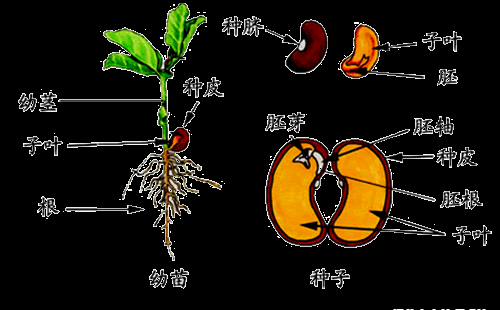
Soak soybean or broad bean seeds in water overnight. After the seed coat is broken, split the cotyledons and recognize where the embryo, radicle and hypocotyl are. The cycle of life in nature Man and animals eat plants, feces and corpses return to the soil, and plant remnants return to the soil; microorganisms, fungi, and earthworms in the soil decompose these animal and plant residues into nutrients that plants can absorb; plants absorb water and these nutrients from the soil, grow, and provide food for man and animals. Any failure at any one link in this cycle will cause chaos in the entire system and give rise to many headaches. Plants bloom to bear fruit, and the fruit contains seeds, which fall into the ground and grow again, so that the life of the plant can be multiplied. This type of reproduction is called sexual reproduction. Of course, some plants can also be propagated by cuttings or by burying their tubers in the soil. This method of reproduction is called asexual reproduction. Of the more than 350,000 known plant species, more than 250,000 are sexually reproducing. Plant flowers are composed of calyx, receptacle, petals and stamens. Flowers with all these parts are called perfect flowers, but many plants have incomplete flowers. The pistil is divided into stamens and pistils. Some plants have both pistil and stamens in their flowers, such as peach, tomato and rape flowers; but some plants have only pistil or stamens in their flowers, such as corn, pumpkin and cucumber flowers. Some plants are monoecious, such as corn, pumpkin, castor, a plant has both male and female flowers; some plants are dioecious, such as ginkgo, mulberry, asparagus, a plant has only male flowers or only female flowers. The anther is at the top of the stamen and produces pollen grains. The pistil tip is the stigma, connected to the ovary by the style. Please pick a flower to observe. Is it a perfect flower? Does it have pistils? Any stamens? Stigmas secrete a sticky substance that sticks to pollen grains when they fall on them. Pollen grains are stimulated to grow pollen tubes, and two sperm cells develop in the tubes. Pollen tubes gradually elongate and enter the ovule, one sperm cell combines with the egg cell to form an embryo, and the other sperm cell combines with other cells in the ovule to form an endosperm that stores nutrients. Insectivorous plants teach you about Utricularia
Utricularia is a small insectivorous plant with a movable sac-like catching structure, which can suck small organisms into the sacs and digest them. Utricularia has many varieties and different shapes. Generally, they grow in patches on mossy trunks in wetlands, ponds and even tropical rainforests. Most of them have long flowering periods and will open lovely flowers.
A brief overview of Utricularia
Lentibulariaceae insectivorous plants include Utricularia, Genlisea and Pinguicula. There are about 300 species in 3 genera. There are about 218 species of Utricularia, which are distributed in most parts of the world and are the most widely distributed and most diverse insectivorous plants in the world. Utricularia can be divided into three groups according to their ecological habits: terrestrial, aquatic and epiphytic groups. Terrestrial groups account for about 80% of the total, aquatic groups account for about 15%, and the rest are epiphytic groups.
Morphology of Utricularia
Utricularia is a perennial herb (a few are annual), which can be born in ponds, ditches, wetlands, trunk of tropical rain forest, etc. Utricularia has long stolons, rootless, whorled or simple leaves on stolons, aquatic species have filiform leaves, often bifurcated, and insect traps on stolons or at the base of leaves. Stems slender, racemes or a flower terminal, corolla 2-lipped, base more spurs. Capsule globose, dehiscing at maturity to shed fine seeds.
tricularia trap
The insect catching sacs of Utricularia are born at the base of stolons or leaves, most of which are oblate and translucent, with a diameter of 0.25-10 mm. There are antennae around the opening of the insect catching sac to attract small creatures and to guide prey to the mouth of the insect catching sac. The opening of the insect catching sac has a membrane flap that can be opened and closed, and the outer side of the membrane flap has induction hairs. When small organisms such as daphnia and larvae (mosquito larvae) are attracted to the mouth of the insect trap for shelter or nectar secreted by the captured insect sac, once the sensing hair is touched, the originally half-deflated insect trap quickly rises to form a strong suction force, and at the same time the membrane flap opens, sucking the water flow from the mouth of the sac together with the prey, and quickly closing the membrane flap. The whole process takes only about one hundredth of a second. At this time, the insect catching sac begins to secrete digestive juice, and the bacteria will also have greater help in the decomposition of nutrients. Generally, it only takes a few hours to several days for the prey to be digested, the nutrients are absorbed by the captured insect sac wall, and the excess water is also discharged. The insect catching sac returns to its original state and waits for the next prey. The fastest time between hunts is 15 minutes, and the residue from multiple hunts accumulates in the bag, darkening it and eventually decaying.
- Prev

Teach you about the flowers of plants.
Plants blossom in order to bear fruit. The seeds are wrapped in the fruit, which fall on the ground and grow again, so that the life of the plant can multiply. This mode of reproduction is called sexual reproduction. Of course, some plants can also propagate by cutting or burying their tubers in the soil.
- Next

What matters should be paid attention to in raising lotus bowls?
Bowl lotus, also known as bowl lotus, pot lotus, bowl lotus is planted in the bowl of lotus, specially for Chen on several tables in the room, in order to beautify the living environment. If the bowl lotus is cultivated properly, it will grow flowers with a diameter of only about 5 centimeters, petite and exquisite, with outstanding grace. Then it is pruned when the flowers are luxuriant and leafy, so that it is sparse and scattered.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

