Establish a goal-oriented systematic review framework for agricultural development and reform
Share + 1 Tweet Email
Recently, on the website of the "Agricultural Science and Technology decision Information platform" set up by the Council of Agriculture, I saw the article "Strategic Planning for Sustainable Utilization of Agricultural Land Resources" published by Guo Hongyu, the senior leader of agriculture. I am attracted by the title of the article; because I have paid close attention to the related issues of China's agricultural development for a long time, and have a slight understanding of some long-term problems and bottlenecks encountered in China's agriculture, I would like to see if there are any suggestions in the content.
Agriculture is the foundation for the establishment of a country. although the output value of agriculture in countries with developed industry and commerce is generally much lower than that of industrial and commercial activities, if a country does not have a stable supply of all kinds of agricultural products, everything depends on the supply of other countries. its foundation is based on an unstable foundation. Therefore, providing a stable self-sufficient supply of agricultural products and maintaining a good operational development environment are issues that all powerful countries will attach importance to.
Land is the mother of agriculture, but in the rapidly developing industrial and commercial countries, there will be improper or excessive use of land resources by industrial and commercial activities, and will compete for land resources with agricultural activities. Therefore, China promulgated the Land Planning Law in 105, looking forward to the effective distribution, management, development and utilization of "limited" land and resources under the norms of this law. In view of the hidden worries of food shortage expected in the world in the future and an example of the development of the sustainable management and use of agricultural land in advanced countries, team leader Guo called on the government to attach importance to the use of agricultural land resources in land planning and planning. and issued reminders and appeals from the perspectives of agricultural land protection policy, efficiency of agricultural land use, agricultural labor shortage and the concept of cultivating new farmers.
Team leader Guo's multi-faceted way of thinking once again inspires a perplexity in the author's mind for many years; that is, what are the effects and benefits of hundreds of billions of government budgets, funds invested in agricultural environment improvement, agricultural science and technology research and development, farmers' production subsidies, farmers' living care and agricultural policy promotion every year? What are the values and contributions to the sustainable development of agriculture in China? What are the priorities and standards for annual budget allocation and allocation? ,... Wait, a lot of curious questions.
If you look at some of the government's agricultural development programs or work results from time to time, for example, the new agricultural innovation promotion plan put forward by the Council of Agriculture in December 1995 (which is not compared with the focus of the new agricultural movement put forward in 1995) and the 520 handover briefing put forward in April 1995. Whether it is the three major promotion axes and ten key promotion policies mentioned in the new agricultural innovation promotion plan, or the 21 major policies promoted by the 27 major policy achievements completed in recent years and the follow-up recommendations listed in the 520 handover operation. For many people, it should be agreed that these jobs are really important, but what is the importance? What is the benefit to the prospect of agriculture in our country? And other issues are often foggy and unable to say why. What kind of positive and negative impact will these changes have on China's agricultural development? Presumably not only the general public cannot make it clear, but even the power and responsibility units of the agricultural authorities may not be able to explain this issue systematically for a time.
Therefore, it took a little time to propose a systemically constructive inspection framework using the concepts and skills of information planning and engineering design. Through this framework, management decision-makers, field scholars and experts, and even practical participants at all levels can establish a cognitive basis of integrity and commonality under this framework, and on this basis, let all kinds of discussion, plan formulation, work implementation have a complete and directional thinking, focus on the focus and take into account the coordination and integration of other related issues, resources, organization and other aspects. This is explained below to provide advanced reference for the industry.
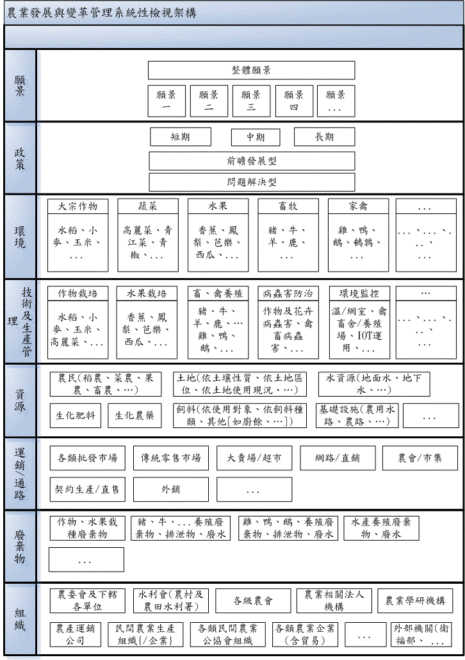

Figure: a systematic review of agricultural development and change management architecture
As shown in the figure above, this management architecture diagram is divided into eight levels (adjustable changes), namely vision, policy, environment, technology and production management, resources, transportation / marketing / access, waste, and organization. From the point of view of the management of agricultural development and change, the significance represented by all levels of this framework and the information and basic data needs that should be included are explained in turn as follows:
1. Vision:
It is the duty of the central agricultural administration unit to draw up a vision for agricultural development. Individuals do not understand the formation and formulation of China's agricultural vision. Cognitively, every 3-5 years or after a new chairman takes office, the Committee of Agriculture will put forward a set of agricultural development vision for the next 3-5 years. Is there any relevance or continuity between these new and old visions? What is the degree to which the vision will achieve the goal after several years? Whether there is an objective review and measurement mechanism within the Government may be a topic worth exploring.
It is proposed that agricultural vision is a good tool to consolidate agricultural development and reform policies and promote agricultural policy goals. therefore, the systematic formulation and review of the vision content will affect whether China's agriculture can develop efficiently and continuously in the established and correct direction.
This class suggests that the formulation of agricultural vision in China can be divided into two levels of thinking. The overall vision at the top is an abstract concept that is idealistic, imaginative and takes a long time (for example, 20 ~ 30 years), which is put forward by Xuheng International Agricultural Development trend and considering the overall agricultural development needs of our country. For example: "the construction of a sustainable high-quality agricultural production and farmers' living environment". Take this vision as an example, it contains important key elements that require long-term and sustained efforts, such as sustainability, quality, production and life.
After that, the secondary visions that can be put into practice in the medium and short term (such as 3, 5, 10 years) are drawn up according to different sub-industries or fields of agriculture. The content of the secondary vision should be more vivid and the situation promoted by policy implementation can be fine-tuned; for example: "to establish a self-sufficient and pollution-free pig industry in China"
After the construction of such a hierarchical and comprehensive vision, when the future rulers conduct regular reviews of agricultural policies and administrative priorities, they can have a comprehensive and objective basis for the review. there will be no hidden worries that great changes will arise as a result of personnel changes or the failure of the old and new policies to connect effectively.
2. Policy:
Apart from suggesting that policy areas should be divided into short-term, medium-term and long-term formulation, they should also be divided into forward-looking development and problem-solving categories for review.
A problem-solving policy shall be based on the collection of major and minor problems identified or faced at all levels below the framework and shall be formulated through an appropriate review process. The policies formulated should be divided into short-term, medium-term and long-term, and arranged in order according to sub-industries and sub-areas, and then prioritize and allocate resources according to annual government funds, available resources and governance priorities. The size policies obtained by this process must be fed back to the vision layer for comparison and be integrated with the vision layer.
The content of the forward-looking development-oriented policy should be drawn up after the vision layer has provided the direction, reviewed the current situation of the industries or areas at the level below the policy level, and formulated it after an appropriate review process. The policies formulated should also be divided into short-term, medium-term and long-term, and classified according to sub-industries and sub-areas, and then priority promotion and resource allocation will be made according to the annual government funding, available resources and governance priorities.
When the policy and implementation objectives are established, the further implementation plan can identify the relevant factors related to the policy plan, such as industry, technology, resources, access, waste disposal, organization, etc., from all levels below the level. further develop specific contents such as promotion details and work / responsibility allocation.
Similarly, after the completion of this hierarchical and comprehensive policy inventory and construction, it is believed that when regular reviews of agricultural policies and administrative priorities are conducted in the future, there will be a comprehensive and objective basis for review, and when personnel change, new supervisors do not have to bother to come up with new ideas or the hidden worries of great changes with personal subjective consciousness or the failure of new and old policies to connect effectively. This long-term and stable policy content and implementation direction will accumulate considerable implementation results and effectively achieve the vision of agricultural development or change in various fields.
3. Environment:
This framework comes from all levels below its own stratum, and its main content is the collection and filing of current information, and then, through an inventory of the current situation, problems and needs, it is uniformly gathered to the policy level for overall assessment, as a basis for policy and countermeasure research.
The scope of inspection referred to by this "environmental" class refers to the environment for the production, living and maintenance of all kinds of broad agricultural activities (or under the management responsibility of the Council of Agriculture). Basically, the basic data that need to be collected and integrated will vary with projects in different areas. For example, in terms of staple crops, it is necessary to collect, such as major crop types, planting area (including location), mode of production (if different need to be distinguished with location, farmers, etc.), number of farmers, number of participants (such as temporary workers), … In the pig industry, we need to collect such as pig species, farming area / number (including location), breeding method, number of farmers, number of participants, … In the aspect of rare species conservation, it is necessary to collect rare species, species distribution area, species number, distribution area environment, existing conservation measures, etc. Wait. Its content shall be worked out by experts in the field and the competent authority.
As for the data collection of farmers' living environment (mainly farmers), it should include the number of households, the area of farmhouses (including location), the types of farmhouses, the life styles of various categories, and so on. In addition, the environmental basic data collection and filing discussed by the six-tier chemical industry, such as agricultural processing, direct marketing, rest, and so on, can also be handled at this level.
In addition to the relevant basic data, in view of the progress, backwardness, shortcomings, unsolved problems, etc. It also needs to be collected and recorded here.
The main purpose of establishing such information is to understand and (as far as possible) accurately and instantly grasp the current situation of the environment in various agricultural industries / areas, to identify the problems and needs in the agricultural environment, and to provide a comprehensive review of the use of policies and vision. After the policy and promotion plan has been finalized, we can quickly and accurately grasp the implementation priorities or participation targets of the policy promotion according to the environmental data of this level.
It is believed that there are quite complete and rich contents in our country. We only need to strengthen the deficiencies and establish a complete and convenient index and access mechanism.
IV. Technology and production management
The technology and production management discussed in this class should be divided into two types: on-site use and research and development.
For the technology and management used in the field, it needs to correspond to the project at the upper level of the environment; that is, the technology and production management discussed here are the contents used in the production site (including pest control methods, etc.). Basically, the records should be collected according to the individual classification of production / operation farmers and then collected.
The categories of technology and management that are still under research and development can be classified as the main body of technology and management. to collect relevant data on the current independent research, commissioned research and foreign advanced technology, management and application of domestic learning and research units and farmers (/ agricultural enterprises), which have not yet been introduced in China.
For the collection and filing of basic data on the use of technology and management on the spot, on the one hand, we can understand and classify and analyze the activities of technology and management in various fields, and through the classification and analysis of the results, it will be possible to evaluate the degree of on-site implementation, effectiveness, advantages and disadvantages of various technologies and management methods, so as to find the improvement, improvement and guidance needs of farmers in the use of technology and management. And other useful information as a reference for follow-up administration and decision-making.
For the collection of basic data of research and development, in addition to analyzing and grasping the key points, achievements and allocation of research resources in China year by year, it can also meet the on-site needs of agricultural activities and the future needs of agricultural development to more effectively guide the application and implementation of research results, the in-depth demand of research content and the objective evaluation of research direction adjustment, new and other inspection items.
V. Resources
The resources discussed by this class should include various needs to support agricultural production or promote agricultural development in a broad sense, such as farmers, soil (agricultural) land, water, fertilizers, feed, pesticides, funds, infrastructure, various agricultural-related decrees and administrative orders, … Wait. The contents of the items collected by this class and reviewed regularly vary greatly according to the types of resources, as illustrated by the following examples:
Farmers: most of the information about farmers here should be collected from the environmental class, but from the perspective of resources, it is necessary to collect and understand the number, age, distribution areas, skills, average farming income of farmers in different agricultural fields. And through the inventory of this information, this paper preliminarily lists the existing problems and needs of our country under this resource, in order to make accurate decisions on the basis of the follow-up review of farmers' resource needs / gaps and policies such as the cultivation of new farmers and skills training.
Water: water resources can be divided into surface water and groundwater. The basic data that need to be collected and examined, as far as surface water is concerned, should include the above-ground water sources in each agricultural area, the annual estimate of each water supply source, the relevant data of the current waterway, the demand of each waterway water supply area (estimated), … Wait. As far as groundwater is concerned, it should include the estimation of accumulation content / annual recharge in each agricultural region, the current use status and utilization of groundwater in each agricultural area, and … Wait. In conjunction with the inventory of these data, we will also collect and uniformly list and manage the current problems in the use of surface water and groundwater, such as pollution of water supply sources and water supply waterways, water delivery efficiency of water supply waterways, over-pumping of groundwater, … Wait.
Feed: from the perspective of resource management, the data to be reviewed include feed types, annual feed demand in various sub-fields, various feed sources / producers / suppliers, feed independent supply capacity, feed production / supply industry chain and circulation mode, … Wait. Recently, the discussion of ramming kitchen waste can also be regarded as a kind of feed for filing. While taking stock of such information, it is also necessary to collect, uniformly list and manage various issues under this resource (such as the supply, treatment and use of food waste as feed, etc.) and improve demand, so as to serve as basic information for follow-up policy development and policy promotion.
Funds (government budget), … , and so on.
Many materials of this class should be co-built with other institutions or reviewed and processed with experts in fields other than agriculture, such as agricultural land data, water source and waterway data, … Wait. The review, allocation, management and development of limited resources are the basis for the sustainable (/ benign) development of agricultural industry, so the construction of a good inspection and management mechanism must be given priority.
VI. Transportation and marketing / access
The data needed by this class for the collection of archival transportation and marketing / channels refers to the channels and practices of various agricultural products (including primary agro-processed products). The details of the data would be ideal if we could grasp the source and quantity of supply in each channel.
On the one hand, the establishment of such data is to ensure the stability and fluency of the transportation and sale of agricultural products to the terminal market, and on the other hand, to identify weaknesses or problems in the current transportation and marketing system or practice for improvement. For example, the issues of loss rate and quality assurance of agricultural products in different channels, how to establish a stable export channel and overcome the problems of quality and inspection standards required for export products, and when the imbalance between production and marketing occurs, whether we can find ways to mitigate the impact from various channels. Wait.
Almost every year, agricultural administrative units are exhausted by the problem that the imbalance between production and marketing leads to the sharp rise and fall of agricultural products' producing areas and terminal market prices. It is true that the source of this problem is caused by production, but how many turning points and practices of transportation and marketing can accommodate changes in quantity and improve farmers' income is an issue that needs to be constantly reviewed and dealt with.
VII. Waste
There are many kinds of agricultural wastes, all wastes that will cause environmental pollution and environmental safety harm will affect sustainable management, no matter how much or less, they should be included in data filing and inspection, such as pig manure, urine culture wastewater, aquaculture wastewater, pesticide containers, rice stalks and rice husks, … Wait.
It is suggested that there should be various waste sources, (estimated by each peasant household) quantity, current collection and disposal methods of each peasant household / agricultural production unit, … Wait. Then the advantages and disadvantages of the inventory, as well as the problems to be solved and suggestions for solutions, will be imported into the policy level for overall review.
VIII. Organization
There should be no less than thousands of organs and organizations belonging to agriculture, such as the Council of Agriculture (and its subordinate organs), peasant associations at all levels, water conservancy associations (rural areas and irrigation and water conservancy departments), fruit and vegetable companies, various production cooperatives, various industrial associations / associations / councils, various academic and research schools / institutions, agricultural enterprises specializing in agricultural products production and marketing services. Among them, there are government agencies, public institutions, corporate bodies, private institutions / enterprises, and other government departments that are closely related to agricultural affairs (such as the Environmental Protection Department / Ministry of Environment, the Food and Drug Administration of the Ministry of Health and Welfare, local government agricultural bureaus, etc.).
From the point of view of the competent agricultural authorities, many of these organizations are not under the jurisdiction of the Council of Agriculture, but for the sake of agricultural development and the promotion of government affairs, we still need to rely on the division of labor and cooperation between these organizations and institutions. Therefore, to understand the positioning of these organizations, structural mechanisms, contact channels and promote the good function of these organizations are also projects that the governing organs need to be concerned about.
After the establishment of this basic data, we will continuously examine the advantages and disadvantages of each organization and whether the contact channel is smooth. If there is a need for review and improvement, we can quickly grasp the key ideas for improvement, so as not to deal with public grievances with the stroke of a pen.
The above briefly explains the basic ideas and ideas of the agricultural authorities in charge of establishing this systematic review framework. Then it gives examples to illustrate the impact of the establishment of this framework on agricultural governance and its application.
Take raising pigs with kitchen waste as an example:
Raising pigs with food waste is extremely sensitive in the shadow of the spread of classical swine fever in Africa on the mainland today, so many farmers and pig farmers who use general feed strongly urge the government to ban the raising of pigs with food waste. As a result, it not only affects the production management methods and rights and interests of a relatively small number of pig farmers, but also gives rise to the question of where the existing food waste (regarded as waste) should go.
If this framework has been established first, we should have discovered at the environmental level the problem that pig farmers with food waste should not meet the cooking standards and quickly grasp the distribution area of pig farmers and other information. and from the feed level to grasp its supply channels and methods and understand the lack (if such information has not been established in advance, it can be supplemented under this framework).
When we know this issue in advance, it should have been included in the policy under this framework, perhaps this policy has promoted the implementation so that the problem can be effectively mastered and responded to without causing too much trouble, or it may be included as an urgent priority in response to this emergency. Therefore, it will not happen that we can only choose whether we can raise pigs with food waste, or once we decide not to use food waste to raise pigs, we can quickly work out specific guidance programs to assist pig farmers in the transformation by using the information of the environment, feed, technology and management, resources, organization, and other levels in the structure.
Take the goal of raising China's grain self-sufficiency rate to 40% as an example:
This policy objective should be a forward-looking developmental policy formulated by the competent agricultural authorities to take into account national security and the forecast of future world food shortages.
Through this framework, we can find out the crops and the required quantity that should be specifically increased from the environmental level, and then examine the relevant information from this level, such as increasing production or adjusting production contents, items and production areas. and then draw up specific and feasible plans on the basis of basic materials such as environment, technology and management, resources, organization, etc.
If it is necessary to increase the production area, we can identify the possible agricultural areas and agricultural land from the resource level, examine the supply sources of other required resources, technology and management demand, and then formulate a concrete and feasible overall (or phased) promotion plan.
Take reducing the utilization of agricultural water resources to less than 70% as an example:
This goal should be the agricultural reform policy produced by the government from the outside in response to the shortage of water resources.
The reduction of agricultural water use is not a uniform reduction, but will have different distribution needs according to the water needs of different regions. Through the information at the resource level of this framework, we can understand the current distribution of aboveground water use in agriculture, and then review the amount of agricultural water that needs to be released in the light of the water demand of different regions; at the same time, use environmental and resource-level information to review the reduction practices that can be coordinated by different regions, such as improving crop planting methods, counseling conversion, improving waterway water transport efficiency, redeveloping water sources or using groundwater, etc. When the various measures are systematically reviewed and the reduction targets are coordinated with other departments, specific plans are drawn up to use organizational forces to promote them step by step.
At present, of course, there are simple and immediate effective measures, such as reducing the cropping area of rice and the use of water for irrigation. however, such short-term measures at the expense of farmers' rights and interests (or subsidies without productive benefits to make up for the loss of farmers' farming income) and the long-term prospects of agricultural development should not become the norm.
Apart from the benefits of the above-mentioned policy review and planning, it is important for the agricultural authorities to comprehensively grasp the long-term and stable administration of agricultural development and change. All kinds of agricultural problems or development needs, big or small, will not be ignored and unable to link up because of personnel and organizational changes. What is more, it can enable various types of administrative needs and problems to be managed by designated power and responsibility units and promoted in conjunction with the annual review of policy priorities. In this way, the results of the policy can be effectively demonstrated, reducing the exhaustion of leaders from all walks of life due to the lack of mastery of the handling of emergencies, affecting work efficiency and damaging staff morale.
Of course, it is not difficult to establish the ideal of this systematic review framework. Even though the Government has collected and set up files and developed information systems to assist in the application of the basic information needed by the above-mentioned strata over the years, it is believed that there will still be considerable barriers and difficulties to overcome in order to further integrate and establish this framework and mechanism. there is also a lot of manpower and work to be invested. However, if the ideal goal of establishing this framework can be achieved, the follow-up effect will be considerable, so whether we should consider the development of this architecture mechanism, perhaps from a strategic point of view.
The above viewpoints provide advanced reference for the industry.
Share + 1 Tweet Email
Related
- A course of planting techniques and methods on how to grow carrots
- How to plant the latest tulips?
- Is it better to pick tea in the morning or in the afternoon? When is the best time for tea to be picked? what is the third or fifth tea?
- Launch Yuanxiao Happy combination Haocha + Tea Yuan healthy Taste
- Penghu Tourism "Fireworks 20 Parade with You"
- 2022 West Lake Happiness holds "Digital Revitalization Voucher" and draws iphone13 and laptop.
- Banqiao Fuzhou social houses are designed to change start-up combined with police elimination to create a safe and livable environment
- The convenient measure of "mechanical weeding" in Xinbei has been abused and the Agriculture Bureau has imposed heavy penalties on the illegal land consolidation.
- Changgeng University Joins Hands with Four Memory Factories to Rescue Memory Talent Shortage
- The list of Taiwan's top 100 MVP managers is listed by the Director-General of the Farmers' Association of Sanxia District.



