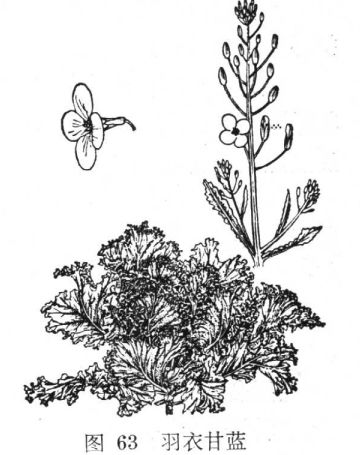
Cultivation and planting techniques of kale
[alias] leaf peony, peony, cauliflower. Cruciferae, cabbage. [morphology] biennial overwintering herbs, plant height 30 Mel 40 cm (even inflorescences up to 120 cm), erect unbranched, stem base Lignification. Leaf moment round-Obovate, broad, up to 20 cm long, glaucous. The petiole is thick and winged, overlapping on the short stem, the petiole node scar is triangular, and the leaf margin is wavy. Raceme terminal, with 20-40 florets, flowering in April. Siliques are fine cylindrical, with globose seeds and a thousand-grain weight of 1.6 grams.
[varieties, forms and varieties] are divided into two categories: red and purple leaves and white and green leaves. The heart leaves of the former are purple and lavender red.
Or snow cyan, the stem is purplish red; the latter heart leaves are white or light to yellow, the stem
Green. The seeds are reddish brown in the former and yellowish brown in the latter. (this article is from the Encyclopedia of Agriculture.
[Origin and distribution] originated from Western Europe.
[habit] hardy, like sunny places and fertile soil.
[reproduction] sowed in the open field seedbed in mid-January, germinated quickly and neatly, but should pay attention to noon shade.
[cultivation] after the first or second transplant, the seedlings are planted in the garden with a distance of 30 cm. Thin fertilizer and water should be applied frequently to promote the overcoloration of the trees as soon as possible. If it is used as a potted plant, it can be planted on the border head at the time of planting, and the 7-inch 8-inch pot can be dug up in November. After installation, if the weather is sunny and dry, it should be slightly shaded, and after the occurrence of new roots, fertilization will promote the restoration of vitality. The pot should not be too late, otherwise the basal leaves fall off too much, hindering beauty.
You can also repeatedly beat the soil to be very solid, install it in a 3-inch basin, dig a small hole, sow 3 seeds, and leave one plant after germination. The growth is slow, and the plant can only cover the mouth of the basin in winter, but its leaves can change color as usual.
When the seedlings are left to flower in the spring of the next year, pillars should be set up in time to protect them from lodging in the wind.
[seed collection] this species is easy to cross, and there should be a certain interval between teaching varieties. When harvesting, the pods should be cut when most of the pods on the inflorescence have turned yellow and dried so that the seeds are fully ripe and then threshed.
[use] the whole plant can be used as feed. Because of its cold resistance and bright leaves, it is an important material for winter flower beds and can also be watched in pots.
Planting techniques and pest control of kale
Kale belongs to cruciferous kale, it is a biennial herb, is a horticultural variety of edible kale, usually cultivated in scenic spots, high ornamental value, there are many people like it. At ordinary times, some people also want to grow kale at home, but they do not know its planting skills, and they do not know how to prevent diseases and insect pests during planting, so that the fruit of their own kale is always not very good. Today, the editor will take you to know the professional knowledge related to the cultivation of kale.
Planting skills of kale
Kale is a plant that is extremely cold-resistant in cold climate and can endure short frosts, but it also has strong heat resistance. It must be planted in sunny soil and keep the soil fertile. It is found that kale grows fastest when the temperature is between 20 and 25 degrees. In addition, kale this plant has a great demand for water, usually can not appear drought, but also can not let the field stagnant water, otherwise it will make kale more disobedient, not conducive to its growth.
Pest control of kale
1. Aphids
The vitality of kale is relatively strong, and the planting method is relatively simple, but we must pay attention to the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests during planting, especially aphids, which have a strong fecundity and can reproduce many times a year. After these aphids appear, they can gather on the tender stems of kale leaves and absorb their juice. At this time, the best way to deal with them is to spray medicine. 40% omethoate can be sprayed to significantly control diseases and insect pests.
2. Leaf roll moth
Leaf roll moth, also known as leaf curler, is one of the most common diseases of kale. After the disease occurs, the leaves of kale will be rolled up with silk and hide inside to eat the leaves of kale. In order to reduce the occurrence of this disease, the withered grass and fallen leaves in the planting site should be destroyed in winter, and the overwintering insects should be cleaned up as much as possible. When a large number of leaf rollers were found on the leaves of kale, dichlorvos EC or phoxim emulsion was sprayed in time.
Sharing of planting techniques of kale
Introduction: in our life, there are many kinds of vegetables, among which kale is a very gorgeous vegetable. Kale looks like a flower and looks better than many flowers. Kale can be used not only as a vegetable, but also as an ornamental plant. Kale presents purple, is very beautiful, and because of their own relatively large, so give people a very atmospheric sense of beauty, the following editor will introduce the planting technology of kale.
Planting techniques of kale:
1. Spring sowing in the open field: seedlings were raised in the protected field in mid-late February, the seedling age was 35-40 days, and the open field was planted from late March to early April. About 25-30 days after planting, that is, from mid-late April to early May, the harvest began.
2. Autumn sowing in open field: sunshade and rain-proof sowing and seedling raising in late June. The seedling age is about 30 days, planted from late July to early August, and harvested from mid-late August to early September.
3. Solar greenhouse cultivation in winter and spring: sowing from late July to late August, planting from late September to mid-October, and harvest from late October to March of the following year.
4. Improved sunny bed cultivation in spring: sowing from the first ten days to the middle of January, planting from the first ten days to the last ten days of February, and harvesting from late March to June.
Main points of cultivation:
1. Seedling transplanting: the seedling site is selected according to different seasons. Spring cultivation, seedling raising is generally carried out in the solar greenhouse from the first ten days of January to the end of February, and the temperature is kept at 20 ~ 25 degrees after sowing. Less watering at the seedling stage and proper ploughing to loosen the soil to prevent the seedlings from overgrowing. On the 25th day after sowing, the seedlings were divided into 2-3 leaves and planted at 5-6 leaves. Summer and autumn open-field cultivation of seedlings from the first ten days of June to the last ten days of June, the higher temperature should be built on the seedling bed shade shelter against rain, pay attention to drainage.
2. Colonization: kale is barren and fertilizer-tolerant, and can grow in barren soil, but the product quality is poor and easy to aging. Therefore, in order to obtain high-quality products, we should choose sandy loam or loam which is rich in humus and loose and fertile. Make a small high border of 100cm to 120cm, and the planting time is determined according to each season.
3. Field management: ploughing in the middle after watering planting water, watering the seedling water slowly after 5-6 days, and loosening the soil in the middle ploughing to increase the soil temperature and promote growth when the land is slightly dry. In the future, we should always keep the soil moist and do not accumulate water in summer. Appropriate topdressing during the growing period, and topdressing for every harvest. Pay attention to the control of cabbage insects, aphids and black spot.
4. Harvest: it takes about 55 to 65 days from sowing to harvest, and 25 to 30 days from planting to harvesting. The tender leaves can be harvested and eaten when the outer leaves are unfolded for 10 to 20 leaves. Each plant can pick 5 leaves and 6 leaves, leaving the heart leaves to continue to grow and harvest one after another. It is usually harvested every 10 to 15 days. In late spring and summer, if it is well managed and free from cabbage insects, it can be harvested until early winter. The flavor is better after a little frost in autumn and winter. In the summer high temperature season, the leaves become hard, slightly more fiber, poor flavor, so they should be picked earlier, but from early spring and late autumn. The quality and flavor of young leaves harvested in cold seasons such as winter are better.
The above is the knowledge sharing about the planting technology of kale, which is a kind of vegetable with cabbage, cabbage and so on, which is very good and sweet. Kale also has a high nutritional value, and the nutritional content is very high. Kale is a biennial herb and a variant of cabbage. When planting kale, a lot of things need to be paid attention to, such as watering, disinfestation, sun and rain shading and so on.
- Prev
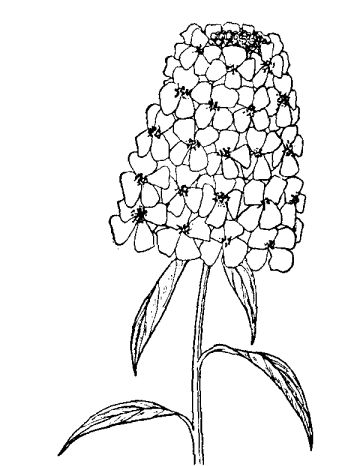
Cultivation and planting techniques of Fragrance Quji Flower
[family genus] Cruciferae, flexion flower genus. [form] Annual erect herbs, much branched, 15-30 cm tall, pilose. Leaves opposite, oblanceolate to spatulate, 3mm long, apex obtuse, with a few large and irregular obtuse teeth. The flowers are white and fragrant. 4 petals
- Next

Cultivation and planting techniques of mallow
[Alias] Little hollyhock, chessboard flower, potato banana flower. [Family] Malvaceae, Malvaceae. [Description] Biennial herb, plant height 60--100 cm, stem erect, branched, coarsely hairy. Leaves alternate, cordate or reniform, 7-13 cm in diam., margin obtusely toothed, veins palmate
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

