Cultivation and propagation methods of lily of the valley
[alias] Jun Yingcao, Cao Yuling.
Liliaceae, Liliaceae.
Herbs perennial, up to 30 cm tall, underground with transverse and branched rhizomes. Leaves 2murmur3: basal and erect, elliptic or oblong-ovoid, 13-15 cm long and 7. 5 cm wide, apex acute, petiole narrow and decurrent in sheath-like embrace, with several sheath-like membranous scales outside. The scales are drawn from the armpit, the top is slightly curved, and the raceme is skewed to one side, with 6-10 flowers, milky white and fragrant. The florescence is from April to May. The berries are globose and red when ripe.
[varieties, forms and varieties] the main cultivated varieties are: var.fortuneiBailey: large flowers and leaves; pink lily (var.roseaHort.): pink stripes on perianth; double-petal lily (var. Less oiificansWittm.): flowers double; flower lily (var.variegataHort.): yellow stripes on leaves.
[origin and distribution] this species is native to the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, is common in Asia, Europe and North America, and is wild in the forest region of northeast China and the Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi Province.
[habit] sexual preference for semi-overcast, humid environment, good cool, avoid heat. It is required to be rich in humus loam and sandy loam. Withstand the severe cold.
[reproduction] the rhizome is often divided and propagated, and the budded rhizome of the mother plant is cut into segments for planting in October. It can also be divided into sprouts for planting.
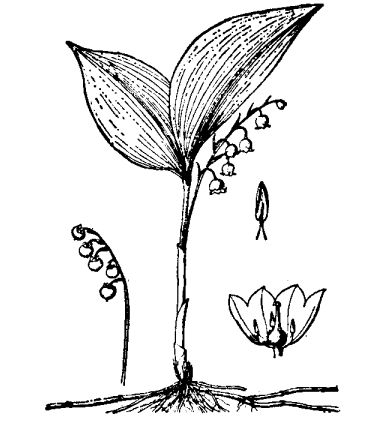
[cultivation] it is better to plough deeply and fertile in the planting land of lily of the valley. After 3-4 years of planting, you have to change the land and replant, or rotate with other flowers, the growth is better. For promoting cultivation, the root crown was cut in autumn and placed in 2-3 ℃ chamber. After 2-3 weeks of dormancy, the upper pot was placed in the leeward and sunny place, and moved into the greenhouse 5 weeks before the required flowering period. First, properly watering, placing in the dark, keeping 12-14 ℃, after 10 ℃ 15 days, room temperature rose to 20 ℃, base temperature 22 ℃, and increased watering and topdressing, flowering after 3 weeks. If the cultivation is not given low temperature and darkness first, it is often unable to germinate or the scape does not grow well with the leaves, which hinders the ornamental.
[use] the plant is short and the flowers are fragrant, so they should be used as flowers under the forest, or planted on the edge of the forest or on the lawn slope. It can also be used for potted plants and cut flowers. The whole herb is used in medicine to strengthen the heart, promote diuresis and treat congestive heart failure.
How to propagate and cultivate lily of the valley, and the methods of propagation and cultivation of lily of the valley
Lily of the valley plant is short, elegant and beautiful, fragrant and pleasant, is an excellent potted ornamental plant, usually used in flower beds, can also be used as ground cover plant, its leaves are often used as flower arrangement material. There are milky white, pink and variegated leaves and other varieties. At the beginning of autumn, the red fruit is delicate and attractive. So how to propagate and cultivate the lily of the valley? The following is to introduce the methods of breeding and cultivation of lily of the valley.
How to propagate and cultivate lily of the valley, propagation and cultivation methods of lily of the valley
1. Reproduction
Lilia lanceolata is usually propagated mainly by ramet, and seed reproduction can also be carried out. The best time for ramet propagation is in spring and autumn. There are buds of different sizes on the rhizome of the lily, and each terminal bud should be cut off with a rhizome for cultivation.
Seed propagation can be carried out in autumn and can be sown with seeds from ripe berries.
2. Soil cultivation
(1) site selection: select shady hillsides, forests and grasslands with thick humus. Contour line or Hengshan belt, the bandwidth is 1.5m, the belt spacing is 2m, and the row point distance is 50x20cm. Hole ploughing, soil crushing, suppression, in the shape of steamed bread.
(2) planting: deep ploughing and fertile soil is better. Need to change land and replant every 3-4 years, or rotate with other flowers. The row spacing of the planting plant is 2530 cm, each clump has 2 buds, and the depth of the covered soil is 5 cm 6 cm.
3. Potted plants
In November, fat and large rhizome buds were selected and stored in 3 ℃ ~ 5 ℃ for 14 days. Then they were taken out and planted in pots with 4 buds per pot.
Matters needing attention in planting lily of the valley
1. Native wild species often grow in groups and seldom invade by diseases and insect pests.
2. Planting in greenhouse is easy to breed diseases and insect pests, such as stem rot, anthrax, leaf spots and other fungal diseases.
3. Copper fungicides should be used regularly at ordinary times, and seed collection and reproduction from diseased plants are strictly prohibited. Once diseased plants are found, they should be destroyed and cleared immediately to prevent spread.
4. If you have brown spot, spray with 75% chlorothalonil wet powder 700 times.
The propagation method and cultivation management of the lily of the valley [propagation method] to divide the rhizome and the bulb at the end of the rhizome to propagate, that is, split propagation.
Ramet propagation: both in spring and autumn, and November is the best. There are young buds of different sizes on the rhizome. After the aboveground part withered in autumn, the rhizome was dug up, and each terminal bud was cut off with a section of rhizome to plant, and a new plant could be formed. The hypertrophic buds can blossom in the following spring, and the small ones will blossom after a year interval. Seeds washed from red-ripe berries in autumn can be sowed directly on the seedbed in the open field and germinated the following spring.
A ramet propagation was carried out in 2 to 3 years, and in late autumn, after the aboveground part of the plant withered, the young buds at the end of the rhizome were dug up and planted. After the ramet of the large bud, it blossoms in the next spring, and the small one blossoms the next year. There are flower buds and leaf buds at the top of the underground rhizome of the lily, the flower buds are obtusely conical and fat, and can bloom in the second year; the leaf buds are long conical, pointed and thin, and can only bloom in the third year. The first ramet had better leave 6 buds, including both flower buds and leaf buds, and it is better to plant them on deep ploughing and fertile ground. During the period from autumn to early March, the rhizome can be divided into several segments, each with 4 to 6 buds, the wound smeared with some plant ash or sulfur powder, and the hole is covered with soil of about 5 cm. For example, when breeding or introduction from a remote place, seeds can be used to propagate, sow in autumn and germinate the following spring.
[cultivation conditions] Lily of the valley prefers semi-shady, moist, cool environment, cold tolerance, avoid heat. As long as there are proper shady conditions, it will propagate rapidly by spreading roots. Shading and moist and fertile soil are important conditions for good planting. Humus and sandy soil are ideal, which are both fertile and hydrophobic. In modern factory greenhouse commodity production, pollution-free cultivation is adopted to improve the quality and yield of flowers, avoid excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer, and use less ammonium nitrogen fertilizer, which is worthy of attention and attention.
[cultivation management] it is better to plough deeply and fertile the planting land. Change the land and plant again after 4 years, or rotate with other flowers. The row spacing of the planted plants is 2530 cm, each clump has 2 buds, and the soil depth is 5 cm 6 cm. During the growing period, the soil should be kept loose and moist, and fully fermented topdressing should be applied in early spring and late autumn respectively. There is appropriate sunshine before flowering, shade tolerance after flowering, after defoliation at the end of autumn, to facilitate cultivation, cut the root crown, put it indoors at 2-3 degrees Celsius, after 2-3 weeks of low temperature treatment, take out the upper pot and place it to the shade, move it into a greenhouse at 12-14 degrees Celsius 5 weeks before the required flowering period, properly water and place in the dark, gradually turn to light after 10 days, the room temperature rises to 20 degrees Celsius, the bottom temperature is 22 degrees Celsius, and increase watering and topdressing. It can bloom in 3 weeks. If the cultivation is not given low temperature and darkness, it often does not germinate or although it germinates, the scape and leaves do not grow neatly, which hinders the ornamental. Plant more than 5 cm of covered soil and water thoroughly after planting. After germination in spring, topdressing once every 15 days, watering should be paid attention to during drought, fertilization should be stopped after flower stems are drawn out, pedicels should be cut off in time after flower withering, and topdressing for 1 or 2 times. After the shoot withered in late autumn, it was covered with rotten leaves and cow dung to protect the rhizome and its dormant buds to survive the winter. The ground should be planted every 3-4 years. Potted plants often choose fat and large rhizome buds, with 4-5 buds per pot, which need to be changed once a year. Promoting cultivation: the rhizome treated with low temperature is planted, and the temperature is maintained at about 18-20 ℃ during the whole cultivation period. Pay attention to fertilizer and water management, keep the soil moist, and blossom for about a month. After flowering, it is appropriate to cut off the stems and branches as soon as possible, so that nutrients are concentrated to supply the rhizome. When the open field is overwintering, the ground can be covered with grass or fine soil to prevent the cold. If the potted plant can dig out the budding rhizome in November and store it in 3 ℃-5 ℃ for 21 days, then take it out and plant it in a pot without making it see the light. The temperature is kept at 12 ℃ 14 ℃, and the temperature is controlled between 20 ℃ and 22 ℃ after the bud is unearthed. Then appropriate watering and topdressing. If it is properly cultivated, it can blossom later. If you do not give low temperature and dark treatment in advance, the growth of leaves will be uneven and flowers and plants will not germinate.
- Prev
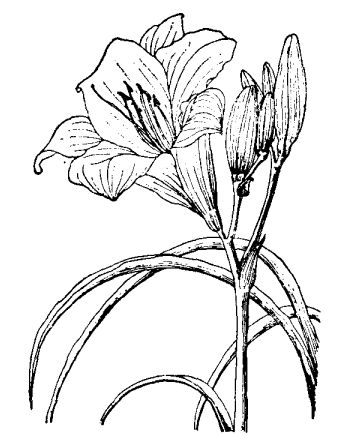
Introduction to the main species of Hemerocallis
1. North cauliflower (Hemerocallis, H.litioasphodclusL-LvaL.): leaf blade dark green, banded, 30 Murray 60 cm long, 0.5 Murray 1.5 cm wide, arched. 6-9 flowers in a terminal open panicle, pale lemon yellow
- Next

Cultivation and planting techniques of Violet
[alias] Osmanthus fragrans, grass violets. Cruciferae, Violet. [morphology] Subshrubby biennial herbs, stem base lignified, erect, sometimes branched, plant height 30-50 cm, whole plant gray stellate pilose. Leaves alternate, rectangular orbicular or oblanceolate, apex obtuse
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

