What are the two kinds of flowers belonging to the same genus as pineapple
1. Q. coccznea Moench. Also known as orange rose. Annual twining herb, up to 4 m long. Leaves alternate, ovate, entire, apex acute or acute, base cordate, petiole as long as leaf blade. Cymes axillary, with 3^6 flowers. Corolla salverform, orange-red, throat yellow, crown margin 5-lobed. Capsule small, oblate, ca. 5 mm in diam., seeds ovoid or subglobose. Native to tropical America.
2. Q.sloterz House_: also known as big flower, big red and palm leaf. This species is a hybrid of P. pinnata and P. rotundifolia. Annual twining herb. Leaves alternate, broadly triangular-ovate, palmate, lobes 7 - 15 branched, apex long acute; petiole and leaf blade equal. Cymes axillary, with 1-3 flowers. Pedicel stout, corolla salverform, deep red, ca. 3-5 cm long. Capsule conical or globose, smooth; seeds l--4, puberulent, blackish brown. Seedling early that is, rapid growth, flowering, plant robust and powerful.
Knowledge and planting exchange of flowers
Flowers have two meanings: broad sense and narrow sense. In a narrow sense, flowers refer to herbs with ornamental value. Such as impatiens, chrysanthemum, a bunch of red, cockscomb, etc.; in a broad sense, in addition to ornamental herbs, flowers also include herbaceous or woody ground cover plants, flowering shrubs, flowering trees and bonsai, such as Ophiopogon japonicus, sedum, tufted ground cover plants, plum blossom, peach blossom, rose, camellia and other trees and shrubs. In addition, tall trees and shrubs distributed in the south, moved to the cold regions of the north, can only be used as potted plants in greenhouses, such as magnolia, Indian rubber trees, and palm plants are also included in the broad sense of flowers.
Flower definition
Flowers have two meanings: broad sense and narrow sense. In a narrow sense, flowers refer to herbs with ornamental value. Such as impatiens, chrysanthemum, a string of red, cockscomb, etc.; in a broad sense, flowers not only have ornamental value of herbs, but also include herbaceous or woody ground cover plants, flowering shrubs, flowering trees and bonsai, such as Ophiopogon, Sedum, tufted Fulukao and other ground cover plants.
Flowers in a narrow sense
The mature performance of plants, with a variety of flowers, with ornamental effect.
Classification of flowers and plants: herbs: perennial herbs, annual herbs.
Woody: divided into trees and shrubs
Flowers in a broad sense
In addition to ornamental herbs, herbaceous, woody ground cover plants, flowering shrubs, flowering trees, bonsai and greenhouse ornamental plants.
Bopomofo: hubbuzhu
Edit the use of the flowers in this paragraph
In modern society, people often plant, buy and wear flowers in various ways because of their pleasant appearance and fragrance. Around the world, people use flowers in a variety of activities and occasions throughout their lives:
Used to celebrate new life or religious baptism
Used as a corsage or button flower at social gatherings or festivals
Used to express love or respect
Used for wedding decoration
For home decoration
To be used as a souvenir gift at a farewell or welcome banquet to place thoughts.
Used in funerals to express mourning and to worship or worship gods.
explain
1. Flowers and plants.
two。 Chinese painting with flowers and plants as the theme.
An overview of flowers
In a popular way
"flower" is the reproductive organ of a plant, which refers to the ornamental plant with beautiful posture, bright color and fragrant smell, and "Hui" is the general name of grass. It is customary to include shrubs with ornamental value and small trees that can be potted, collectively referred to as "flowers".
Classification of flowers
Overview
There are a wide range of flowers, including not only flowering plants, but also moss and ferns. Its cultivation and application methods are also varied. Therefore, because of the different basis, there are many methods of flower classification.
According to ecological habits
Classification according to ecological habits
This classification method is based on the life form and ecological habits of flowers and plants, and it is the most widely used.
Open field flowers
That is, under natural conditions, the whole growth process is completed without the need for protected cultivation. Flowers in the open field can be divided into three categories according to their life history.
⒈ annual flowers.
A plant that completes its life cycle in a growing season. That is, from sowing to flowering, fruiting and dying are all completed in one growing season. Generally sow in spring, grow in summer and autumn, blossom and bear fruit, and then die, so annual flowers are also called spring sowing flowers. Such as Fengxianhua, cockscomb, zinnia, half lotus, marigold and so on.
⒉ biennial flowers.
A flower that completes its life cycle in two growing seasons. Only vegetative organs grew at that time, but flowered, fruited and died later. This kind of flowers are usually sown in autumn and blossom in the following spring. Therefore, this kind of flowers are often called autumn sowing flowers. Such as colorful carnation, violets, kale, chrysanthemum and so on.
⒊ perennial flowers.
Individuals who live for more than two years can blossom and bear fruit many times. According to the morphological changes of the underground part, it can be divided into two categories:
⑴ perennial root flowers: the underground part is normal and does not have metamorphosis. Such as peony, hairpin, day lily and so on.
⑵ bulbous flowers: metamorphosis and hypertrophy of underground parts. According to its abnormal shape, it can be divided into the following five categories
①: bulbs, underground stems in the shape of fish scales. Those with a papery skin are called leathery bulbs, such as daffodils, tulips and Zhu Dinghong. The outer part of the scale without outer covering is called skinless bulb, such as lily.
②: bulbs. The underground stem is spherical or oblate, with a leathery outer skin. Such as Gladiolus, Champagne and so on.
③: rhizome. The underground stem is hypertrophic and root-shaped, with obvious nodes above, and new buds are born at the top of the branches, such as canna, lotus, water lilies, hairpins and so on.
④: tubers. The underground stem is irregular block or strip, such as calla lily, cyclamen, paulownia, evening jade and so on.
⑤: block root class. The underground taproot is hypertrophic and lumpy, and the root system grows from the end of the tuber root, such as Dahlia.
⒋ aquatic flowers
Flowers that grow in water or marshes, such as water lilies, lotus flowers, etc.
⒌ rock flowers
Refers to the flowers with strong drought tolerance and suitable for cultivation in the rock garden. It is often used in gardens. Generally, subshrubs with persistent roots or Lignification at the base, as well as flowers such as ferns and other damp flowers. Planting and cultivation of garden flowers
[cultivation measures]
For some annual flowers or plants, the method of staging or can be used to make the flowering early and late. The flowering period can also be controlled by pruning, coring and other measures. If the stump branches are often cut off, they can blossom again after the branches are renewed, and the flowering can be delayed by picking the heart before flowering.
[temperature regulation]
Most flowers blossom ahead of time by heating up in winter. For flowers and trees that bloom continuously in summer, such as jasmine, heating and budding are often used to make them bloom ahead of time in spring, and heating in time before cooling at the end of autumn can prolong the flowering period. For the flowers and trees which were still dormant before the temperature rose in early spring, the artificial low temperature (1 ~ 4 ℃) could prolong the dormancy period and delay the flowering. For budding or blooming flowers, they can also be put into a cold room of 2-5 ℃ to slow down plant metabolism and delay flowering. Some flowers that stop growing and do not blossom in extreme heat, such as hanging the golden bell upside down, can be promoted to blossom continuously by taking cooling measures in the high temperature season. Making use of the induction effect of low temperature on the flowering of some plants, the newly germinated seeds or seedlings of 2-year-old flowers originally sown in autumn were treated with low temperature so that they could blossom in the same year through vernalization. The temperature and time required by different flower species or vernalization treatment are different, and 1: 2 ℃ is generally the most effective.
[light adjustment]
It includes different methods such as adding light, shading and reversing light and dark. In order to make long sunshine flowers blossom in autumn and winter with short natural sunshine, artificial light can be added for 3 to 4 hours after sunset, supplemented by appropriate heating; delayed flowering, such as shading with black for several hours during the day, can postpone flowering. For short-day flowers, such as poinsettia and poinsettia, they can blossom early if they are shaded for several hours in the evening or in the morning; on the contrary, if the light is increased artificially for several hours, the flowering can be delayed. In addition, for flowers with nocturnal flowering habits, such as epiphyllum, shading during the day and pedestrian lighting at night can make them blossom during the day.
[water and fertilizer control]
Under dry conditions, the flower buds of some bulbous flowers still stay in the bulbs after dormancy and differentiation, and do not grow and blossom until water supply. Therefore, sooner or later flowering can be controlled by adjusting the time of water supply. Some flowers and trees have differentiated at the turn of spring and summer, such as man-made drought conditions, leading to early defoliation or leaf peeling, and then spraying water supply, often blooming for the second time in the same year. For the herbaceous flowers that bloom one after another, the flowering period can be prolonged by applying one more time at the end of flowering, and the flowering will often be delayed if too much nitrogen fertilizer is applied in the early stage of flower growth. After the vegetative growth of the plant reaches a certain degree, it can blossom earlier.
[application of growth regulators]
Gibberellin, ethephon and dwarf are the most commonly used growth regulators in flowering control, among which gibberellin can promote flowering significantly. It is often used to deal with the dormant buds of peonies, daffodils, orchids, etc.
In addition to the above measures, methods can also be used to peel off the lateral buds so as to accelerate the flowering of the main buds and remove the main buds to promote the flowering of the lateral buds.
Some of the various measures for florescence control play a leading role, some play an auxiliary role, and can be used at the same time or successively. It should be selected according to different plant species and varieties, and attention should be paid to the cooperation of other corresponding measures and environmental conditions.
Greenhouse flowers
Refers to flowers native to tropical, subtropical and warm areas of the south. Cultivation in cold areas of the north must be cultivated in a greenhouse or protected in a greenhouse in winter. It can be divided into the following categories:
⒈ annual or biennial flowers. Such as melon and leaf chrysanthemum, balsam flower, fragrant pea and so on.
⒉ perennial flowers. Such as African chrysanthemum, gentleman orchid and so on.
⒊ bulbous flowers. Such as cyclamen, Zhu Dinghong, big rock tree, calla lily, flower leaf taro and so on.
According to their ecological habits, ⒋ Orchidaceae can be divided into:
⑴ terrestrial orchids: such as Cymbidium, Cymbidium, Jian Orchid, Han Orchid, Mulan, Chunjian and so on.
⑵ epiphytic orchids: such as Dendrobium, Magnolia, Paphiopedilum and so on.
⒌ succulent plant: refers to a plant with well-developed water storage tissue in its stems and leaves, showing a hypertrophic, succulent metamorphosis. Including cactus, crassulaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Compositae, pineapple, tequila and other families.
⒍ ferns. According to the different viewing methods, it can be divided into the following four categories:
Green ferns in ⑴ garden. Such as green cloud grass, Alsophila spinulosa. Among them, Alsophila spinulosa, also known as tree fern, is the largest fern, up to more than 10 meters high. It is an ancient group, an endangered species in China, and a first-class protected plant in China. In addition, Huaiyeping and Manjianghong are good materials for water surface greening.
⑵ potted foliage ferns. Such as stone pine, black fern, centipede grass, iron fern and so on. Among them, stone pine, kidney fern and iron fern are important materials for cutting flowers and leaves.
⑶ hanging ferns. Such as kidney fern, nest fern and so on.
⑷ mountain stone bonsai ferns. Such as Selaginella officinalis, fan fern. Among them, Dryopteris is the smallest among ferns, only a few centimeters in size.
⒎ insectivorous plants. Such as pitcher plant, bottle grass and so on. In some cut flower art, it is often used as a material for artistic flower arrangement.
⒏ (Pyraceae). Such as water tower flowers, wind pears and so on.
⒐ is a plant of the family paulownia. Such as sunflower, brown bamboo, pocket coconut and other foliage flowers.
10. Flowers and trees include poinsettia, variegated trees and so on.
11. Aquatic flowers such as Wang lotus, tropical water lilies and so on.
Classification according to garden use
1. Flowers in flower beds
Refers to one or two-year-old open-field flowers that can be used to decorate flower beds. For example, there are tricolor pansy and carnation that bloom in spring; balsamines and daisies are often planted in flower beds in summer; a string of red, marigold and September chrysanthemums are selected in autumn; and kale can be properly arranged in flower beds in winter.
two。 Potted flowers
It is a potted flower that decorates the interior and garden in the form of potted plants. Such as papaya Begonia, Fusang, asparagus, poinsettia, kumquat and so on.
3. Indoor flower
It refers to a kind of flowers that carry out the dark reaction process of photosynthesis through C4 pathway. General foliage plants can be used as indoor ornamental flowers. Such as fortune tree, Brazilian wood, Hulk, green basket, colorful corn and so on.
4. Cut flowers
⑴ perennial root class: such as African chrysanthemum, all over the sky star, crane orchid.
⑵ bulbs: lilies, tulips, calla lilies, fragrant snow orchids, etc.
⑶ woody cut flowers: such as peach blossom, plum blossom, peony, rose, rose, etc.
5. Foliage flowers
It is mainly determined according to the viewing part. Such as Hulk, iron tree, fern and so on.
6. Flowers in the shade shed
In landscape design, flowers growing in the shade of a pavilion. Ophiopogon, safflower and ferns can all be used as shade flowers.
7. Positive flowers
Flowers that need enough sunlight to blossom are called positive flowers. Positive flowers are suitable for growing in full light and strong light. If the light is not enough, it will grow poorly, blossom late or cannot blossom, and the flower color is not fresh, the aroma is not strong. Like positive flowers, such as:
(1) Spring flowers: plum blossom, daffodil, spring, peach blossom, white orchid, purple magnolia, Qionghua, stick stem begonia, papaya begonia, weeping begonia, peony, peony, clove, rose, bauhinia, brocade flower, forsythia, Yunnan yellow flower, sparrow flower, cyclamen, hyacinth, tulip, calla lily, Changchun chrysanthemum, geranium, primrose, melon leaf chrysanthemum, dwarf morning glory, Yu beauty, goldfish grass, beauty cherry, etc.
(2) Summer and autumn flowers: White jade, jasmine, Milan, Jiuli incense, woody night incense, sweet-scented osmanthus, magnolia, Fusang, hibiscus, hibiscus, crape myrtle, oleander, triangle flower, pineapple, June snow, dahlia, five-colored plum, canna, sunflower, hollyhock, Fulang flower, chicken egg flower, safflower onion, chrysanthemum, a bunch of red, cockscomb, impatiens, half branch lotus, wild goose red, daisy, marigold, chrysanthemum, chrysanthemum, Lotus, water lilies, etc.
(3) Winter flowers: wax plum, poinsettia, silver willow, tea plum, freesia and so on.
(4) Fruit trees: Mengshan papaya, ginkgo, pomegranate, kumquat, orange, grape, loquat, jujube, persimmon, kiwifruit, figs, Koba, firethorn, winter coral and so on.
(5) vines: wisteria, Lingxiao, rose, wood incense, honeysuckle, Parthenocissus, morning glory, pineapple, etc.
(6) foliage: five-needle pine, black pine, brocade pine, cedar, dragon cypress, shackle wood, poplar, Tamarix, red maple, palm, big-leaf yellow poplar, rubber tree, cycad, dragon blood tree, plantain, variable-leaf tree, false-leaf tree, colored leaf grass and so on.
(7) succulent: cactus, triangle dwelling, cactus, cactus mountain, gemstone flower, fluffy cactus, etc.
Classified by economic use
1. Medicinal flowers
For example, peony, peony, Platycodon grandiflorum, morning glory, Ophiopogon, cockscomb, impatiens, lily, Fritillaria and Dendrobium are important medicinal plants. In addition, honeysuckle, chrysanthemum and lotus are common traditional Chinese medicines.
two。 Spices and flowers
Fragrant flowers are widely used in food, light industry and other fields. For example, sweet-scented osmanthus can be used as food spice and wine, jasmine and magnolia can be smoked tea, chrysanthemum can be used to make high-grade food and dishes, and Magnolia, rose, daffodil, wax plum and other flavors can be extracted, among which the rose oil extracted from roses is known as "liquid gold" in the international market. Its value is more expensive than gold, and only a rose bud in the market is worth 6 cents.
3. Edible flowers
Use the leaves or flowers of flowers to eat directly. Such as lilies, can be used as cut flowers, but also edible; chrysanthemum brain, cauliflower can be used as green seedlings, but also edible.
Classification according to the origin of flowers
Climatic type
A Chinese climatic type
Also known as the climate type on the east coast of the mainland. This climate type can be divided into warm type and cool type because of the difference of temperature in winter.
1. Warm type (low latitude) such as Chinese daffodils, Chinese carnation, camellia, rhododendron, lily and so on.
two。 Cool type (high latitude) such as: chrysanthemum, peony, purse peony, sticking peony.
2 European climatic type
Also known as the climate type on the west coast of the mainland, such as: pansy, daisies, kale, violets and so on. This kind of flowers are usually cultivated biennially in our area, that is, they are sown in summer and autumn and bloom in the following spring.
Tri-Mediterranean climate type
Because of the dry summer climate in these areas, perennial flowers often form bulbous roots. Such as hyacinth, freesia, tulip, cyclamen, sorrel and so on.
The Mexican climate type, also known as the tropical plateau climate type, is found in tropical and subtropical alpine areas. Yunnan Province of China also belongs to this type. Its original flowers are: Dahlia, poinsettia, marigold, Yunnan camellia, rose and so on.
Five tropical climatic flowers native to the tropics are cultivated in greenhouses in temperate zones, and annual flowers can be cultivated in open fields during frost-free periods:
1. Tropical famous flowers originating in Asia, Africa and Oceania are: cockscomb, tiger tail orchid, colored leaf grass, variable leaf wood and so on.
two。 The famous tropical flowers originating in Central and South America are: candle, Catharanthus roseus, Canna, Petunia and so on.
Six desert climate type
Most of these areas are deserts in barren land, mainly serous plants.
1. Aloe. The main varieties planted in the Science and Technology Park of Shuyang Agriculture and Forestry Bureau are Curacao, zebra, Muli, Yuanjiang, soap, and so on.
two。 Cactus. There are two kinds of common ornamental cactus and edible cactus.
3. Single tree. Also known as green jade tree. Originally from tropical South Africa, it can be cultivated in open field in Southwest and South China.
4. Tequila. Sisal, which is a common green tree species, is the same genus.
Climatic type of seven cold zones
Mainly distributed in Alaska and Siberia. The climate in these areas is long and cold in winter and short and cool in summer. The plant growth period is only 2-3 months. Because of this kind of climate, the days are long and windy in summer, so the plants are low and grow slowly, often in the shape of a cushion. The main flowers are: fine leaf lily, gentian, snow lotus.
Classify according to natural distribution
Divided into tropical flowers, temperate flowers, cold zone flowers, alpine flowers, aquatic flowers, rock flowers, desert flowers.
There are two interpretations of "flowers" in a narrow sense and a broad sense. In a narrow sense, "flower" refers to herbaceous plants with ornamental value, such as chrysanthemum, impatiens and so on. In a broad sense, "flower" refers to all flowers, stems, leaves, fruits or roots that have ornamental value in shape or color. So in a broad sense, flowers include not only herbs, but also trees, shrubs, vines and ground cover plants.
Classify according to the amount of water needed
Drought-resistant flowers: such as cactus, sedum, Yushu, lotus, tiger tail orchid, aloe and purslane, etc. These flowers adapt to the dry and hot growth environment, the leaves are often metamorphosed, some even degenerate, and the flowers have the structure of storing water, so they can endure drought. The amount of water must be less, and the principle of "better dry than wet" should be grasped to keep the basin soil dry, otherwise it will easily cause root or stem and other organs to rot, and in serious cases, it will also lead to death.
Semi-drought-tolerant flowers: such as plum blossom, camellia, rhododendron, wax plum, geranium, asparagus, pine and cypress and other plants. Most of the leaves of these flowers and plants are herbaceous or waxy, or the branches and leaves are needle-like. When watering, we should grasp the principle of "dry and thoroughly irrigated", that is, wait until the surface of the basin soil is all dry before watering.
Mesophytic flowers: most kinds of flowers belong to this type. Such as pomegranate, rose, jasmine, Fusang, Milan, crane orchid, gentleman orchid, ornamental bamboo and 2012 grass flowers, perennial flowers and so on. They grow well in moist soil and grow poorly in over-wet or over-dry soil, so they should grasp the principle of "dry and wet" in watering. The so-called "see dry" means that the surface soil of the basin should be watered when the color of the surface soil becomes lighter; "see wet" means that each watering just irrigates all the basin soil and cannot be poured into a "half of the water" that is wet up and down. This watering method can not only meet the water needed for the growth and development of this kind of flowers, but also ensure the oxygen needed for root respiration, which is conducive to the healthy growth of flowers.
Wet flowers: such as Guangdong evergreen, wind grass, calla lotus, Saxifraga, Artemisia cattail, tortoise back bamboo, ornamental fern and so on. They require that the growing environment should have a large amount of water in order to grow and develop well, so watering should grasp the principle of "rather wet than dry", but not stagnant water, otherwise it will often wither and injure the branches and leaves.
Aquatic flowers: such as lotus, water lily, hyacinth, etc., their roots or stems must be in the water to survive, therefore, we must create conditions to meet their requirements.
Classification of flowers
Classified according to biological characteristics
Different flowers have different biological characteristics. They have different requirements for light, temperature, moisture and other environmental conditions, and it is customary to divide flowers into the following four types according to these differences.
I. positive and negative-tolerant flowers
(1) most positive flowers, such as rose, jasmine, pomegranate and so on, need sufficient sunlight. This kind of flower is called Xiyang flower. If the light is not enough, it will be stunted, developed late or can not be developed, and the flower color is not fresh and the aroma is not strong.
(2) shade-tolerant flowers, such as jade hairpin, hydrangea, azaleas, etc., only need weak scattered light to grow well, which is called shade-resistant flowers. If they are often exposed to the sun, they cannot grow and develop normally.
Second, cold-resistant and temperature-loving flowers
(1) Cold-resistant flowers, such as rose, marigold, carnation and pomegranate, are generally able to withstand the short-term low temperature of minus 3 Mel 5 °C, and they can survive the winter outdoors in winter.
(2) temperature-loving flowers, such as dahlias, canna, jasmine, begonias, and so on, generally can only grow normally under the humidity of 15 °C and 30 °C. they are not tolerant to low temperatures and need to spend the winter indoors with higher temperatures.
Long-day sunshine, short-day sunshine and neutral flowers
(1) long-sunshine flowers, such as eight immortals, melon-leaf chrysanthemum, etc., need sunshine for more than 12 hours a day, which is called long-sunshine flowers. If the requirements of this particular condition can not be met, there will be no bud development.
(2) short-day flowers, such as chrysanthemums and clusters of red flowers, need less than 12 hours of sunshine every day. After a period of time, they will be able to develop buds. If the sunshine time is too long, there will be no bud development.
(3) Neutral flowers such as geranium, carnation, begonia, Chinese rose, etc., are not sensitive to the length of sunshine every day. Whether in long or short days, they will normally bud and develop, which is called neutral flowers.
Aquatic, xerophytic and moist flowers
(1) Aquatic flowers, like water lilies, must live in water in order to grow normally. They are called aquatic flowers.
However, due to the development of science and technology, hydroponic flowers are developing in the Chinese market. Hydroponic flowers are a new generation of high-tech agricultural projects that adopt modern bioengineering technology and use physical, chemical and biological engineering means to domesticate ordinary plants and flowers so that they can grow in water for a long time. Hydroponic flowers are full of fragrance above and fish swimming below, which is hygienic, environmentally friendly and convenient, so hydroponic flowers are also known as "lazy flowers".
(2) xerophytic flowers, such as cactus and sedum, can grow normally with very little water, which is called xerophytic flowers.
(3) moist soil flowers, such as rose, gardenia, sweet-scented osmanthus, dahlia, carnation and other flowers, are required to grow in soil with high humidity and good drainage. Embellish soil flowers consume more water every day in the growing season, so we must pay attention to replenishing water to the soil in time to maintain a warm and moist state.
Flower cultivation methods
Planting includes transplanting and colonization. The method is the same, planting is no longer moving after planting, while transplanting is a cultivation measure before planting to change the planting distance for plants to meet their growth needs.
1. Transplant
The purpose of transplanting is to enlarge the row spacing of all kinds of seedlings, so that the seedlings can get enough nutrition, light and air. At the same time, the main roots of the seedlings are cut off during transplantation, which can make the seedlings produce more lateral roots and form developed roots, which is beneficial to their growth.
Before transplanting, the seedlings sown should generally be thinned between the branches to remove those that are too dense, thin or diseased. The sparse seedlings can also be planted separately. The seedlings planted in the ground were transplanted for the first time at 4 to 5 real times. Seedlings planted in pots are often transplanted when there are 1 or 2 true leaves. The distance between the rows of the transplanted plants depends on the size of the seedlings, the growth rate of the seedlings and the bed retention period after transplantation. The preparation of seedling bed for seedling transplanting is basically the same as that of sowing seedling bed. When transplanting, the soil should be dry and wet properly, and generally should be transplanted when the soil is dry, but when the soil is too dry, it is easy to wilt the seedlings. It should be watered on the border the day before planting, and the sandalwood should be moved when the upper grain absorbs water and does not stick to the hand. When the soil is wet, it is not only inconvenient to operate, but also the soil is hardened after planting, which is disadvantageous to the growth of seedlings. Do not press too tightly when transplanting, so as not to get hurt. When the soil particles sink with the water, they can be closely connected with the root system. It is better to transplant on a windless and cloudy day, and if the weather is sunny, bright and hot, it should be transplanted in the evening. Before transplantation, it is necessary to distinguish the varieties and avoid confusion. Cut off the main root when digging seedlings, do not hurt the roots, and transplant them with protective roots as far as possible. Digging seedlings and planting should be coordinated, along with digging and planting. If the wind is strong and the evaporation is strong, dig up the young Zhuo to cover and shade. The transplantation hole should be slightly larger to make the root stretch smoothly. The planting depth should be the same as the original planting depth, or a further depth of 1 cm to 2 cm. If it is too shallow, it is easy to lodge; if it is too deep, it will not develop well. Immediately after planting, it should be fully watered and re-watered to ensure sufficient quantity. In times of drought, we should plant and water at the same time. Shade should be provided at the initial stage of summer transplantation to reduce evaporation and avoid wilting.
two。 Colonization
Planting includes planting large seedlings, potted seedlings, stored bulbs, persistent root flowers and native flowers in places where they no longer move. Before planting, according to the needs of plants, improve soil structure, adjust pH, improve drainage conditions, general plants need fertile, loose and well-drained soil. Fertilizer can be mixed during soil preparation or applied to the bottom of the hole after digging. The distance between plants used in planting should be determined according to the adult size of flower plants or the requirements of planting. Digging seedlings, generally should take root soil, the soil is too wet or too cadres should not dig seedlings, how much soil depends on the size of the root system. When trees fall, there is no need to bring soil when they are planted during the dormant period. Evergreen flowers and trees and species that are not easy to transplant must bring complete clumps of mud and tie them up with grass ropes. When planting, holes should be opened, which should be larger and deeper than the root system or mud mass of the seedlings, and the stem base of the seedlings should be raised close to the soil surface. Then shovel the soil around the hole into the hole for about 2 / 3, shake the seedlings so that the soil particles and roots are closely connected, then press the soil outside the root system, and finally fill the hole with loose soil to make it flat and slightly concave with the ground. Water twice immediately after planting. After the grass flower seedlings are planted, they should be watered again the next day. Bulb flowers generally do not need to be watered at the initial stage of planting, but should be watered once if it is too dry. Large persistent root flowers and native flowers should be combined with hate pruning, root damage, rotten roots and withered roots should be cut off. After the seedlings are planted, props should be set up, or rope traction should be set up at three diagonal angles to prevent dumping.
Distribution of Flower growing areas in China
The advantages of planting flowers in China are shown in germplasm resources, climate resources, labor resources, market advantages, flower culture advantages and so on. During the 10th five-year Plan period, the area of flower cultivation in China has reached 640000 hectares, an increase of 326.7 percent over the 150000 hectares at the end of the Ninth five-year Plan period. Among them, the provinces with an planting area of more than 50,000 hectares are Henan, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Guangdong, and Hebei, Shandong, Hunan and Gansu provinces with more than 20,000 hectares. The area of flowers in China accounts for 1/3 of the total area of flower production in the world. In 2005, there were 2586 flower markets and 64908 enterprises, including 8334 large and medium-sized enterprises with a planting area of more than 3 hectares or an annual turnover of more than 5 million yuan, 1251313 flower farmers, 4401095 employees and 132318 professional and technical personnel. At the end of the 10th five-year Plan period, the national key flower producing areas were initially formed, and the variety structure was further optimized. The regionalization industry has formed southern tropical and subtropical flower producing areas focusing on Yunnan, Sichuan, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Hainan, southern tropical foliage plant producing areas focusing on Guangdong and Fujian, ornamental seedling producing areas focusing on Zhejiang, Sichuan, Henan and Hebei, northern flower producing areas mainly in Beijing, Shandong and Hebei, and northeast flower producing areas centered in Liaoning.
Flower language
Flower language means that people use flowers to express people's language, express certain feelings and wishes, gradually agreed to form under certain historical conditions, and is recognized by a certain range of people as a form of information exchange. Flower appreciation needs to understand flower language, which constitutes the core of flower culture. In flower communication, flower language is silent, but it is more moving than sound at this time, in which the meaning and emotional expression are more than words. Do not want to express their feelings and do not understand the language of flowers to send flowers to others, the result will only lead to other people's misunderstanding.
Flower language first originated in ancient Greece, at that time not only flowers, leaves, fruit trees have a certain meaning. It is recorded in Greek mythology that the god of love created roses when he was born, and roses have become synonymous with love since that time. Hua Yu in the early 19th century
Originated in France and then became popular in Britain and the United States, it was created by some writers and was mainly used to publish gift books, especially for upper-class ladies to read at leisure at that time.
The real flower language prevailed in the French royal period, when the aristocrats sorted out the folk materials about flowers, including the information of the flower language, which was perfectly reflected in the garden architecture in the later stage of the court.
The acceptance of flower language by the public was in the middle of the 19th century, when the social atmosphere was not very open, and it was embarrassing to express love in public, so the flowers given by lovers became the messengers of love.
With the development of the times, flowers have become a social gift, and a more perfect flower language represents the intention of the giver.
- Prev
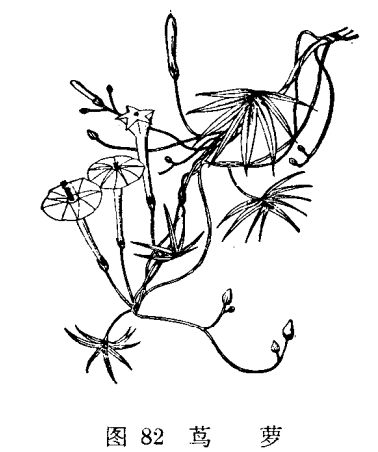
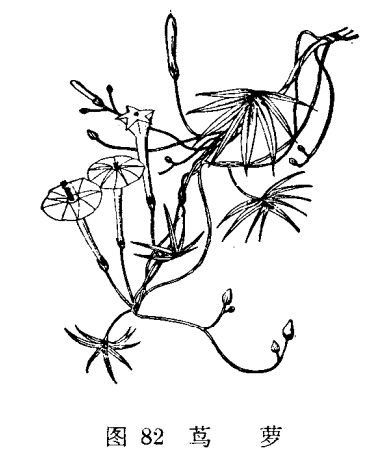
How to cultivate and reproduce pineapple
[alias] feather leaf pineapple, pineapple pine, dragon flower, dragon grass, brocade screen seal. [family genus] Convolvulaceae, genus Prunus. [form] annual weak twining herbs with smooth stems up to 4 meters long. Leaves alternate, pinnatifid, 4-7 cm long, lobes striate, basal two lobes again. Cymes axillary
- Next
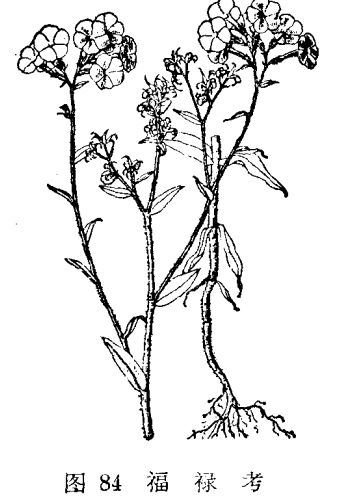
The main producing areas and planting methods of Fulukao
[alias] oleander, plum blossom, Platycodon grandiflorum. [families and genera] Carpinaceae, Phlox. Annual herbs, plant height 15-45 cm. Stem erect, much branched, with glandular hairs. Basal leaves opposite, others occasionally alternate, broadly ovate, rectangular orbicular to lanceolate. Cymes terminal
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

