Control of Spodoptera litura in Brazil
Spodoptera litura is a quarantine Lepidoptera pest in the world, which has spread rapidly from south to north in China in recent years. The research shows that the sugarcane flat moth is harmful not only to Brazilian iron (wood), but also to many kinds of flowers, such as wealth tree, dragon blood tree, Hainan iron, pocket coconut, poinsettia, iron tree, palm bamboo and so on. At the same time, because sugarcane flat moth is a stem-boring pest and grows in flower plants, it is difficult to kill pesticides and difficult to control, so this pest spreads quickly and is one of the main destructive pests in flower production at present. The sugarcane moth eats the epidermis of Brazilian iron with its larvae, and all the transport tissues are destroyed, leaving only a thin layer of outer skin and xylem. The bark and xylem are easily separated, and those with mild harmful symptoms are not easy to detect. It will seriously hinder the normal growth and development of the plant, causing the plant to dry up, not sprouting, or even the whole plant to die.

Morphological characteristics. The adult is yellowish brown, the forewing is dark brown, there are 1 black spot in the middle chamber and the posterior edge, the hind wing is yellow-brown, the posterior edge has long hair, the egg is light yellow and round, the larva is about 30 mm long, the head is reddish brown, there are rows of rectangular spots on the back of the body, there are hair flakes on the side of the body, and the pupa is brown. Life habits. It occurs about 5 to 6 generations a year in Guangdong and other places, and 3 to 4 generations a year in the northern region. The larvae overwintered in the pot soil of potted flowers in greenhouse and greenhouse. In the following year, when the temperature and humidity are suitable, the larvae crawl on the flowers, generally eating the cortex and sometimes into the xylem epidermis, and a few larvae eat the plants into the pith from the wound. The larvae have about 7 instars and the larval stage is more than one month. The mature larvae are mostly on the top of the stake in summer and cocoon and pupation in the soil in autumn. The pupal period is about 15 days. Adults have the habit of supplementary nutrition. The eggs are scattered or concentrated into lumps, and the egg period is about 4 days. The newly hatched larvae are silking and sagging, that is, drilling into the cortex, especially the Brazilian iron stake which has been more than 3 years old. The prevention and cure method ① strengthens the quarantine. We must recognize the harmfulness of this pest, strengthen the quarantine management of the exchange and transportation of flowers and trees, strictly prohibit the expansion and spread of Brazilian iron stakes with insects, and burn them in time when pests are found. ② destroys the insect source. The soil exchange work of potted Brazilian iron in large greenhouse and greenhouse must be strengthened, and the overwintering larvae and pupae in the pot soil should be eliminated by spraying in time to prevent their reproduction and development. ③ chemical control. To master the incubation period of each generation of eggs, spray the stem with 1500 times of 20% quinathion EC or 1000 times of 50% fenitrothion EC. Insect pests found in summer should be controlled by spraying in time. From autumn and winter to the beginning of spring, 1500 times of 20% quinathion EC, 1000 times of 50% phoxim EC, 1000 times of 50% fenitrothion EC, 1000 times of dichlorvos EC, 1000 times of 80% trichlorfon EC and 1000 times of 40% omethoate EC were sprayed every 7 days, or the stems were sprayed continuously for 2 to 3 times, or 1500 times of 75% phoxim EC and 1000 times of 40% methyl isophos emulsion were injected into the basin. 50% carbaryl powder 1 ∶ 200 times can also be used to mix soil. Sprinkled in the topsoil of flowerpot, once every 15 days, 2 to 3 times in a row, can kill the overwintering larvae. The control of Spodoptera litura in Brazil is a quarantine Lepidoptera pest in the world. It has occurred in all provinces and regions in the south, and has rapidly spread to the north in recent years. According to the investigation, in addition to harming Brazilian iron (wood), sugarcane flat moths also harm more than 50 kinds of flowers, trees and cash crops, such as rich trees, poinsettias, iron trees, pocket coconuts, Hainan iron, dragon blood trees, brown bamboo, and so on. Sugarcane moth is a stem borer, which can not be killed by pesticide spraying, so it is difficult to control, so this pest spreads quickly and is one of the main destructive pests in flower production at present. The sugarcane moth eats the epidermis of Brazilian iron with its larvae, and all the transport tissues are destroyed, leaving only a thin layer of outer skin and xylem. The bark and xylem are easily separated, and those with mild harmful symptoms are not easy to detect. It will seriously hinder the normal growth and development of the plant, causing the plant to dry up, not sprouting, or even the whole plant to die. The morphological characteristics of the adult are yellowish brown, the forewings are dark brown, there are 1 black spots in the middle chamber and the posterior edge, the hind wings are yellowish brown, there are long hairs on the trailing edge, the eggs are light yellow and round, the larvae are about 30 mm long, the head is reddish brown, there are rows of rectangular spots on the back of the body, and there are hairs on the side of the body. Pupa brown. Life habits occur for about 5 to 6 generations a year in Guangdong and other places, and 3 to 4 generations a year in the northern region. The larvae overwintered in the pot soil of potted flowers in greenhouse and greenhouse. In the following year, when the temperature and humidity are suitable, the larvae crawl on the flowers, generally eating the cortex and sometimes into the xylem epidermis, and a few larvae eat the plants into the pith from the wound. The larvae have about 7 instars and the larval stage is more than one month. The mature larvae are mostly on the top of the stake in summer and cocoon and pupation in the soil in autumn. The pupal period is about 15 days. Adults have the habit of supplementary nutrition. The eggs are scattered or concentrated into lumps, and the egg period is about 4 days. The newly hatched larvae are silking and sagging, that is, drilling into the cortex, especially the Brazilian iron stake which has been more than 3 years old. Http://www.yuhuagu.com prevention and control method ① strengthens quarantine. We must recognize the harmfulness of this pest, strengthen the quarantine management of the exchange and transportation of flowers and trees, strictly prohibit the expansion and spread of Brazilian iron stakes with insects, and burn them in time when pests are found. ② destroys the insect source. The soil exchange work of potted Brazilian iron in large greenhouse and greenhouse must be strengthened, and the overwintering larvae and pupae in the pot soil should be eliminated by spraying in time to prevent their reproduction and development. ③ chemical control. To master the incubation period of each generation of eggs, spray the stem with 1500 times of 20% quinathion EC or 1000 times of 50% fenitrothion EC. Insect pests found in summer should be controlled by spraying in time. From autumn and winter to the beginning of spring, 1500 times of 20% quinathion EC, 1000 times of 50% phoxim EC, 1000 times of 50% fenitrothion EC, 1000 times of dichlorvos EC, 1000 times of 80% trichlorfon EC and 1000 times of 40% omethoate EC were sprayed every 7 days, or the stems were sprayed continuously for 2 to 3 times, or 1500 times of 75% phoxim EC and 1000 times of 40% methyl isophos emulsion were injected into the basin. 50% carbaryl powder 1 ∶ 200 times can also be used to mix soil. Sprinkled in the topsoil of flowerpot, once every 15 days, 2 to 3 times in a row, can kill the overwintering larvae. Control methods of Spodoptera litura in Brazil
Spodoptera litura is a worldwide quarantine dangerous pest of Lepidoptera. It has occurred in all provinces and regions in the south, and has rapidly spread to the north in recent years. According to the investigation, in addition to harming Brazilian iron (wood), sugarcane flat moths also harm more than 50 kinds of flowers and economic crops, such as rich trees, poinsettias, iron trees, pocket coconuts, Hainan iron, dragon blood trees, brown bamboos, sweet taros, pineapples, lilies, orchids, goose palm wood, sugar cane, bananas, pineapples and so on. Sugarcane moth is a dry-borer pest, which can not be killed by pesticide spraying, so it is difficult to control, so this pest spreads quickly and has become one of the main destructive pests in flower production at present. The sugarcane moth eats the epidermis of Brazilian iron with its larvae, and all the transport tissues are destroyed, leaving only a thin layer of outer skin and xylem. The bark and xylem are very easy to separate, and those with mild harmful symptoms are not easy to detect. But in serious cases, it will hinder the normal growth and development of the plant, resulting in wood section drying up, not sprouting, or even the death of the whole plant, completely losing its ornamental value.
1. Morphological characteristics: the adult is about 9 mm, the body is yellowish brown, the forewing is dark brown, there are 1 black spot in the middle chamber and the posterior edge, the hind wing is yellow-brown, the posterior edge has long hair, the egg is light yellow, the egg is oval, the larva is about 30 mm long, the head is reddish brown, and there are rows of rectangular spots on the back of the body. there are hair patches on the side and pupa brown.
2. Life habits: there are about 5-6 generations a year in Guangdong and other places in South China, and 3-4 generations in the north. The larvae overwintered in the pot soil of potted flowers in greenhouse and greenhouse. In the following year, when the temperature and humidity are suitable, the larvae crawl on the flowers and eat quickly in the upper and lower sides of the cortex, sometimes into the xylem epidermis, and a few larvae eat hollow from the wound into the pulp of the wood section. The larvae have about 7 instars and the larval stage is more than one month. The mature larvae are mostly on the top of the stake in summer and cocoon and pupation in the soil in autumn. The pupal period is about 15 days. Adults have the habit of supplementary nutrition. The eggs are scattered or concentrated into lumps, and the egg period is about 4 days. The silking and drooping of the newly hatched larvae, that is, the damage caused by drilling the skin of wood piles, especially the Brazilian iron piles which have been more than 3 years old.
3. Prevention and control methods:
① strengthens quarantine inspection. We must recognize the harmfulness of this insect, strengthen the quarantine management of the exchange and transportation of flowers and trees, strictly prohibit the expansion and spread of Brazilian iron wooden piles with insects, and burn them in time when pests are found.
② destroys the insect source. The soil exchange of potted Brazilian iron in large greenhouse and greenhouse must be strengthened, and the overwintering larvae and pupae in the pot soil should be eliminated by spraying in time to prevent reproduction and development.
③ chemical control. Master the incubation period of each generation of eggs spray 1-2 times, you can use 20% quinathion EC 1500 times, or 50% fenitrothion EC 1000 times spray stem. When insect pests are found in summer, they should be sprayed in time, especially from autumn and winter to the beginning of spring, 1500 times with 20% quinathion EC, 1000 times with 50% phoxim EC, 1000 times with 50% fenitrothion EC, 1000 times with 80% dichlorvos EC, 8000 times with 80% trichlorfon EC and 1000 times with 40% omethoate EC. Spray once every 7 days, spray the stem 2-3 times continuously. Or pour it into the basin with 1500 times of phoxim EC and 40 times of methyl isophos emulsion, or mix the soil with 1000 times of 50% carbaryl powder and sprinkle it in the topsoil of the flowerpot and apply it every 15 days for 2-3 times in a row, which can kill the overwintering larvae.
- Prev
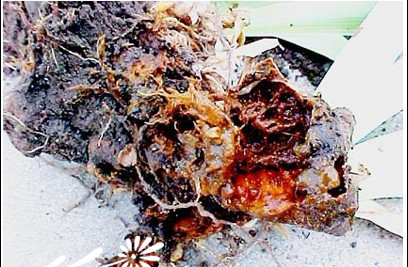
Control methods of bacterial soft rot of Iris
Bacterial soft rot is one of the most common diseases of Iris, which often occurs in both corm and rhizome Iris. The following combined with years of breeding experience, to talk about the prevention and control of Iris soft rot. The pathogen of Iris soft rot is bacteria, and two species are known at present.
- Next
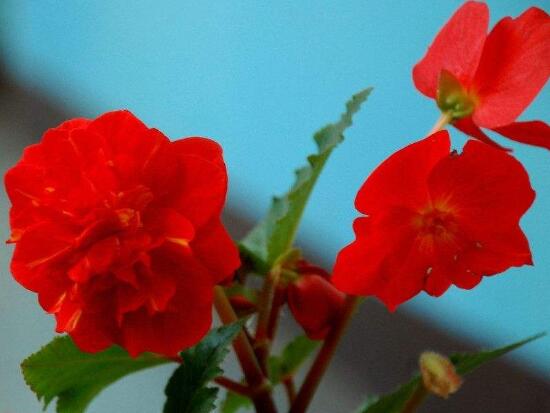

Efficacy and function of glass jade / indoor culture can purify the air / beautify the environment
Glass Cui is a kind of plant introduced to China from Africa, and it is also a common flower in people's life today, which is highly ornamental. But beyond that, it has many other functions. What are the specific effects and effects of glass jade? Next, the editor will take you to learn about it.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

