Control methods of bacterial soft rot of Iris
Bacterial soft rot is one of the most common diseases of Iris, which often occurs in both corm and rhizome Iris. The following combined with years of breeding experience, to talk about the prevention and control of Iris soft rot.
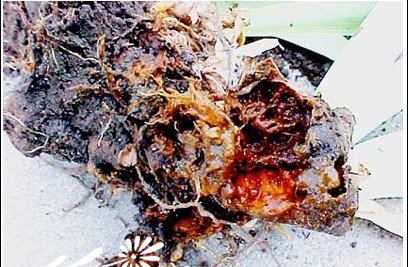
The pathogen of Iris soft rot is bacteria. At present, there are two known species, namely, carrot soft rot Erwinia carrot pathogenic variety of carrot and Amorphophallus Owens, both of which belong to Bacteriacea and Owens. In addition to irises, it also harms many kinds of flowers and plants, such as cyclamen, hyacinth, lilies and tulips. The law of the disease is that germs generally survive the winter in the soil and stubble. They can survive in the soil for several months, and if they are in the remains of diseased plants, they can survive for a long time. It is easier to survive when the temperature and humidity are high. Therefore, in general, the disease occurs more when the soil is moist, where the planting is too dense and the shade coverage is large. If the disease has already occurred, the method that should be taken immediately is to choose the mixture of streptomycin or streptomycin plus oxytetracycline (10:1) to spray the plant and the ground for 2-3 times with good results. After the disease, agricultural streptomycin can also be sprayed once a month, so that the spread of the disease can be controlled in parallel. Control techniques of bacterial soft rot of Iris
Distribution and harm
Bacterial soft rot is a common disease of Iris, which is distributed in the United States, Canada and Japan. It has occurred in Shanghai, Hangzhou, Hefei and Qingdao. The pathogen has a wide host range, including not only Iris, but also cyclamen, hyacinth, lily, tulip and other flowers and plants.
Symptom
After the damage to the bulbous iris, the apex of the new leaves turned yellow, and soon the outer leaves also turned yellow, and the whole plant withered. Waterlogged soft rot occurred in the root neck of the diseased plant, the aboveground part was easy to be pulled up, the corm was mushy and rotten, and the malodorous disease occurred in the iris. After other irises are injured, they expand from underground stems to leaves and roots. At the beginning, the leaves are water-stained soft rot, dirty white to dark green and withered, and the aboveground plants are easy to pull up. The root of the neck is soft and rotten and smells. When the bulb occurs before planting, there are water stains like frostbite, the lower part becomes tea-brown, smelly, with dirty white sticky stains. After the mildly diseased bulb seed, the leaf apex produced watery brown disease spot, the leaf development stopped, and soon the whole leaf turned yellow, withered, and the whole bulb root rotted.
Pathogen
The pathogen is bacteria, which is caused by carrot soft rot Erwinia carrot variety erwinia carotovora pv.carotovora (jones) bergey and Amorphophallus e.aroideae (townsend) holl. All of them belong to the genus Erwinia. The bacteria are short rod-shaped and move with weekly flagella. It was gram-negative. The size of erwinia carotovora pv.carotovora (jones) bergey is 0.7 × 2 μ m. The size of Owenia mandshurica is 1.2-3.0 μ m × 0.5-1.0 μ m. The most suitable temperature for their growth is 27 Mel 30 degrees Celsius, and the highest temperature range is 32 Mel 40 degrees Celsius. Can ferment glucose, oxidase negative. Control techniques of Iris bacterial soft rot [distribution] bacterial soft rot is a common disease of Iris, whether it is bulbous Iris or rhizomatous Iris, distributed in the United States, Canada and Japan. It occurs in Shanghai, Hangzhou, Hefei and Qingdao in China. Symptoms: when the disease occurred in Iris bulbosa, the root neck of the diseased plant had water-stained soft rot, mushy rot and stench. With the development of underground diseases, the front end of the new leaves on the ground turned yellow, and soon the lateral leaves also yellowed. The aboveground part is easy to pull up, and the whole plant is withered and yellow; when other kinds of irises occur, they expand from underground stems to leaves and roots, the leaves begin to water-stained soft rot, dirty white to dark green, the aboveground parts of plants are easy to pull up, the root neck is soft rot, and there is a stench. Before planting, when the bulb became sick, like frostbite, the lower part became tea-brown, smelly, with dirty white mucus. After the light bulb was planted, the leaf apex became watery brown, the leaf expansion stopped, and soon the whole leaf turned yellow and withered, and the whole bulb root rotted. [pathogen] the pathogen is bacteria, and there are two known pathogens of Iris soft rot, namely, Erwiniacarotovorapv.Carotovora (Jones) Bergey and E.aroideae (Townsend) Holl. Both of them belong to the genus Erwinia. The bacteria are short rod-shaped and move with weekly flagella; it is gram-negative. The size of the former is 0.7 × 2 μ m, and the size of Erwinia is 1.2-3.0 μ m × 0.5-1.0 μ m. The most suitable temperature for their growth is 27-30 ℃, and the highest temperature range is 32-40 ℃. Can ferment glucose, oxidase negative. The host range of bacteria is very extensive. In addition to Iris, it also harms many kinds of flowers and plants, such as cyclamen, hyacinth, lily and tulip. [incidence regularity] the pathogen overwinters on the soil and stubble, can survive in the soil for several months, and can survive for a long time in the remains of diseased plants in the soil. Germs are transmitted by water flow, contact with insects and diseased leaves or operating tools, and invade from insect wounds, split wounds, transplant injuries and other wounds. In particular, the wounds caused by the larvae of Iris on the young leaves or by transplanting opened the door for the invasion of bacteria; the disease spread through Rain Water, irrigation water and insects, and the disease occurred from June to September under natural conditions. The disease is serious when the temperature and humidity are high, especially when the soil is moist, the corm is easy to occur in places with too dense planting and large shade coverage, and the disease is serious in continuous cropping land. German Iris and Austrian Iris are common. [control methods] 1. Select disease-free bulbs; avoid wounds when digging; do not need diseased roots when dividing roots and propagate; change new soil in greenhouse cultivation, timely cut off diseased leaves or pull out diseased plants and destroy them; thoroughly dig up rotten bulbs and remove diseased bulbs in time during storage. Seriously diseased soil can be disinfected with 0.5% Mel 1% formalin 10g/m2 before planting, or after replacing new soil; contaminated tools can be soaked and sterilized with boiling water or 70% alcohol, or 1% copper sulfate solution. Tools for cutting flowers, disinfect with 0.5% potassium permanganate. 2. At the initial stage of the disease, the mixture of 100,150 × 0.000001 streptomycin or streptomycin plus oxytetracycline (10:1) was sprayed for 2-3 times with good effect. After the disease, spraying 1000 times of agricultural streptomycin once a month can control the spread of the disease. Spraying insecticide to control the harm of Iris borer can reduce the occurrence of the disease. 3. When harvesting bulbs, wounds should be avoided, and withered leaves should be removed from the nursery in autumn to prevent pests from laying eggs on them. 4. Select healthy bulb planting; nursery land should be well drained; planting should be shallow rather than deep; watering should be avoided in management. 5. During the growing season, pay attention to the prevention and control of the iris drill borer that causes iris wounds. The control can be carried out with 1000-2000 times of 50% malathion EC or 2000-3000 times of 2.5% deltamethrin EC.
- Prev

Control of Root Rot of Flowers in Family hydroponic Culture
Hydroponic flowers are popular in recent years, according to the way of oxygen supply, hydroponic flowers can be divided into two kinds, one is to use dissolved oxygen in nutrient solution, the other is to absorb oxygen directly from the air. For hydroponic flowers, the occurrence of root rot is mainly due to the lack of dissolved oxygen in nutrient solution.
- Next

Control of Spodoptera litura in Brazil
Spodoptera litura is a quarantine Lepidoptera pest in the world, which has spread rapidly from south to north in China in recent years. The study shows that the sugarcane flat moth not only harms Brazilian iron (wood), but also harms many kinds of flowers, such as wealth tree, dragon blood tree, Hainan iron, pocket coconut, poinsettia, iron tree, palm bamboo and so on.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

