Classification and characteristics of interstitial pneumonia

Interstitial pneumonia is a newly prevalent disease, which is not only the name of western medicine, but also a saying of western medicine. many patients and their families and relatives are easy to understand as a disease. In fact, it can be divided into four types: common interstitial pneumonia (UIP), exfoliative interstitial pneumonia (DIP), acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) and non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). Most interstitial pneumonia is a prelude to pulmonary fibrosis.
Common interstitial pneumonia (UIP), which has increased by 87% in the last 10 years or so, is easy to form more than 200 diseases, which can be said to be a combination of diseases. On the whole, it is a group of diseases with various causes and manifestations, but all of them mainly damage the respiratory membrane, such as thickening, degeneration, gas diffusion dysfunction and so on. However, the lesions were uneven, including interstitial inflammation, pulmonary fibrosis and honeycomb-like changes.
Exfoliative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) can be said to be respiratory bronchiolar interstitial pneumonia (RBILD). Pathologically, a large number of macrophages were evenly distributed in the alveolar cavity, especially in the air cavity around the bronchiols. nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) was characterized by inflammation of the alveolar wall, infiltration of plasma cells and lymphocytes, and the tendency of pulmonary fibrosis, and obvious lesions occurred around the bronchioles.
Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) is a rapidly developing explosive lung injury, showing alveolar epithelial damage, type II epithelial tissue hyperplasia, alveolar septum edema, intraalveolar hemorrhage and hyaline membrane formation, which is very similar to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). There was no gender difference in acute interstitial pneumonia, the case fatality rate was more than 60%, and the life expectancy was 1-2 months.
- Prev

The necessity of Cold cough and Dialectics of traditional Chinese Medicine
When traditional Chinese medicine talks about syndrome differentiation and treatment, many people will feel unnecessary. In life, many people cough and catch a cold, so they casually take some medicine to treat colds and coughs. Some people are very effective, while others are not effective at once and need to be changed.
- Next
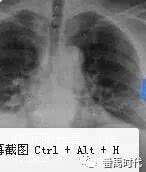
Causation of immunity and pulmonary consolidation
Immunity in western medicine is people's resistance to disease, which is called Zhengqi in traditional Chinese medicine. As early as in the "Huang Di Nei Jing Su question", it is said: "good qi is stored in, evil can not be done; where evil is put together, its qi will be empty." That is to say, when a person gets sick, righteousness is already.
Related
- Wuhan Hospital Iron Tree Blooming Result Was Instantly Frightened by the Gardener Master
- Which variety of camellia is the most fragrant and best? Which one do you like best?
- What is the small blue coat, the breeding methods and matters needing attention of the succulent plant
- Dormancy time and maintenance management of succulent plants during dormancy
- Minas succulent how to raise, Minas succulent plant pictures
- What are the varieties of winter succulent plants
- How to raise succulent plants in twelve rolls? let's take a look at some experience of breeding twelve rolls.
- Attention should be paid to water control for succulent plants during dormant period (winter and summer)
- Watering experience of twelve rolls of succulent plants
- Techniques for fertilizing succulent plants. An article will let you know how to fertilize succulent plants.

