Production Technology of pollution-free Apple in Yongji, Shanxi Province
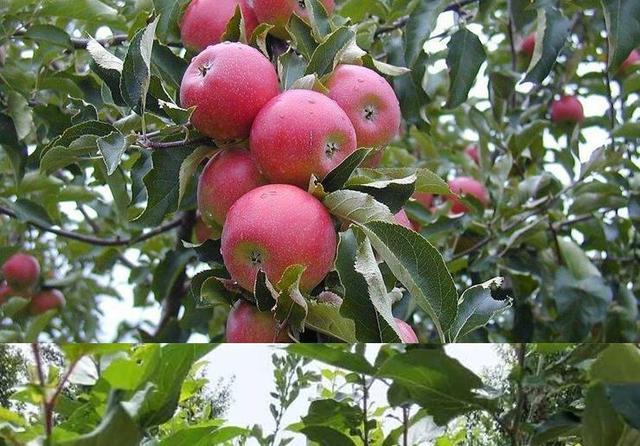

Production Technology of pollution-free Apple in Yongji, Shanxi Province
Pollution-free apple production is for the purpose of high yield, high efficiency, safety and high quality, and on the basis of improving the ecological environment and raising the level of cultivation and management. Pesticides, fertilizers and water must comply with the relevant standards or guidelines. It is strictly forbidden to use pesticides, fertilizers and plant growth regulators that are explicitly prohibited by the state and whose components are unknown or not approved by the state. Agricultural measures and biological agents are given priority to minimize the use of pesticides. Reduce pesticide residues and control diseases and insect pests below the economic threshold. In the use of fertilizer, we advocate planting green manure and returning straw to the field, mainly organic fertilizer fermented at high temperature, and scientific and rational use of chemical fertilizer. Industrial wastewater and municipal sewage are prohibited to be used as orchard irrigation water.
1 production technical standard
The production base construction, cultivation techniques, fertilizer and water management techniques, pest control techniques and harvest requirements of pollution-free apples are suitable for the production of pollution-free apples in Yongji City, Shanxi Province.
The guidelines for the use of green food pesticides "NY/T 5012mur2001" and "NY/T 393mur2013"; the guidelines for the use of green food fertilizers "NY/T 394mur2000"; the technical regulations for apple production "NY/T 441mur2001"; and the environmental conditions of apple producing areas for pollution-free food "NY/T 5013" The environment of the producing area meets the air, water quality and soil quality standards stipulated by the Ministry of Agriculture "NY 5010mur2001" and the technical regulations for the production of pollution-free agricultural products in Shanxi Province "DB 14pachi 2001".
2 production operation rules
2.1 selection of production base
(1) the choice of garden site. The pollution-free apple production base must be far away from cities and traffic roads, and there are no direct pollution sources of industry or mines (discharge of "three wastes") and indirect pollution sources (pollution of upstream and upstream waters). The base should be 100 meters away from the highway. The atmosphere, soil and irrigation water in this area have been tested to meet national standards.
(2) selection of varieties. Varieties should meet the market requirements, beautiful appearance, good internal quality, that is, red, big, sweet, fragrant, crisp, resistant to storage and transportation. The apple varieties suitable for the development of Yongji are mainly early-maturing and medium-maturing varieties, such as Australian green apple, Shanxia, Qin Guan, Jinfu No.1, Honggala and Pink Lady.
2.2 soil management
The active soil layer of the orchard is required to reach 80 cm, the permeability is good, the oxygen content of soil porosity is more than 5%, and the content of soil organic matter in the main root distribution layer (50 cm range) is 1%. Soil management includes three items: deep ploughing and soil improvement, tree plate covering grass and interrow grass.
(1) turn the soil deeply. The apple was ploughed deeply after harvest combined with organic fertilizer in autumn. The whole garden is turned deep once every 2 years, with a depth of 30cm to 40cm. When the soil is backfilled, it is mixed with organic fertilizer and grass cover on the ground into the pit, and then fully filled with frozen water.
(2) covered with grass on the tree plate and grass between the rows. The combination of tree plate grass mulching and grass growing between rows can not only store water and preserve soil moisture, but also increase the content of soil organic matter. Advocate raising pigs and chickens in orchards, building biogas digesters, and taking the road of combining planting and breeding.
Tree plate grass mulching is carried out after fertilization and irrigation in spring, with wheat straw, corn straw and so on under the tree plate, the thickness of 20 cm is appropriate, when the material is insufficient, it can be carried out batch by batch, the thickness of grass mulching must be ensured. Press a small amount of soil to prevent fire, turn it shallowly every 2 years, and dig deep into the soil 4 years later. When topdressing, peel off the grass and apply it.
Interrow grass can be artificially planted green manure (hairy vetch, flat stem astragalus, clover, etc.), or intercropping peanut, beans and other low-stalk crops, or grass in the garden. The grassy orchard should be cut 3 or 4 times a year to cover the ground, and the highest growth height should not exceed 25 cm, which can not affect the normal growth of fruit trees. No matter covered with grass or raw grass orchard, spray disinfection in dormant period every year to kill the source of overwintering diseases and insect pests.
2.3 fertilization
(1) the principle of fertilization. With the application of rotten organic fertilizer (including high-temperature heap retting fertilizer, biogas fertilizer, human manure, sheep manure, chicken manure, etc.) or commercial organic fertilizer, biological fertilizer, supplemented by chemical fertilizer. The fertilizers applied must meet the relevant national standards, have the approval number, and should not adversely affect the orchard environment and apple quality.
(2) base fertilizer. When base fertilizer is applied after fruit harvest, the amount of organic fertilizer is calculated according to 1.5-2kg per kilogram of apple production, and the orchard with insufficient fertilizer source should also meet the standard of kilogram fruit kilogram fertilizer. In general, according to the difference of yield, 2000-4000 kg of organic fertilizer is applied per mu. The main method of fertilization is ditch application or sprinkling, and the most suitable part of fertilization is the vertical projection around the crown.
(3) topdressing. The amount of topdressing was calculated as 1.0 kg of pure nitrogen, 0.3 ~ 0.5 kg of pure phosphorus and 1.2 ~ 1.3 kg of pure potassium per 100 kg apple. The method of fertilization is to open a shallow trench under the canopy for 15-20cm. For the first time, nitrogen fertilizer was applied before and after budding (mid-April), accounting for 70% of the total amount of nitrogen fertilizer used in the whole year, and the second time in the period of flower bud differentiation and fruit expansion (early and middle June), mainly phosphorus and potassium fertilizer, plus a small amount of nitrogen fertilizer, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer and potash fertilizer accounted for 20%, 25% and 35% of the whole year, respectively. The third time was applied in the late stage of fruit growth (late July to early August), mainly potash fertilizer, accounting for 65% and 70% of the whole year. Irrigate immediately after topdressing.
(4) foliar fertilizer. Spray 4 times 5 times in the whole year, spray 2 times during spring shoot growth period (late April to mid-May), mainly nitrogen fertilizer, spray 0.3% 0.5% urea, the interval is 15 days. The spring shoot was sprayed once from the spring shoot to the early stage of flower bud differentiation (from late May to mid-June) and twice during the autumn shoot growth period (from early July to early August), mainly with amino acid series micro-fertilizer (400 times liquid) or 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate.
2.4 Irrigation
It must be irrigated three times a year, that is, after sprouting or spring shoot flourishing period, fruit expansion period and soil freezing period. According to the rainfall, irrigation can be increased for 1 or 2 times in case of drought. The amount of irrigation is subject to the infiltration of the root distribution layer (30-40 cm), that is, 60%-70% of the field capacity. Attention should be paid to timely drainage and waterlogging prevention in rainy years.
2.5 shaping and pruning
(1) Tree phase index. After winter pruning, the number of branches retained per mu is 80 000 ~ 100000, with a maximum of no more than 100000. The tree height is not greater than the row spacing, the dry height is not less than 40 cm, and the cross rate between plants is less than 30%. The average annual growth of new shoots in the periphery of the crown is 30cm to 40cm. The ratio of fruiting branches to vegetative branches was 1 ∶ 3, and the proportion of medium and short branches was 90%. The orchard coverage rate is 75%, and the leaf preservation rate is 80%.
(2) principles and requirements. ① young trees to early fruit trees. The main task is to reshape and cultivate a good tree structure. The methods of light pruning, long release and more branches should be adopted, permanent branches and temporary branches should be treated differently, auxiliary branches should be fully utilized, and shaping should be made while bearing fruit without affecting the ventilation and light transmission of the whole plant. ② trees in full fruiting stage. Using the technical measures of light adjustment, branch adjustment, flower adjustment and potential regulation, using the methods of sprouting, branch thinning, angle opening, top cutting, cutting (peeling), control, etc., mainly summer tube and winter shearing, cultivate good fruiting branch group, reduce peripheral branches, control auxiliary branches, remove erect branches, competitive branches, happy falling head, control crown, improve ventilation and light transmission conditions of the whole garden. ③ senescence tree. Retract in time, renew and rejuvenate. The specific approach is to remove the weak and stay strong, to obliquely stay straight, to keep the old and stay new, to go to the outer inner chamber branch, to leave strong branches and strong buds, and so on.
(3) density and tree shape. According to soil fertility, management level, variety habits and other different planting density, using different tree shape. The distance between rows and plants is 4 meters ×
2cm (553m / mu) adopted small crown sparse layer shape and free spindle shape. The small crown of ① is sparsely lamellar. The stem is 40 cm high, the tree is 3 meters high, and the crown diameter is 2.5 meters, with a central leading stem. There are 6 main branches, arranged 3-2-1 from bottom to top, the angle of the main branch is 60-70 °, the lower branch is large and the upper branch is small, there are 2-3 lateral branches on the main branch, the distance between the first and second layers is 70 cm, and the distance between the second and third layers is 50 cm. ② is free spindle-shaped. It is shaped like a cedar in shape, with a stem height of 50 cm and a tree height of 2.5 M. there are 10-15 main branches uniformly on the middle trunk, with an angle of 80-90 °, regardless of layers, evenly inserted and spirally arranged. There are no lateral branches on the main branch, and the length of the main branch is 1.5 m, 1 m and 0.7 m respectively from bottom to top, the distance between the two adjacent main branches is 20 cm, and the crown is compact.
2.6 Flower and fruit management
(1) thinning flowers and fruits. Thinning flowers and fruits should be done sooner rather than later. Follow the three steps of flower thinning, fruit thinning and fruit fixing. The flower thinning began 7 days after inflorescence separation and completed in 15 days. First, the edge flowers were removed and the central flowers were retained. Fruit thinning begins 7 days after falling flowers, and it is completed within 20 days, leaving fruit according to distance, 1 fruit every 20 cm for large fruit and 1 fruit for medium fruit every 15 cm. Deformed fruit, damaged fruit and tip fruit can be removed, and the amount of fruit retained can be reserved by about 15%. The fruit was fixed in 1 month after falling flower and completed in 3 to 5 days. When the stunted fruit was removed, the fruit retention should be suitable. When the yield per mu was 1500-2500 kg, 8000-13000 was left, and the average single fruit weight could be more than 200 grams.
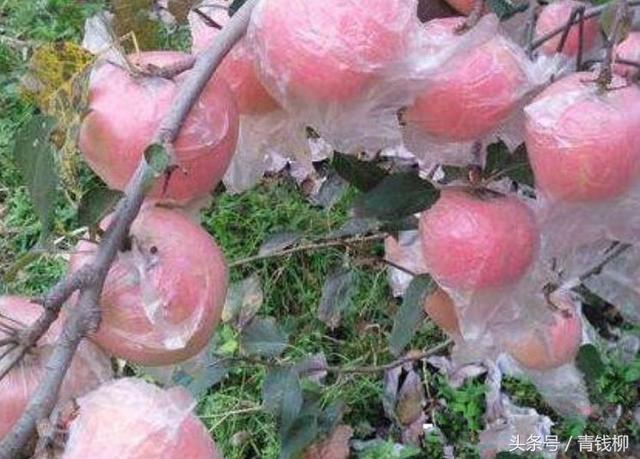
(2) bagging and bagging. Bagging after setting fruit (starting 40 days after anthesis). Bagging can choose high-quality plastic film bag or paper bag, spray protective fungicide + calcium amino acid for 2 times before bagging, and then bag after the solution is dry. if it is not finished 5-7 days after spraying, it should be bagged again after spraying. Bagging time should avoid the high temperature period at noon. The orchard with double-layer paper bags should take off the bags about 15-20 days before harvest, untie the outer bag first, and then take off all the bags after 3 sunny days. It is appropriate to remove the bags before 10:00 and after 14: 00, in order to promote the overall coloring of the fruit and prevent sunburn. After taking off the bag, the leaves around the fruit should be removed and the fruit should be turned in time. The amount of leaves should not exceed 20% of the total leaves of the whole tree, and the orchards covered with plastic bags can be harvested with bags.
2.7 Disease and pest control
Adhere to the plant protection policy of "giving priority to prevention and comprehensive control", on the basis of agricultural and physical control, in accordance with the occurrence law and economic threshold of diseases and insect pests, scientific and rational use of chemical control techniques to effectively control diseases and insect pests, minimize the use of pesticides. The use of pesticides is carried out according to the standard of "NY/T 5012 Mel 2001" to ensure that the quality of apples conforms to the national standards.
(1) dormant period (after falling leaves to before sprouting). The trunk, main branch and large side branch were whitened. The formula of whitening agent was quicklime 12 parts, salt 2 parts, soybean juice 0.5 parts, water 36 parts. Thoroughly clean the withered branches, fallen leaves, diseases and insect pests in the garden, cut off the disease and insect branches on the tree, scrape off the old thick and warped skin on the trunk, concentrate on burying or burning, and eliminate all kinds of overwintering disease and insect sources. The soil under the canopy is 20-25 cm deep, and the winter low temperature is used to eliminate overwintering pests in the soil.
(2) 7 days before germination. The whole garden is washed and sprayed with 5 Baumedu stone sulfur mixture, focusing on the control of scale insects and leaf mites. The formula of stone-sulfur mixture is 2 parts of sulfur, 1 part of quicklime and 12 parts of water. Use the slurry of stone-sulfur mixture or boil-stone-sulfur mixture to seal the shearing and large wounds.
(3) florescence. Spraying is prohibited during flowering, and physical methods such as artificial capture and trapping with sugar and vinegar are used to focus on the prevention and control of beetles.
(4) from anthesis to leaf expansion. Focus on the control of aphids and leaf rollers, prevent all kinds of diseases, spray fungicides for 3 times, each time at an interval of 10 days. For the first time, 10% imidacloprid wettable powder was sprayed 2000 times + 1.5% multi-antimycin wettable powder + amino acid micronutrient solution at 7 days after anthesis. Leaf rollers can manually cut off the buds and burn them. For the second and third time, starting from 15 to 20 days after anthesis, fungicides were sprayed twice, and 1.5% multi-antimycin wettable powder 400 times, 70% methyl topiramate wettable powder or 60% carbendazim wettable powder 800-1000 times each were selected, and 400 times calcium amino acid solution was added. Start bagging after spraying the medicine for the third time.
(5) the spring shoot stops for a long time before the wheat harvest. To control leaf mites and Spodoptera litura, spray 25% diflubenzuron 3 suspension 1000-1500 times + 1.8% acaridin EC 6000-7000 times + amino acids 400 times.
(6) fruit expansion period (autumn shoot growth period). Protect leaves and promote flower bud differentiation. Spray multi-dose Bordeaux solution or other fungicides + 0.3% potassium dihydrogen phosphate twice (only once for medium-ripe varieties), with an interval of 25 days, and stop using drugs 30 days before harvest.
2.8 timely harvest
Different varieties have different fruit development periods, the harvest time should not be too early or too late, too early affect coloring, quality and flavor, too late is easy to cause a large number of fruit drop. The order of fruit picking is first outside then inside, first down and then up, and handle it gently to prevent squeezing, bruising and stabbing of the fruit.
2.9 Fruit graded packaging, storage and transportation
(1) graded packaging. Fruits should be graded and packed strictly according to the standard before storage or export. 7.5 kg per carton is suitable for single packing. The materials used for packaging (including cartons, wrapping paper, tape, etc.) must be clean, non-toxic and odorless. There should be 4 or 8 air vents on both sides of the box, and the box should be marked with variety, origin, weight and pollution-free apples.
(2) Storage. The most suitable temperature for the storage environment is 0: 3 ℃ (the lowest is not less than 0 ℃ and the highest is not more than 5 ℃). Chemicals are not allowed to be used during the storage period. They should be kept in a constant temperature or refrigerated air-conditioned storage, and the storage environment should be kept clean, hygienic and odorless. The boxes of apples should not touch the ground and against the wall directly. There should be 150cm ventilation duct, no more than 5 layers of stack and 40cm-50cm working passage between the stacks.
(3) Transport. The tools for transporting fruits should be clean and hygienic and should not be mixed with toxic, harmful and odorous objects.
- Prev

Apple shaping and pruning and Pest Control in Lingwu City
Lingwu City Apple shaping, pruning and Pest Control Lingwu City is located in the central part of Ningxia Hui Autonomous region with superior natural conditions such as temperature, light and precipitation. Apples and other fruits are widely planted and are known as the "hometown of flowers and fruits".
- Next
Research on the content production of KAA Video making Mobile phone Registration short Video
Research on content production of KAA Video money Mobile phone registered short Video Network short video has a different content production mode from traditional video, and has a close relationship with the characteristics of the Internet in terms of content expression and production.
Related
- Wuhan Hospital Iron Tree Blooming Result Was Instantly Frightened by the Gardener Master
- Which variety of camellia is the most fragrant and best? Which one do you like best?
- What is the small blue coat, the breeding methods and matters needing attention of the succulent plant
- Dormancy time and maintenance management of succulent plants during dormancy
- Minas succulent how to raise, Minas succulent plant pictures
- What are the varieties of winter succulent plants
- How to raise succulent plants in twelve rolls? let's take a look at some experience of breeding twelve rolls.
- Attention should be paid to water control for succulent plants during dormant period (winter and summer)
- Watering experience of twelve rolls of succulent plants
- Techniques for fertilizing succulent plants. An article will let you know how to fertilize succulent plants.

