Improved trunk shape and simplified pruning of pear trees

The pear tree is an improved trunk with a height of 60-70 cm and a height of 3.5 m. There are 4-5 large main branches in the middle and lower part of the central leader's trunk. The distance between the main branches is about 20 cm. The base angle of the main branch is 60 degrees. The waist angle is 30-50 degrees. The tip angle is erect; the main branch extends uniaxially. There are medium and small fruiting branches or branches on it, and the ratio of main branch to trunk is controlled at 0.3: 0.5. The central leader bears small and medium-sized fruiting branches or groups of small and medium-sized fruiting branches in the upper half of the trunk. Because there are no lateral branches in the middle and lower part of the crown. There are no big branches in the upper part, and the canopy is well ventilated and transparent. The simplified pruning method, that is, the "three noes" pruning method: planting seedlings with indefinite stem; pruning the branches of the central leading stem and the main branches of young trees in winter are not short; the opening angle of the main branches is not more than 70 degrees, so that it shows an oblique upward growth trend. Instead, it adopts "shaping with growth" in which competitive shoots are treated as the main means in the growing period. 1 if the upper part of the seedlings planted in the garden is branched (formed in the nursery) or damaged, cut off the branches or damaged parts (leaving full buds under the cut), if it is an unbranched or undamaged strong seedling at the apex. Practice has proved. As long as the seedlings are strong, the leaf buds are full and the roots are well developed, all leaf buds can germinate except necrotic buds and several hidden buds at the base of the seedlings. Generally, 2 or 4 vigorous branches are produced at the top, and they are regulated when the new shoots grow to about 20 cm from May to June, so as to ensure the absolute superiority of the growth potential of the central leaders. The method is: when the growth of the tip of the top bud is obviously dominant. The 2nd ~ 4th shoots (competitive shoots or shoots with narrow angles) should be removed when the growth of top shoots is obviously weak. Using competitive shoots instead of apical shoots as branches, the new shoots with competitive situation and small base angle in the lower part of the shoot were also removed. Excluding the competitive shoot and the new shoot with narrow angle, the base angle of the lower shoot is generally more than 60 degrees, and the growth of the lower shoot is weaker and thinner than that of the competitive shoot, so it is easy to control the thickness of the main branch. There were more shoots in the first year of seedling planting, but the growth was not large, and the tree height was about 1.8 meters in that year. (2) during winter pruning and winter pruning in the second year (January to February), the branches of the central leader and the main branch are generally not short, only individual lateral branches on the main branch and confirmed useless branches are removed. If the central leader trunk and the main branch are injured (such as insect pests, etc.) and send out secondary branches, the decentralized parts should be cut off in winter pruning, and full buds should be left under the cut. In addition to the necrosis of leaf buds and several hidden buds at the base, the germination rate of robust erect branches can reach 100%, and several strong shoots (competitive shoots) can be produced at the apex of non-short cutting shoots. When the new shoot grows to about 20 cm (May), pruning is carried out to dredge competitive shoots and overgrown shoots. Or use the competitive tip to turn the main head to keep the central leading stem branch growing upward alone and the main branch extending uniaxially. The growth of seedlings increased obviously in the second year of planting, the average height was about 2.8 meters, and some plants formed flower buds. (3) after 2 years of cultivation, the height of the tree was close to 3 m, and several larger main branches were formed in the middle and lower part of the crown. The method of winter pruning and summer pruning in the third year is the same as that in the previous year, that is, the trunk branches and main branches of the central leadership are generally not cut short in winter pruning, and competitive shoots are treated in May. For the larger main branch in the lower part of the crown, it should maintain an oblique upward growth trend (waist angle 30-50 degrees), and it should not be opened to 70 degrees, let alone pulled horizontally. For the upright and even centrally embraced branches, the waist angle should be adjusted to 30-50 degrees. The upright shoots of the main branch and the central leading stem are more likely to sprout, but only the first 3 buds are easy to draw growth shoots. Other axillary buds produce short shoots and form flower buds. If the main branch is flattened, a row of long shoots will emerge on its back and affect the growth of the main branch. After 3 years of shaping and pruning, the height of the tree can reach about 3.5 meters, and the lower part of the crown is cultivated into 3 to 5 larger main branches, the middle and short fruiting branches are distributed on the main branches, the medium and short branches are formed on the central leading trunk of the upper part of the crown, and the tree shape is improved. (4) the pruning in the fruiting stage entered the fruiting stage, and the branches of the central leadership and the main branches were mainly thinning. Prevent the formation of lateral branches on the main branches and prevent the central leadership from growing larger branch groups. The number, orientation and size of main branches are artificially regulated according to the actual needs of growth and fruit. During the fruiting period, the expansion and growth of the crown slowed down obviously, and the main purpose of pruning was to control the elongation and growth of the main branches and the height of the tree. At the right time, the ratio of the thickness of the main branch to the trunk should be controlled at 0.3: 0.5. The main branch that is too thick should be retracted in the appropriate period until it is thinned (changing branches).
- Prev

Control of scab in pear trees
1. Strengthen the management of orchards. The growth of pear trees is weak and is easy to be infected by bacteria. Therefore, the application of fertilizer, especially organic fertilizer, can enhance the tree potential and improve the disease resistance. two。 Chemical control. About 70% of pear trees should be sprayed before flowering and about 70% of falling flowers to protect inflorescences, shoots and new leaves. In the future, according to the rainfall.
- Next
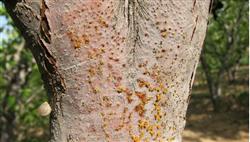
Pear tree rot and its control
1. Disease prevention of strong trees: (1) reasonable burden: according to the growth status of the tree and the level of fertilization, determine the appropriate amount of fruit, do not let the tree burden too much, let alone take too many measures to increase fruit, such as branch pulling and ring peeling for short-term benefits. It is necessary to properly thinning flowers and fruits so that the fruit can grow without mistake. (2.
Related
- Moge, come on! The staff of the peasant association in the producing area of cantaloupe were frightened when the crowd gathered.
- Causes and Solutions of low Fruit setting rate of Apple
- Symptoms and control measures of passion fruit virus disease
- Fruit growing lesson: how do apple orchards keep high yields?
- Can you build orchards in the mountains? What are the pros and cons?
- How to manage the coloring period of Crisson grape?
- This paper introduces the processing technology of two kinds of fig products.
- How much is a month for retired teachers in rural areas by 2020?
- How can strawberry planting increase sugar content? We should pay attention to management in many aspects.
- What are the cultivation techniques on how to improve the yield of golden fruit?

