Control of physiological diseases in mushroom emergence stage of Pleurotus ostreatus

1. The symptom of mycelium overgrowth (false hyphae) is that the hyphae covered with soil surface can not lodge in time. The causes of the disease are as follows: the culture temperature of the strain is too high (more than 22 ℃), the ventilation in the mushroom shed is poor, the air humidity is high, the aerial hyphae of the strain is too prosperous, the culture material is too mature, and there are many available nutrients. Prevention and treatment methods: select the semi-aerial hyphae in the semi-base to inoculate; prevent the medium from being too wet and decompose too fast, control the temperature and water content to avoid excessive ripening; reduce the temperature of the strain culture room and keep it at about 22 ℃; cut the skin of the mycelium with a knife in time, increase ventilation, reduce the relative humidity of the air, spray heavy water, and promote the mycelium to produce mushrooms in time. Second, the symptom of mycelium caking is the appearance of short and dense mycelium blocks on the culture material surface or soil layer. The cause of the disease is mainly caused by high temperature in mushroom shed, excessive ripening of culture material, late soil covering, poor ventilation, high air relative humidity and so on. If the aerial hyphae grow too much, it can also cause mycelium caking. Prevention and treatment: spray water reasonably, grasp the relative humidity of the air, and remove the bacteria, the seed body will be formed soon. Third, the cause of dead mushroom: it is mainly due to the low temperature in the mushroom shed in winter, and it is easy to die mushroom when the temperature in the mushroom shed is below 10 ℃ for 12 hours a day; sometimes the humidity of the mushroom shed is too high, and the amount of water sprayed after covering soil is too high; the temperature difference between day and night is too large, and it is easy to die mushroom if it exceeds 10 ℃ for a long time. In addition, the mushroom is too dense, when picking mushrooms inadvertently loose the surrounding hyphae, affecting the next small mushrooms to absorb nutrients, resulting in the death of some small mushrooms; mushroom parts are too high, there are diseases and insect pests or drug pests are easy to cause dead mushrooms. Prevention and control methods: arrange the production season, strengthen the heat preservation measures in the mushroom shed, strengthen ventilation, prevent the mushroom from being too high, control diseases, pests and miscellaneous bacteria, correctly use pesticides, and be careful not to use pesticides that produce harmful reactions to the varieties of edible fungi. The symptoms of thin skin disease are thin cover, thin stalk and early opening of umbrella. Causes: too high temperature, too dense mushroom production, poor ventilation, excessive humidity. Prevention and treatment methods: ventilation and cooling, reducing water spray, reducing air relative humidity. 5. The cause of hard parachute disease: it is easy to induce the disease when the temperature changes too much and the temperature difference is more than 10 ℃. Prevention and control methods: pay attention to heat preservation and cold protection in autumn, and pay attention to maintaining the relative humidity of the air. 6. Red root or green root disease the symptom is that the mushroom feet are red or green, and the color of the cap is normal. Causes: excessive spraying of water and glucose before mushroom production, acidity of culture material, poor ventilation and so on. Prevention and control methods: should strengthen ventilation, avoid spraying water at high temperature, spraying water and sugar solution, according to the relative humidity of the air and the dry and wet conditions of culture materials and mushrooms, try to control within the most suitable range of seed growth, and the water content of the soil layer should not be too high during the mushroom period. Stop spraying water before picking mushrooms and ventilate properly. 7. Water rust is mainly characterized by rust spots on the seed body, or even spots. Cause of the disease: after the seed body was unearthed, the bed surface was not ventilated in time after spraying water, and the water droplets on the seed body did not evaporate in time. Prevention and treatment: timely and appropriate ventilation after spraying water. Eighth, flat top, concave heart mushroom the main symptom of this disease is the cover flat or concave heart. The cause of the disease: mainly due to the insufficient water content of the overlying soil layer in the culture material or the low relative humidity of the air, there will be a flat roof, a concave center or scales on the surface. Prevention and control method: replenish water in time, and the air relative humidity during the mushroom period is controlled at 85%-90%. 9. The main symptoms of deformed mushroom are uneven cap, irregular cap, long stalk and small cap. The cause of the disease: the diameter of coarse soil particles covered with soil is too large, the hardness is too strong, and the content of carbon dioxide in the air is too high (more than 0.3%). Prevention and control methods: cover soil particles not too large; strengthen ventilation, heating stove should be put outdoors, use fire way to send warmth, reduce the content of carbon dioxide in the air. The main symptom of Pleurotus ostreatus is that there is soil on the top of the fungus cover, which is also called top mud mushroom. The causes of the disease were as follows: the culture medium was too wet and the culture medium was mixed with soil; when spraying water, the temperature of the mushroom shed was too low, the mushroom set too early, too much ventilation, and the fine soil was covered too late. Prevention and control methods: the culture material should not be too wet, and the soil should not be mixed into the culture material; after water transfer, ventilation should be reduced and the air relative humidity should be kept at about 85%; when the small mushroom bud has not yet been formed in the coarse soil layer, the fine soil should be covered to prevent premature mushroom formation.
- Prev

Management of mushroom emergence period of Pleurotus ostreatus: how to make it produce more mushrooms? The omen of high-yield cultivation techniques of Pleurotus ostreatus before mushroom emergence
First, control the temperature and humidity. The cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus begins to produce mushrooms about 20 days after covering the soil, the temperature is maintained at 20: 24 ℃, and the air relative humidity is 80% to 85%. During this period, it is generally impossible to spray water on the material surface, too wet and breathable, the hyphae are difficult to extend into the soil layer, too dry hyphae are sparse, maintain suitable temperature and humidity, and the hyphae are white and exuberant.
- Next
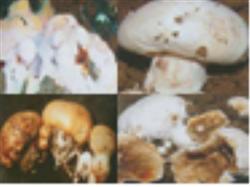
How to control verrucosporium of Pleurotus ostreatus
Disease symptoms verrucosporium disease, also known as brown rot, white rot, wet bubble disease, blister disease, the disease is caused by a pathogen called verrucosporium. Alternaria verrucosa is a kind of soil fungus. In the cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus, Alternaria verrucosa is mainly introduced into the mushroom room with the covered soil, which occurs in the mushroom shed with high temperature, high humidity and poor ventilation.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

