Control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in rape

Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, also known as rotten stem disease, is a fungal disease. Its harm lasts for a long time and can occur from emergence to maturity, especially after flowering. The main results are as follows: 1. After being infected at the seedling stage, reddish-brown spots appear at the base of the stem and petiole, then expand and turn to white, there are white flocculent hyphae above the rot, and finally the pathogen dies, and many black sclerotia are formed outside the diseased tissue. 2. The main symptoms from budding to maturity are round or irregular spots on the leaves, grayish brown in the center, dark cyan in the middle, and black halos in the periphery. 3. In the later stage of the disease, the stem became empty, the cortex was ruptured, the vascular bundle was exposed like hemp, and the stem of the diseased plant was easy to crack and break with green dung-like black sclerotia. After the flower is sick, the color is pale, has no luster, and is easy to fall off. After the pod is damaged, irregular white spots are produced, there are sclerotia inside, and the seeds are dried up. Control methods: 1. Crop rotation: because Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a soil-borne disease, the pathogen mainly exists in the soil, so it is best to rotate with rice. Because sclerotia will rot after soaking in water for 1 to 2 months, if it is a dry land rotation, it will take more than three years to eliminate Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. 2. Selection of disease-resistant varieties: varieties with high yield and disease resistance should be selected. 3. Seed treatment: rinse with 10% brine solution, remove the floating blighted grains and sclerotia, wash the sunken seeds with clean water to dry and sow. 4, clear ditch drainage 5, chemical control: mainly in the early flowering stage for spray control, can choose 40% of the sclerotia net or carbendazim spray, spray as far as possible in the middle and lower part of the plant.
- Prev

Diagnosis and skillful treatment of red and yellow seedlings in rape seedling stage
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, commonly known as "white stalk", "hemp stalk", "mildew" and so on, is one of the main diseases affecting the growth of rapeseed. The prevention and control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum should be based on prevention, and the main technical measures are as follows. 1. To prevent seeds from carrying bacteria through screening, air separation, seed dressing and other methods to eliminate sclerotia and kill seeds.
- Next
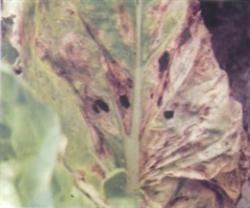
Disease prevention and treatment of stiff seedlings in rapeseed
[distribution and damage] it occurred in all rape producing areas, especially in the Yangtze River Basin and South China. The disease is caused by Alternariabrassicae (Berk.) Sace., A.brassicicola (Sehw.) wiltshire and A. graphaniGr.etS.
Related
- The first cup of black tea in spring, the flavor and history of tea gardens in Kenya, Africa
- The computer can not only choose potatoes, but also grow tea rice. AI will grow winter oolong tea champion.
- It is not only the inflated tea bitten by insects, but also engraved with the four seasons tea in Beipu.
- The Oriental Beauty Tea Festival in Zhuxian County takes the stage at the weekend to experience the plus-size feast of oil tea.
- & quot; Oriental Beauty Tea & Exploration of Emei in Hsinchu, the hometown of quot;
- The new variety of strawberry "Tainong 1" dessert is the first choice with mellow aroma. Crimson gorgeous
- History of Tea in Taiwan: from Wild Inner Mountain to Export Tea Garden
- Two types of Taiwan Oriental Beauty Black Tea won the British three-Star Award for Childhood Tea Xiang Zhang Jiaqi changed from pilot to champion tea maker.
- Banana species and varieties: the planting history of Taiwan Xianren banana and dwarf banana is long, is banana disease resistant?
- Coffee planting Technology: Qianjie Coffee from Seedling to harvesting

