Three keys to the management of Pleurotus ostreatus
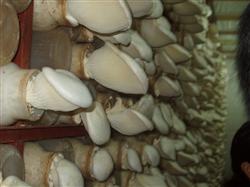
First, in order to grasp the key technology of "exposure", we must firmly grasp the key technology of "exposure" during the period of Pleurotus ostreatus. The specific method is as follows: after the bacteria bag is cultured in the bacteria room for 40-50 days, after the hyphae come to the bottom of the bag, it can be moved into the shed out of the mushroom room and put on the shelf to spread the bacteria bag. Open culture was carried out after 1-2 days. Operation method: the short bag cultivation unlocks the bag mouth, loosens the bag film; the long bag cultivation rips off the tape on the hole mouth, so that the mycelium in the bag can come into better contact with the air, this process is referred to as "open". After exposure, continue to cultivate for 10-20 days. The short bag uses a small rake to reach into the bag to rake off the original strain block and the fungus skin in the range of 3.5 cm around it. Some producing areas call this process "scratching bacteria". But it should be noted that other parts should not be scratched. Then cover the top of the bag with old newspaper and spray paper to moisturize. The long bag can dig up the bacteria block on the mouth of the original hole, which not only increases the air permeability of the mycelium, but also is a measure to locate the mushroom. Similarly, the bag surface is covered with newspaper and water-sprayed paper surface moisturizing. This practice is called "bacteria training" by mushroom farmers. At this stage, the indoor temperature is 15-20 ℃, the constant temperature is cultured, the space relative humidity is 75%, the relative humidity is 80%, and the time is controlled for 5-7 days, so that the mycelium can continue to "store sperm and raise sharpness" for mushroom production and strong mother body in the suitable temperature environment. Second, to grasp the key technology of "low temperature squatting bacteria and variable temperature buds" after open oxygen culture, we must firmly grasp the key technology of "low temperature squatting bacteria, variable temperature buds". In this period, low temperature squatting bacteria of 0-13 ℃, temperature difference of more than 10 ℃ between day and night and stimulation of 300-800 lux scattered light are needed to force the vegetative growth of hyphae to reproductive growth, which is different from other mushrooms in inducing primordium budding. At this time, the temperature in the mushroom room is between 0 and 13 ℃. The relative humidity of the air remains below 80%. Low temperature squatting bacteria for 8-12 days. Then turn to changing temperature to promote bud. Specific methods: close the doors and windows of the house planting, cover the border bed film planted in the shed, make the temperature of the shed reach more than 18 ℃, open the door or uncover the film at night, and let the cold air attack the shed, so that the temperature difference between day and night is more than 10 ℃, and the temperature difference is stimulated continuously for 10-15 days. And increase the ventilation rate, reduce the space relative humidity, force the mycelium lodging, the primordium can appear. When the induction and bud induction period can meet the requirements of the above environmental conditions, the primordium of rice grain can appear in 10-15 days and gradually develop and expand and differentiate into mushroom buds. Third, to grasp the "scientific management" of Pleurotus ostreatus from primordium appearance to fruiting body development, it takes 12-15 days under suitable temperature environment. This stage is called fruiting body growth period, which should be achieved in management: 1. Fruiting body development period. In order to ensure the concentrated growth of high-quality mushrooms, it is necessary to sparse buds and control plants, select the best and get rid of the bad ones, and leave one in each bag; select bud-controlled plants and cut off the bag film at the same time, so that the mushroom body has better contact space. The long bag cultivation is positioned according to the original inoculation hole, one for each, and the extra one is picked out. It is ideal to keep 13-18 ℃ in the mushroom shed without covering the newspaper at this time after thinning buds. The relative humidity of the air is kept between 80% and 90%. Generally, it is not sprayed directly on the mushroom body. When the climate is dry, it can spray space, or splash water on the ground to humidify. The shed can keep the air fresh and the illuminance is 500 lux. 800 lux is ideal. If the above requirements are met, the high quality mushroom body with thick and short handle can be obtained. 2. Mature period of fruiting body. It usually takes 90-120 days from inoculation to harvest. The short age is 60-70 days. In the mature stage, the temperature of the mushroom house was controlled above 10 ℃, and the quality was the best when the temperature was below 20 ℃. During the fruiting body maturity, the relative temperature of the space should be kept at about 85%, which should not be too wet; at the same time, the ventilation should be strengthened, the scattered light should be maintained, and the mushroom body should be thickened and the color is white. 3. Harvest time of fruiting body. When Pleurotus ostreatus is ripe, the cover is flat, swollen or concave in the middle. Cover edge outer roll, cover edge has luster, bacterial fold clear stretch, can be harvested. Pleurotus ostreatus is generally inoculated once and grows once, the bioconversion rate is 80% MUE 120%, and the production cycle is 100-135 days. You can also turn over one end of the short bag after harvest, remove the film, scratch the bacteria, and inject water; the long bag can be taken off and buried in the soil, and the mushrooms can grow again if managed properly.
- Prev

Causes and Preventive measures of abnormal Pleurotus ostreatus
1. The structure of the shed is unreasonable. The cultivation site of Pleurotus ostreatus is divided into indoor mushroom room and field mushroom shed. Often due to unreasonable design, resulting in poor air circulation, serious hypoxia, resulting in deformities of Pleurotus ostreatus. The ideal mushroom shed should sit north to south or west to east. The shed should not be too large, and the general rectangular shed can hold 300.
- Next

Do a good job in the management of the emergence period of Pleurotus ostreatus
1. The hyphae on the bed surface should appear at the right time, indicating that the hyphae have been sent to the bottom of the culture material and have been fully developed in the soil layer, and have the ability to bear mushrooms, so the bacterial water should be sprayed at the right time. Methods: increase ventilation, make the strong wind blow into the mushroom shed, make the soil surface mycelium lodge; according to the soil layer bacteria situation to master the amount of spraying water, generally per.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

