What is soybean gray spot disease and how to prevent it?
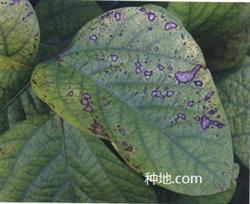
What is soybean gray leaf spot disease how to prevent and cure? Ask for guidance on soybean gray spot: (1) hazards and symptoms of soybean gray spot, also known as brown spot, spot or frog eye disease. Soybean gray leaf spot is not only a worldwide disease, but also an important disease in the main soybean producing areas in China, especially in the three northeastern provinces. The pathogen is the main disease in the low-lying and waterlogging-prone areas in the east of Heilongjiang Province. according to the statistics in 1963, the loss of soybean due to gray spot in Hejiang area reached 10 million kg. Since the 1980s, it has gradually spread westward and has become a soybean disease in the whole province. In recent years, due to the increase of soybean continuous cropping area, the gray spot disease is becoming more and more serious. Soybean gray leaf spot is an intermittent epidemic disease that often occurs in soybean production in our province. In the year when the disease was prevalent, the yield and quality of soybean were seriously lost. Generally, the yield of soybean could be reduced by 5%, 10%, and 30%, 50%, respectively. In severe cases, the 100-grain weight was reduced by 2%, and the content of protein and oil was reduced in varying degrees. Soybean gray leaf spot can cause harm to soybean leaves, stems, pods and seeds, among which leaves and seeds are the most serious. The disease spots on cotyledons are round, semicircular or oval, dark brown, slightly sunken. The disease spot on the leaf is mostly round, oval or irregular, the center of the disease spot is gray-white, the surrounding reddish brown, and the boundary between the disease spot and the healthy part is clear, which is the main feature to distinguish gray spot from other leaf diseases. When the climate is humid, there is a dense gray mold layer on the back of the disease spot, that is, the conidiophores and conidia of the pathogen. In severe cases, dozens of disease spots can be produced on a leaf, which makes the leaves fall off early. The pods on the stems, branches and petioles produce oval or spindle-shaped spots, with brown in the center, reddish brown at the edge, gray at the center and dark brown at the edge, which are covered with tiny black spots. The disease spot on the pod is round or oval, with the same shape and color as the disease spot on the leaf. The disease spot on the seed is round to irregular, gray in the center and reddish brown at the edge, forming frog eyes. The physiological differentiation of soybean gray spot pathogen is very obvious, and there are many types of physiological races. At present, 14 physiological races have been reported in the northeast spring soybean region. Among them, race 1 has the highest frequency of 50%, and its distribution is the widest. Race 1 is dominant in Hejiang, Mudanjiang, Songhua, Nenjiang, Suihua and other areas, followed by race 7 with a frequency of 22%. Race 1 and race 7 have the same frequency in Heihe area. Race 1 and race 7 are the dominant races in soybean producing areas in Heilongjiang Province, and the frequency of race 10 is 9%, accounting for the third place. Relationship between soybean gray leaf spot and temperature and humidity. The temperature of spore germination of Botrytis cinerea is the basic, and the humidity is the key. The lowest temperature of spore germination is 12 ℃, and the optimum temperature is 21 ℃ 26 ℃. The germination rate of spores over 35 ℃ decreases significantly. The lowest humidity of germination is 65%, and the higher the humidity is, the higher the germination rate is. The incidence of soybean gray leaf spot in Heilongjiang Province began in early July, and reached the peak from late August to early September. If the rainfall is heavy, the rainy days are more, and the relative humidity is high, the disease will be serious from early July to mid-August. (2) Control and selection of disease-resistant varieties, in recent years, the soybean varieties approved and popularized in Heilongjiang Province are all new varieties with resistance or high resistance to gray leaf spot, but it should be noted that after planting a disease-resistant variety continuously in a region, due to the pressure of variety selection and push, it will cause the change of physiological races and make the resistant varieties lose their resistance, so several varieties should be used alternately to prolong the useful life of the varieties. Chemical control: 1, 40% carbendazim gel suspension, 100g per mu, diluted into 1000 times spray. 2. 50% bacterial wettable powder or 70% methyl topiramate, diluted to 1000 times with water and 100ml 150g per mu. 3. 2.5% deltamethrin EC, 40 ml per mu mixed with 50% carbendazim wettable powder 100 grams per mu, can also prevent soybeans and heart-eating insects. Chemical control should seize the opportunity of control, and the key period of one application in the field is from the initial pod stage to the full pod stage. Click to see more soybean planting techniques click to see more food crop planting techniques
- Prev

How to control Sclerotinia sclerotiorum?
How to control Sclerotinia sclerotiorum? The solution of soybean Sclerotinia sclerotiorum often occurs from July to maturity. the symptom of the disease is that the wet green spot appears at the base of the stem, which expands quickly, and then the woolly mycelium grows in the spot, and the epidermis breaks into hemp. Black mouse dung-like sclerotia is produced on the inside and surface of the stem.
- Next

What if soybeans have a lot of lodging?
Are there any measures to increase the yield of soybeans? The more detailed the solution, the better. If you want to increase soybean production, you can use the following methods: 1. Interplanting: on the basis of the whole seedling, when two opposite leaves are unfolded, the yield is generally increased by 10-20%. two。 Pressing seedlings: when the first compound leaf of some soybean seedlings unfolds, it is clear.
Related
- The first cup of black tea in spring, the flavor and history of tea gardens in Kenya, Africa
- The computer can not only choose potatoes, but also grow tea rice. AI will grow winter oolong tea champion.
- It is not only the inflated tea bitten by insects, but also engraved with the four seasons tea in Beipu.
- The Oriental Beauty Tea Festival in Zhuxian County takes the stage at the weekend to experience the plus-size feast of oil tea.
- & quot; Oriental Beauty Tea & Exploration of Emei in Hsinchu, the hometown of quot;
- The new variety of strawberry "Tainong 1" dessert is the first choice with mellow aroma. Crimson gorgeous
- History of Tea in Taiwan: from Wild Inner Mountain to Export Tea Garden
- Two types of Taiwan Oriental Beauty Black Tea won the British three-Star Award for Childhood Tea Xiang Zhang Jiaqi changed from pilot to champion tea maker.
- Banana species and varieties: the planting history of Taiwan Xianren banana and dwarf banana is long, is banana disease resistant?
- Coffee planting Technology: Qianjie Coffee from Seedling to harvesting

