How to fertilize soybeans?

How to fertilize soybeans? What are the characteristics of soybean fertilizer requirement? The law of fertilizer absorption of soybean. The growth and development of soybean can be divided into seedling stage, branching stage, flowering stage, podding stage, grain filling stage and mature stage. The whole growth period is from 90 to 130 days, and the law of fertilizer absorption is nitrogen absorption rate. The emergence and branching stage accounted for 15% of the total nitrogen uptake during the whole growth period, 16.4% from branching to flowering stage, 28.3% from flowering to podding stage, and 24% at bean filling stage. The period from flowering to grain filling is the peak period of nitrogen uptake by soybean. Phosphorus uptake rate. 17% from seedling stage to early flowering stage, 70% from early flowering stage to soy bean stage, and 13% from bulging to mature stage. Soybean needs the most phosphorus in the middle stage of growth. Potassium uptake rate. The cumulative potassium absorption before flowering accounts for 43%, from flowering to grain filling stage accounts for 39.5%, and 17.2% potassium is still needed to be absorbed from grain filling to maturity. It can be seen that the period from flowering to grain filling is not only the peak of dry matter accumulation of soybean, but also the peak period of absorbing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients. Technical points of fertilization for soybean. The fertilization system of soybean is generally composed of base fertilizer, seed fertilizer and topdressing fertilizer. The principle of fertilization is not only to ensure adequate nutrition of soybean, but also to play the role of nitrogen fixation of rhizobium. Therefore, no matter in the early or late growth stage, nitrogen application should not be excessive, so as not to affect the growth of rhizobium or cause lodging. On the other hand, it is also necessary to correct the misconception that "if soybean has rhizobium, it does not need nitrogen fertilizer". Fertilization should be a reasonable collocation of a large number of elements of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and trace elements such as boron and molybdenum, and the combination of slow-acting and quick-acting fertilizer. The application of organic fertilizer is the key measure to increase the yield of soybean. Organic fertilizer can be applied to former grain crops on rotation land, while soybeans take advantage of its aftereffect. It is beneficial to nodulation and nitrogen fixation and increase the yield of soybean. Planting soybean on low fertility soil can add 10 kg of superphosphate and 10 kg of potassium chloride as base fertilizer, which is beneficial to the yield of soybean. Seed fertilizer generally uses 10 to 15 kilograms of superphosphate or 5 kilograms of diammonium phosphate per mu as seed fertilizer, and 0.4 to 0.6 kilograms of borax is added to boron-deficient soil. As soybean is a dicotyledonous crop, the top soil of the seed is difficult to emerge, so it is best to apply fertilizer to the lower part or side of the seed, do not make the seed in direct contact with fertilizer. The practice of topdressing shows that in the seedling stage of soybean, when the root nodule has not yet formed, or when the nodule activity is weak, the appropriate amount of nitrogen fertilizer can make the plant grow healthily, and it is necessary to apply a small amount of nitrogen fertilizer in the early flowering stage. Generally speaking, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer should be 7.5 to 10 kg urea per mu. In addition, spraying 0.2% to 0.3% potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution or calcium superphosphate aqueous solution at flowering stage can increase grain nitrogen content and significantly increase yield; spraying 0.1% borax, copper sulfate and manganese sulfate aqueous solution at flowering stage can promote grain fullness and increase soybean oil content. Click to see more soybean planting techniques click to see more food crop planting techniques
- Prev
What is soybean continuous cropping?
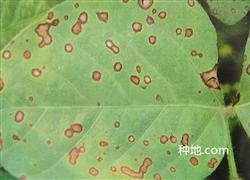
How to prevent and cure soybean leaf spot? What is the cause of the disease? 1. Distributed soybean leaf spot occurred in Sichuan, Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu and other places in China, and autumn soybean occurred more frequently. Second, the symptoms show that the disease spot on the leaf is light brown to grayish white, irregular, and the edge is dark brown. The disease spot is born in the later stage.
- Next

How do you know what kind of fertilizer soybeans lack?
What method is used to treat soybean sclerotinia disease? Soybean Sclerotinia sclerotiorum mostly starts from the middle and lower branches of the main stem of the plant. The disease spot is waterlogged, irregular, light brown or nearly white, which can surround the stem and spread up and down.
Related
- The first cup of black tea in spring, the flavor and history of tea gardens in Kenya, Africa
- The computer can not only choose potatoes, but also grow tea rice. AI will grow winter oolong tea champion.
- It is not only the inflated tea bitten by insects, but also engraved with the four seasons tea in Beipu.
- The Oriental Beauty Tea Festival in Zhuxian County takes the stage at the weekend to experience the plus-size feast of oil tea.
- & quot; Oriental Beauty Tea & Exploration of Emei in Hsinchu, the hometown of quot;
- The new variety of strawberry "Tainong 1" dessert is the first choice with mellow aroma. Crimson gorgeous
- History of Tea in Taiwan: from Wild Inner Mountain to Export Tea Garden
- Two types of Taiwan Oriental Beauty Black Tea won the British three-Star Award for Childhood Tea Xiang Zhang Jiaqi changed from pilot to champion tea maker.
- Banana species and varieties: the planting history of Taiwan Xianren banana and dwarf banana is long, is banana disease resistant?
- Coffee planting Technology: Qianjie Coffee from Seedling to harvesting

