Comprehensive control techniques of green mold in Pleurotus ostreatus
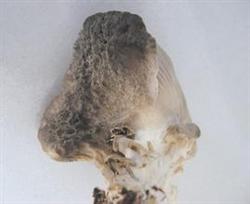
Green mold, also known as Trichoderma viride, is one of the most serious pathogens to Pleurotus ostreatus. It suffers from its harm in different production stages of Pleurotus ostreatus. Once the disease occurs, the light ones will reduce production and the heavy ones will lose harvest, which has become an important obstacle restricting the development of Pleurotus ostreatus production. Through several years of exploration and practice, the comprehensive control measures are summarized as follows: first, do a good job of mushroom room disinfection. The mushroom house and its surroundings should be thoroughly disinfected to eliminate all kinds of sundries. Wipe the seams in the walls with lime or yellow mud. Paint the walls, roofs and bedframes with 10% fresh lime water, spray the floor and roof, sprinkle the ground with quicklime powder, and finally fumigate with 10 milliliters per cubic meter of formaldehyde and 5 grams of potassium permanganate per cubic meter of formaldehyde. During the cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus, 0.1% potassium permanganate or 3-5% carbolic acid was sprayed regularly. Second, select excellent bacteria. The strains of Pleurotus ostreatus should choose high-quality strains with dense mycelium, white, sturdy, strong anti-impurity ability, no pollution and suitable age. Third, select high-quality culture materials. The culture material should be fresh and pollution-free. About 2% lime, 1% gypsum and 0.1-0.2% carbendazim can be added to the ingredients to inhibit the growth of green mold. If the culture material is not fresh or moldy, it should be fermented at high temperature and then reused. Fourth, strengthen cultivation management. The temperature of the mushroom room should not be too high at the initial stage of cultivation, and the air humidity should be controlled at about 70%, which is disadvantageous to the growth of mold in the air, but does not affect the mycelium growth of Pleurotus ostreatus. During cultivation, the amount of seed can be increased, and the amount of general bacteria should account for 10-15% of the dry material weight, so that the hyphae of Pleurotus ostreatus can form a growth advantage in a short period of time. In the process of cultivation, proper ventilation and control of the environmental conditions of the mushroom room are beneficial to the growth of mycelium and inhibition of green mold. Fifth, chemical prevention and control. When a small amount of green mold occurs on the culture material of the bacteria bed or at both ends of the bacteria bag, the affected part is smeared or sprayed with 0.1% methyl topiramate, 0.1-0.2% Dysen zinc, 0.1-0.2% carbendazim or concentrated lime water supernatant, which can prevent the spread of conidia, or treat the infected site with a mixture of 2% formaldehyde and 5% carbolic acid to inhibit the growth of miscellaneous bacteria. If green mold has penetrated into the material in the bacterial bed or bag, soak the sand cloth with 0.2% carbendazim solution in time, then gently dig out the contaminated material block, spray 0.2% carbendazim or other fungicides on the removed material surface, or smear thick lime milk, and then fill it with fresh materials or bacteria to control its development. The bacterial bags with serious pollution can be buried deeply. During the period of mushroom emergence, 70% methyl topiramate, or 50% carbendazim 1000 times liquid, or 10% water agent Shuangxiaoling can be sprayed once every 3-5 days to achieve a certain control effect.
- Prev

Three common diseases of chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemum, alias chamomile, is a perennial herbal medicinal plant of Compositae, and traditional Chinese medicine is called white chrysanthemum and yellow chrysanthemum. The flower is used in medicine, which has the effect of soothing wind and heat, clearing liver and eyesight. It is mainly produced in Anhui, Zhejiang, Henan, Hebei and Sichuan and is cultivated in other parts of the country. The main diseases of cultivated chrysanthemum are chrysanthemum powdery mildew,.
- Next

Occurrence regularity and integrated control techniques of fleshy bacteria in Pleurotus ostreatus and walnut
Recently, many netizens have reported the harm of walnut fleshy bacteria in their cultivated Pleurotus ostreatus, and now reprint an article entitled "occurrence regularity and control techniques of Pleurotus ostreatus and walnut fleshy bacteria" published by Yang Yong an Xiurong, Agricultural Science Research Institute of Taian City, Shandong Province. for growers' reference: in recent years, Taian City and Zhou.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

