Three common diseases of chrysanthemum

Chrysanthemum three diseases refer to chrysanthemum gray mold, rust and spot blight. It is observed that these three diseases often occur in the growing season of chrysanthemum, especially after autumn, which can cause a large number of fallen leaves, affect plant flowering and reduce ornamental value. Prevention and control measures should be taken as soon as possible. Botrytis cinerea mainly harms the leaves, stems and flowers of chrysanthemum. When the leaves were damaged, there were brown disease spots on the edge of the leaves, and the surface was slightly corrugated. The petioles and flower stalks softened at first, and then the outer skin rotted. Seed maturation is affected when flowers are damaged. High temperature and heavy rain, excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer, over-dense planting and heavy soil texture are all conducive to the occurrence of diseases. Prevention and control methods: first, guest soil planting. The pathogen mainly overwinters in the soil, therefore, whether garden or potted, the soil is required to be disease-free new soil; second, diseased leaf disease plants are found to be cleared in time, buried or burned, so as to prevent the spread of the disease; third, before planting, the roots can be soaked with 65% zinc 300 times solution for 15 minutes; fourth, pay attention to cultivation, pay attention to improve ventilation and light transmission conditions, do not bias the application of nitrogen fertilizer, and strictly prevent soil waterlogging. Fifth, in the initial stage of the disease can be sprayed Baume 0.3 degrees 0.5 degrees of stone sulfur mixture, or Dysen zinc, carbendazim fungicide. Rust mainly harms the leaves and stems of chrysanthemum, especially the leaves. At first, light yellow spots appeared on the leaves, and small brown and green spots also appeared at the back of the diseased leaves. After the production of slightly raised blister, blister rupture, scattered a large number of yellowish-brown powder. The color gradually changed from light thirst to yellowish brown, which often caused the death of the leaves of the whole plant. Poor cultivation management, poor ventilation and light transmission, lack of soil fertilizer or excessive nitrogen fertilizer, soil waterlogging and excessive air humidity are all conducive to the occurrence of the disease. The disease can be prevalent from April to October. Prevention and control methods: first, rational fertilization. On the basis of combined fertilization, appropriate application of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer to improve the antibacterial ability of the plant; second, potted chrysanthemum, should often dredge the drainage hole, strictly prevent waterlogging in the basin; third, ecological disease prevention. Protected cultivation of chrysanthemum should pay attention to ventilation and light, temperature and humidity, delay leaf dew time; fourth, chemical control. The epidemic of the disease can be effectively controlled by spraying 65% Dyson zinc 500 times solution, or 0.3: 0.5 Baume degree stone sulfur mixture in the onset season. Leaf spot blight, also known as black spot, mainly harms the leaves of chrysanthemum. At first, small brown spots appeared on the lower leaves, and then gradually enlarged, the edge was dark brown, and then expanded into dark brown round or subcircular irregular spots, about 5 mm in size, with an inconspicuous yellow halo on the outside. In the later stage, the edge of the lesion was dark brown, the center faded slightly, and small black spots appeared when the humidity was high. When the disease is serious, several disease spots are linked together, so that the whole leaf is scorched and black, and the disease of continuous cropping is serious. Prevention and control methods: first, reasonable stubble planting, selection of disease-free plant grafting; second, pay attention to trench drainage, reduce soil moisture; third, regular pruning, eliminate disease and disability, improve ventilation and light transmission conditions. The implementation of chemical control technology to promote plant growth and enhance disease resistance and tolerance; fourth, chemical control. At the initial stage of the disease, 30% basic copper sulfate suspension 400x, or 80% carbendazim wettable powder 500x, or 50% carbendazim suspension 800x or 75% carbendazim 1500 times can be used for prevention and treatment.
- Prev

Prevention and treatment of root cancer of chrysanthemum
Main points of cultivation and management of chrysanthemum 1. Site selection: chrysanthemums like to be wet and afraid of drying, and avoid waterlogging. After being soaked in heavy rain for 48 hours, all of them died. Therefore, it is necessary to choose land with fertile land, convenient drainage and irrigation, and smooth power supply for planting. If the grain field is replanted, it is necessary to strengthen the main enclosure foundation and have sufficient drainage and irrigation capacity to avoid.
- Next
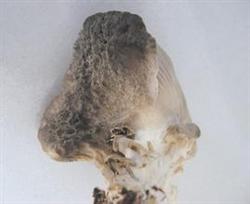
Comprehensive control techniques of green mold in Pleurotus ostreatus
1. The cap of Pleurotus ostreatus is small, the differentiation is poor, and the stalk is longer. The reason was that during the period of primordium formation and differentiation, the mushroom room was anoxic, the light was insufficient, and the temperature was high, which affected the normal differentiation and development of the cap. Prevention and treatment methods: strengthen ventilation, adjust light and temperature. two。 Pleurotus ostreatus lid performance, mainly the edge.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

