Occurrence regularity and control methods of black spot of poplar
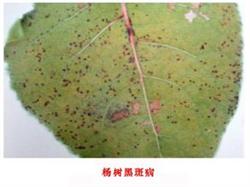
Poplar black spot, also known as poplar brown spot, generally occurs on young shoots and ears of poplar, and spreads from top to bottom, thinking that it is mainly harmful to leaves. At the initial stage of the disease, needle-like sunken and shiny spots first appeared on the back of the leaves, and then the spot expanded to about 1 mm. Black, slightly raised, brown spots also appeared on the front of the leaves, and milky raised spots appeared in the center of the disease spot 5-6 days later, that is, the conidia of the pathogen. After the expansion of the disease spot into a large spot, mostly into a circle, when the disease is serious, the whole leaf becomes black, and the diseased leaf can fall off early for 2 months. When the seedling is young, if all the leaves die, it is easy to lead to plant death; if the seedling is unearthed, the leaflet and seedling neck will all turn black, and the diseased seedling will not be straight. First, the law of the disease: the pathogen overwinters with mycelium in the disease spot of fallen leaves or branches. The disease begins in early May and reaches its peak in summer and autumn until the leaves fall. It can harm poplar leaves, petioles, fruit ears, tender shoots, and so on. On it, horny, nearly round or irregular black-brown spots are formed, with a diameter of about 1 mm, some up to 5 mm. Disease spots can be connected into irregular large spots for a long time, causing early defoliation. The new conidia produced by the pathogen spread by wind in May and June of the following year, fell on the seedling leaves and invaded the leaves through stomata. The disease appeared in 3-4 days, and a conidia disk was formed in 5-6 days for re-infection. Second, prevention and control methods: 1. Strengthen the management of nursery. Disease-resistant varieties should be selected for seedling cultivation, attention should be paid to time seedlings, ventilation and light transmission conditions should be improved, field management such as drainage should be done well, disease conditions should be reduced, continuous cropping should be avoided or the nursery should be set up near susceptible plants, and seedlings can be planted in a planned way. Seeds with bacteria need chemical treatment to prevent seedling disease. Dry seeds can be treated with 85% chlorothalonil wettable powder 1000-1500 times or methyl topiramate and duodine powder. 2. Reasonable close planting and timely thinning to keep the forest ventilated and transparent. Clean up the fallen leaves in the forest in time to reduce the source of the disease. 3. During the onset of the disease, the nursery and adult forest should be sprayed with 200 times Bordeaux solution or 85% mancozeb 250 times solution. During the rainy season, 0.3% gelatin (or soybean powder or soybean milk) should be added to the potion to prevent it from being washed away by water. Diseased leaves and fallen leaves should be cleaned at any time to eliminate pathogens, or 40% carbendazim 800 times or 25% chlorothalonil 600 to 800 times should be sprayed in early June. Or 0.3% urea and potassium dihydrogen phosphate mixture.
- Prev

Identification and Control of Black spot of Poplar
Poplar black spot, also known as poplar brown spot, the disease can infect a variety of poplar, seedlings, young trees, big trees can be susceptible, seriously affect the normal growth of trees, resulting in economic losses. Symptoms: generally occur in leaf shoots and ears, spread from top to bottom, mainly harm to leaves, disease.
- Next

Identification and Control of Brown spot of Poplar
Poplar brown spot is a common leaf disease, which mainly harms Populus tomentosa, Populus tomentosa, steamed bread willow and so on. At the initial stage of the disease, there are small yellow-brown spots on the surface, which gradually expand, the edge color is lighter and neat, to the later stage, the center of the lesion becomes brown, and there are black spots on it. After the black spot breaks, the conidia are released and blown by the wind.
Related
- Fuxing push coffee new agricultural production and marketing class: lack of small-scale processing plants
- Jujube rice field leisure farm deep ploughing Yilan for five years to create a space for organic food and play
- Nongyu Farm-A trial of organic papaya for brave women with advanced technology
- Four points for attention in the prevention and control of diseases and insect pests of edible fungi
- How to add nutrient solution to Edible Fungi
- Is there any good way to control edible fungus mites?
- Open Inoculation Technology of Edible Fungi
- Is there any clever way to use fertilizer for edible fungus in winter?
- What agents are used to kill the pathogens of edible fungi in the mushroom shed?
- Rapid drying of Edible Fungi

