How to control rice drill beetle without pollution?
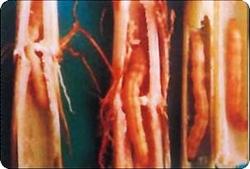
How to control rice drill beetle without pollution? Please introduce the control method of heart borer is the common name of rice stem borer and Chilo suppressalis. Chilo suppressalis is distributed all over the country. Stem borer harms not only rice, but also Zizania caduciflora, corn, sugar cane, Reed and other Gramineae weeds. After overwintering, some larvae can invade broad bean, rape, wheat and so on. Generally, it causes withered sheath and withered heart seedlings at tillering stage, withered booting and white panicle at booting stage and heading stage, semi-withered panicle and insect damage at milking stage and milking stage. Chilo suppressalis has three generations in general years in Hunan, but incomplete or complete four generations in southern Hunan in recent years. The larvae overwinter in rice root, straw, Zizania caduciflora and so on. Generally, moths flourish in the first generation from May to June, the second generation in July and the third generation from August to September. Chilo suppressalis is one of the main pests of rice in Hunan Province. The host of Chilo suppressalis is single and only harms rice. Generally, rice seedlings are harmed at seedling stage, resulting in withered seedlings; at booting stage, causing withered booting; at heading stage, causing white ears. It usually occurs for 4 generations. Overwintering as larvae in rice roots. The overwintering larvae began to pupate in April, the first generation was in May, the second generation was from late June to the first and middle of July, the third generation was in August, and the fourth generation was in mid-late September. Borer moths have the habit of phototaxis and like to lay eggs in fat, green rice fields. Generally speaking, after the temperature dropped in October, the larvae gradually transferred to the base of the rice stem to overwinter. The following techniques can be used to control heart worms. First, agricultural prevention and control. Pull out the white ear. From late September to early October, the third and fourth generations of Chilo suppressalis larvae caused by white ears are usually larvae preparing for winter. At this time, white ears are obvious and easy to find, and the larvae still stay in the upper part of the rice plant, and the white ear plants are uprooted or cut off. Part of the insect source can be eliminated. The rice is cut from the mud. When late rice is harvested, harvesting rice with Qi mud can reduce the source of insects and destroy the overwintering sites of borers. Straw treatment. There are many borer residues in rice straw, if left in the rice field or on the ridge, it can be used as an effective source of insects in the second year. Therefore, the straw should be removed or burned in time after late rice harvest. In the areas where Zizania caduciflora is planted, the remaining plants of Zizania caduciflora should be cut off and treated centrally in winter. The early rice straw should not be placed on the ridge of the field for a long time to reduce the source of the second generation stem borer; the rice straw with a white panicle rate of more than 1% of the early rice stem borer cannot be returned to the field, lest the residual insects directly harm the late rice. Infuse water to kill pupae. In the overwintering generation of rice stem borer pupation stage (usually in the middle and late April), most of the larvae and pupae can be drowned, and in the early stage of pupation of the first generation (when individual larvae pupate), shallow water is injected to improve the pupation position, and then in the peak pupation period (when half of the larvae pupate), deep water for 3-4 days can drown most of the mature larvae and pupae and reduce the occurrence of the second generation. Second, physical prevention and control. The frequency vibrating insecticidal lamp was used to trap moths. Since late April, a frequency vibrating insecticidal lamp has been installed every 150 meters in the paddy field. In the moth stage of each generation of borer, turning on the light at 7 o'clock in the evening and turning off the light at 7 o'clock in the morning can effectively kill the borer moth. The third is chemical control. The principle of "accurate, ruthless and economical" should be grasped in the prevention and control of borer. It must refer to the timely use of medicine according to the disease and pest information of the local plant protection department, and should not be applied too early or too late. It is generally applied in the peak period of low instar larvae. Ruthlessness means grasping the key points, ensuring quality and quantity and applying medicine seriously. For Chilo suppressalis, the first generation should be treated ruthlessly; for Chilo suppressalis, the second generation should be treated ruthlessly. Province is to reduce the use of pesticides, reduce costs and reduce pollution to the environment on the premise of ensuring the effect of prevention and control. At present, 5% fipronil suspension 30 ml, 20% triazophos EC 120 ml, 15% and bang microemulsion 100ml 120 ml per mu can be used to spray 45 kg of water. When using chemical control, the field should keep a water layer 3-5 cm deep and let it dry naturally. Click to get more rice planting techniques click to get more food crop planting techniques
- Prev

When is it good to apply leaf fertilizer to rice?
When is it good to apply leaf fertilizer to rice? Please introduce in detail that the application of foliar fertilizer in the middle and later stages of rice growth can increase grain and weight, generally increase yield by 5% to 10%, and improve quality. Therefore, the following foliar fertilizer can be selected according to the conditions. At heading stage and milking stage, rice with full grain per mu (50 g) was used for 50% water supply.
- Next

Is there any way to increase the yield of rice?
Is there any way to increase the yield of rice? Is there any way to be effective? If you want to increase the yield of rice, you can refer to the following methods: 1. Increase the number of ears. Strong seedlings were cultivated by ①. It provides a good basis for early return to green and early tillering after planting. ② reasonable close planting. According to the number of ears harvested according to the plan and the estimation of tillering after seedling planting.
Related
- The first cup of black tea in spring, the flavor and history of tea gardens in Kenya, Africa
- The computer can not only choose potatoes, but also grow tea rice. AI will grow winter oolong tea champion.
- It is not only the inflated tea bitten by insects, but also engraved with the four seasons tea in Beipu.
- The Oriental Beauty Tea Festival in Zhuxian County takes the stage at the weekend to experience the plus-size feast of oil tea.
- & quot; Oriental Beauty Tea & Exploration of Emei in Hsinchu, the hometown of quot;
- The new variety of strawberry "Tainong 1" dessert is the first choice with mellow aroma. Crimson gorgeous
- History of Tea in Taiwan: from Wild Inner Mountain to Export Tea Garden
- Two types of Taiwan Oriental Beauty Black Tea won the British three-Star Award for Childhood Tea Xiang Zhang Jiaqi changed from pilot to champion tea maker.
- Banana species and varieties: the planting history of Taiwan Xianren banana and dwarf banana is long, is banana disease resistant?
- Coffee planting Technology: Qianjie Coffee from Seedling to harvesting

