Diseases of guava: control of standing blight of common diseases of guava
What to do when guava blight occurs, how to prevent it, what kind of disease is it, let's take a look.

Symptoms: Different guava varieties damaged by Rhizoctonia solani have different disease resistance and symptoms. Generally, after infection, the main symptoms are mainly manifested in the new bud, the new bud becomes brown or black, after the new shoot stops growing, the color of the new leaf turns yellowish green, the leaf shape becomes smaller, occasionally red spots, often starts from the top of a branch of the whole plant, the disease gradually spreads downward, and the disease gradually develops from the branch to the new branch to produce a new infected part, the disease gradually develops to the base of the trunk to the root, and finally causes the plant to wither. The symptom of pear plums and white plums was mainly characterized by epidermal processes on the trunk surface after infection, pale pink spores under the processes, and a large number of spores when the epidermis detached at the later stage. When infected, the mature leaves on the branches turn yellow more easily, the branches wither and gradually spread downward and laterally, finally leading to the death of the whole plant, but the cross-section of the cut branches will appear pale pollen spores, which is slightly different from the symptoms of the old strains.
After the field plants are infected, the symptoms of whole plant death occur at the mature stage of fruit, which has a great impact on farmers 'income. No matter what size guava will be damaged. If guava seedlings are planted in the original planting holes of dead fruit trees, they will also wither in 1~2 years, depending on the speed and degree of infection of the roots of new plants.
Control methods:
1. Treatment of diseased plants:
1. When diseased branches are found, they are sawed off at the points of divergence and then tarred, painted or coated with nanbao resin to protect the wound.
2. Sawn diseased branches and fallen leaves should be collected and burned.
Second, replanting: When replanting, the old soil near the original plant should be dug out and replaced with new soil before planting.
3. Abandoned cultivation: When the diseased plants reach more than 30%, they will be abandoned, the plants will be dug up and burned on the spot, and the orchards will be replanted with other crops.
- Prev
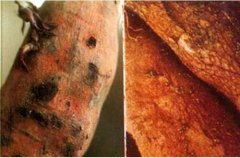
How to cure the underground pests of potato? What is the pesticide of sweet potato to control underground pests?
Sweet potatoes are harmed by underground pests, which will have very serious consequences. In production, we must take the following methods to prevent and control poisoning in time, which can improve the yield and quality. So that the harm to sweet potatoes is reduced. The first kind is tea bran liquid. Tea bran liquid
- Next

What is it like when guava has scab? what kind of medicine does guava have scab?
Do you know what the disease of guava scab is and how to treat it? Let's take a look. Symptoms: when the first infection, the spot is round, slightly raised, the surface of the spot is rough and cracked, such as scab, brown, the edge is light brown or yellowish color, large
Related
- A one-day flower show brings 130 million yuan in orders! Nanhai, this Phalaenopsis exhibition is amazing
- What do the flower language and meaning of Lutheran tree mean? Precautions for planting Lutheran tree
- Encounter Chaoshan Kongfu tea, not without this cup of Phoenix single clump
- The durian market in Vietnam and Thailand is flooded. The price of imported durian has plummeted by 30-40% in a month.
- Shanghai solved the problem of local vegetable supply by planting 80,000 mu of green leafy vegetables.
- Wageningen University has become the best agricultural university in the world for the seventh time in a row.
- The strongest export season of South African grapes is full of challenges, with exports to Russia falling sharply by 21%.
- Sri Lanka is on the verge of bankruptcy, "Tea for debt" Organic Agriculture Revolution aggravates the Food crisis?
- Turning waste into earthworm manure and worm manure into organic fertilizer-A new choice for auxiliary farming
- Organic rice growers shoulder the responsibility of nurturing agricultural talents! Yinchuan Sustainable Farm with Organic Life Camp

